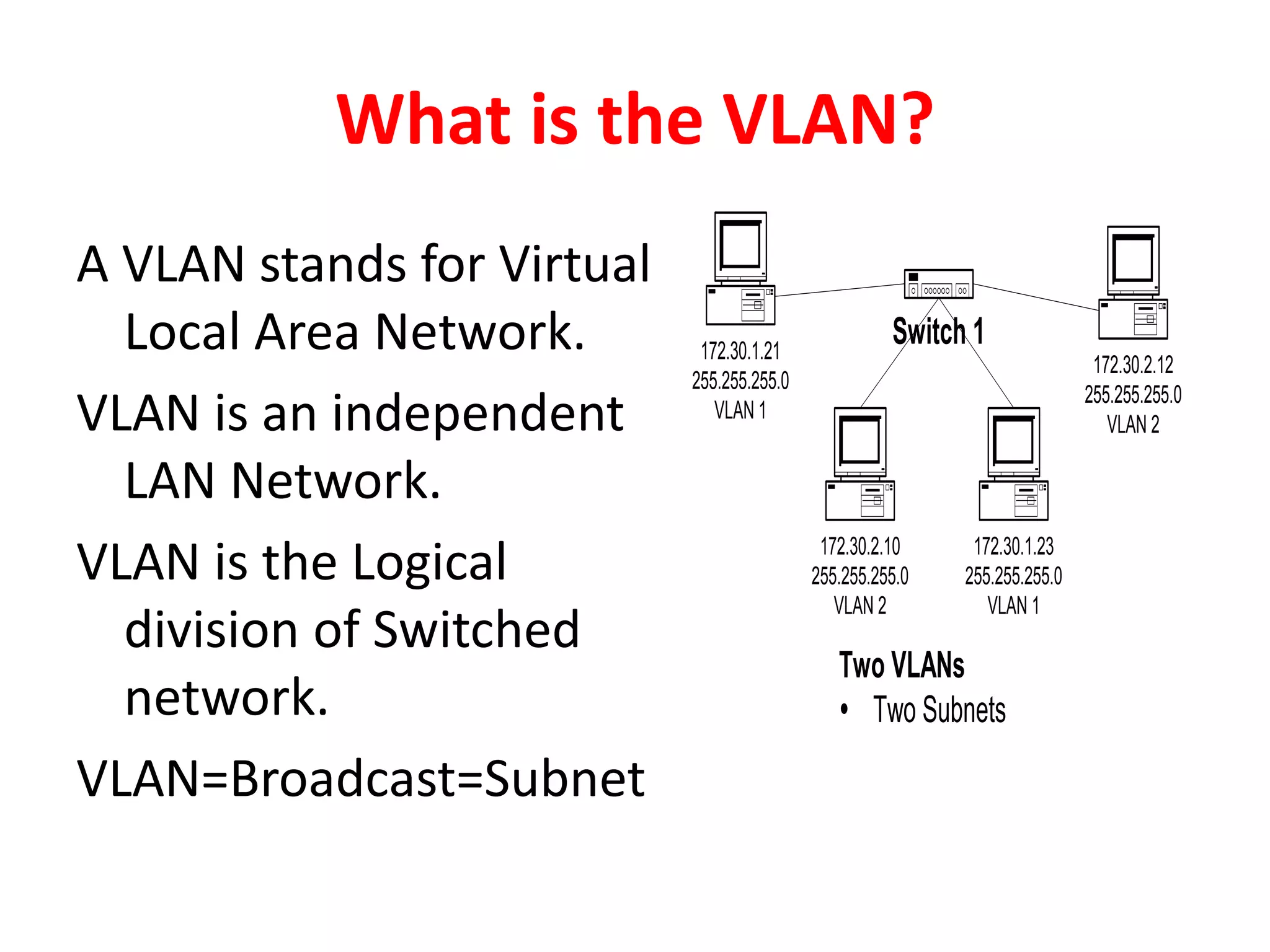
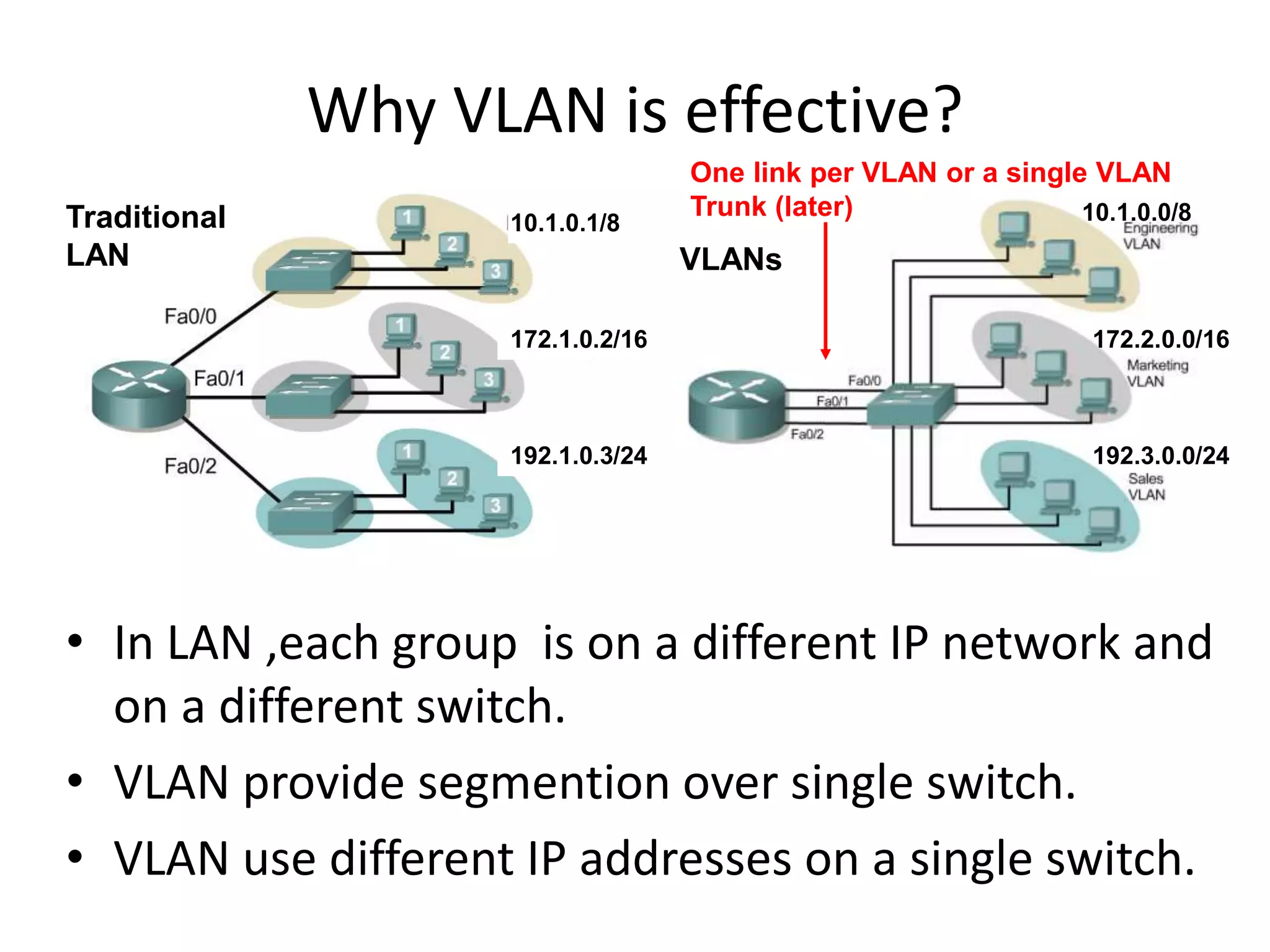
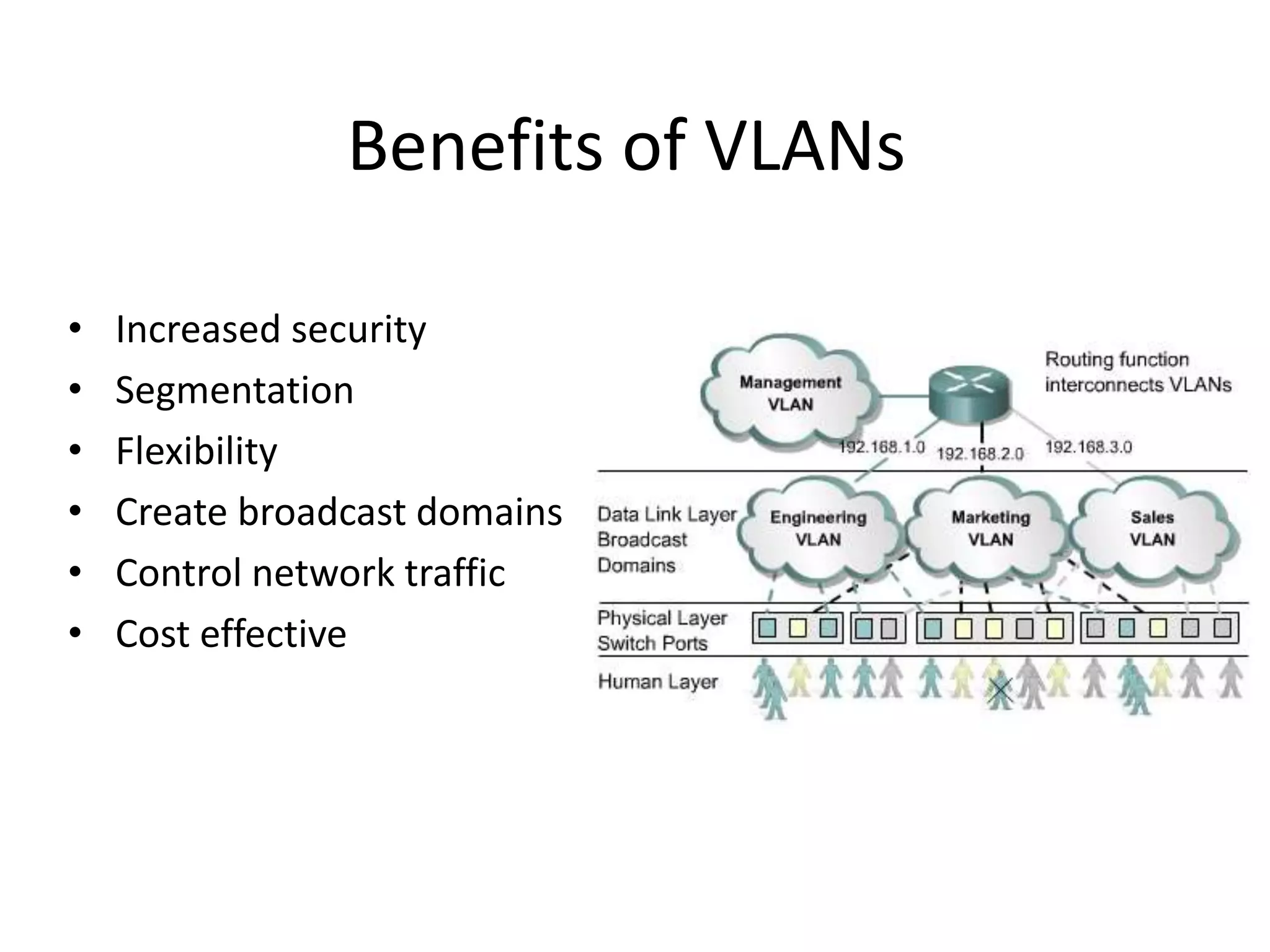
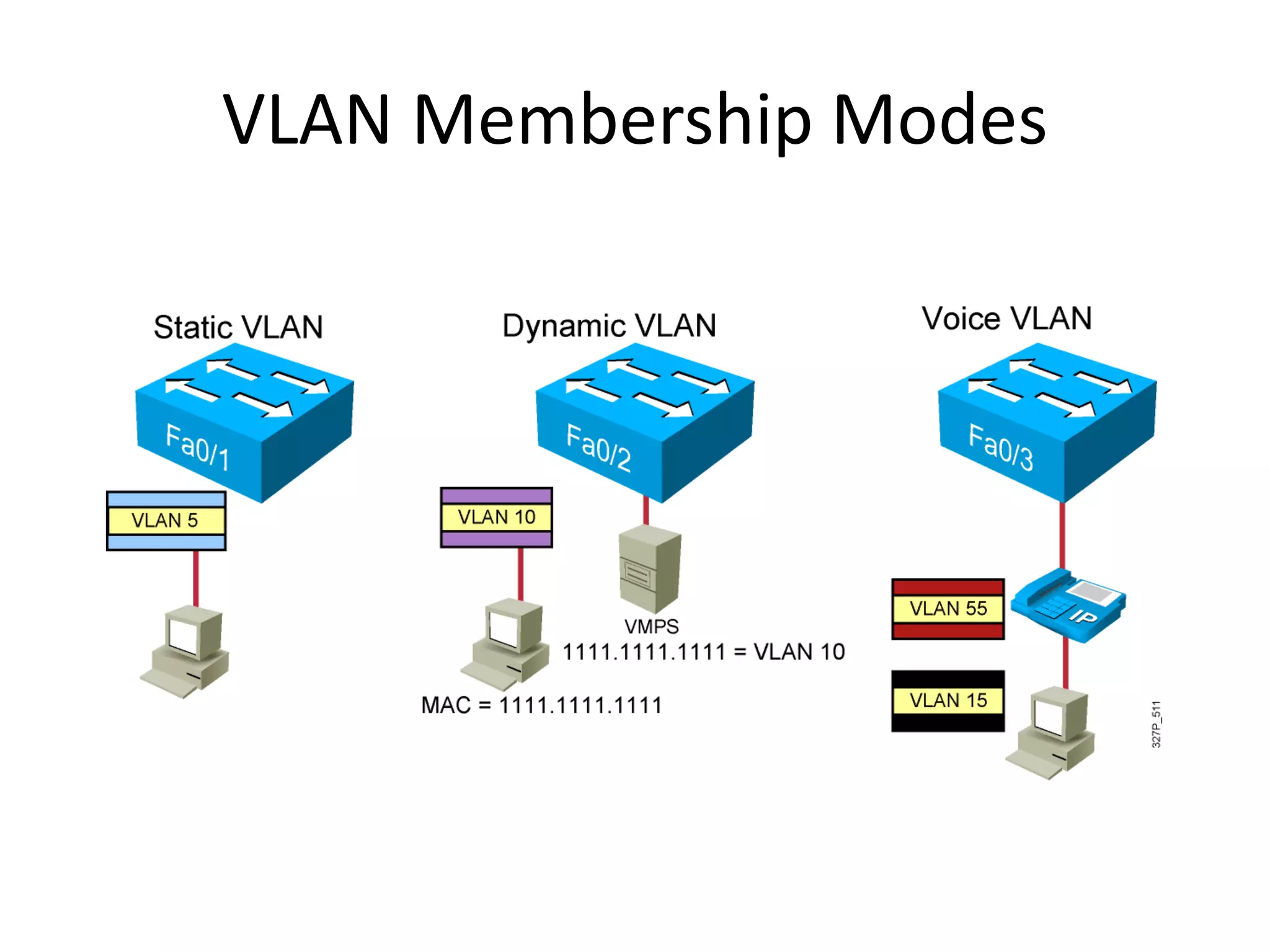
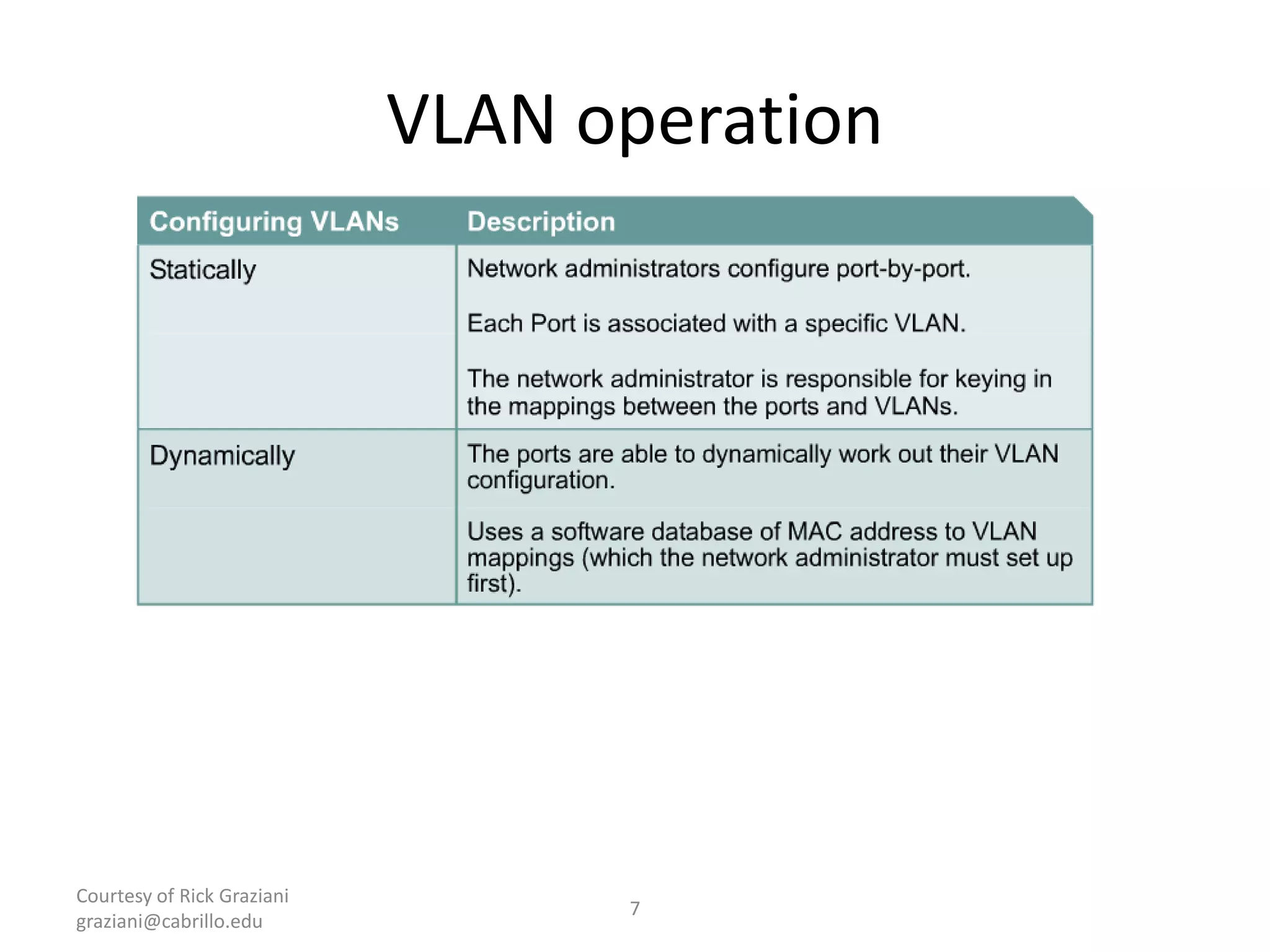
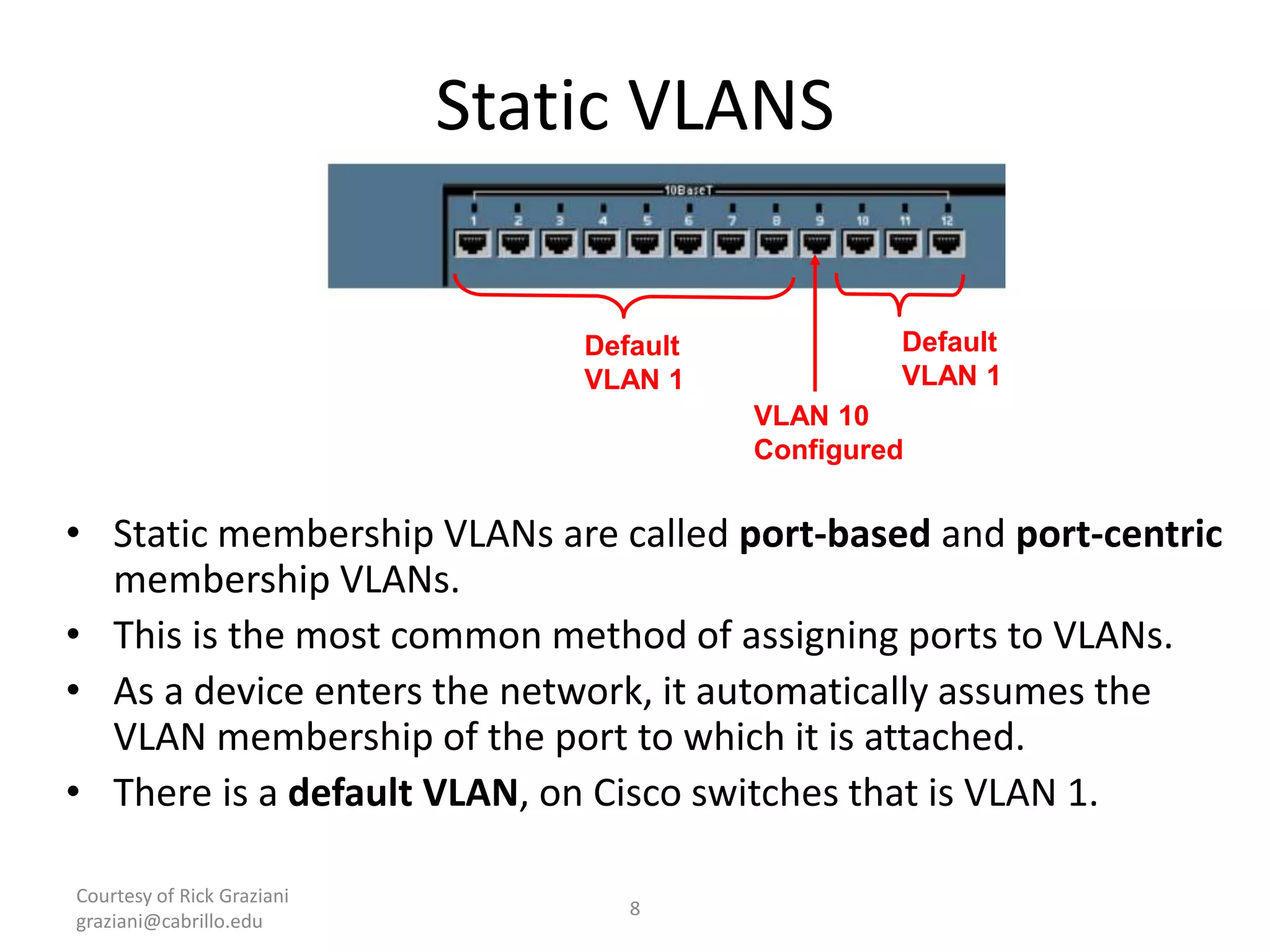
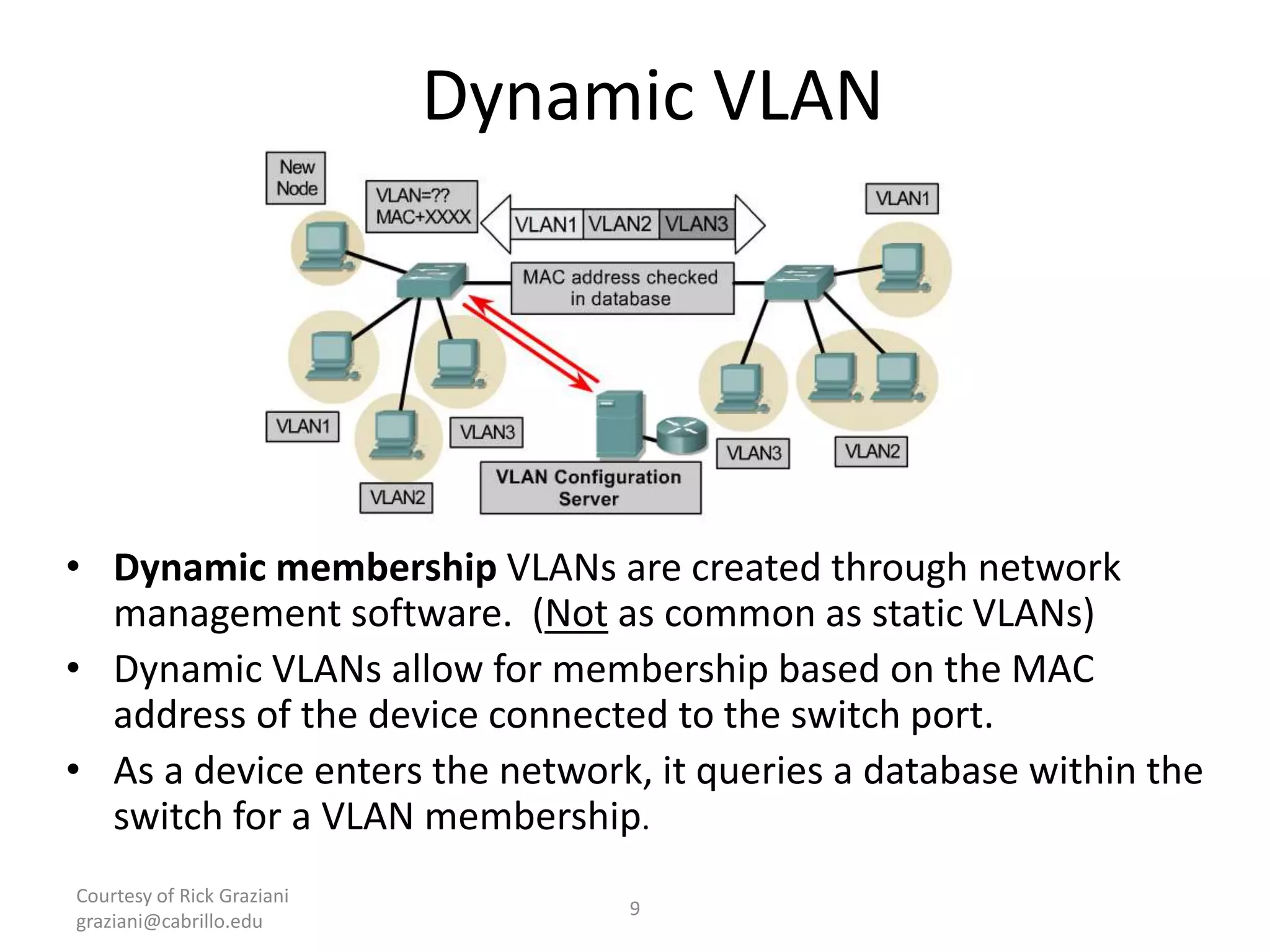
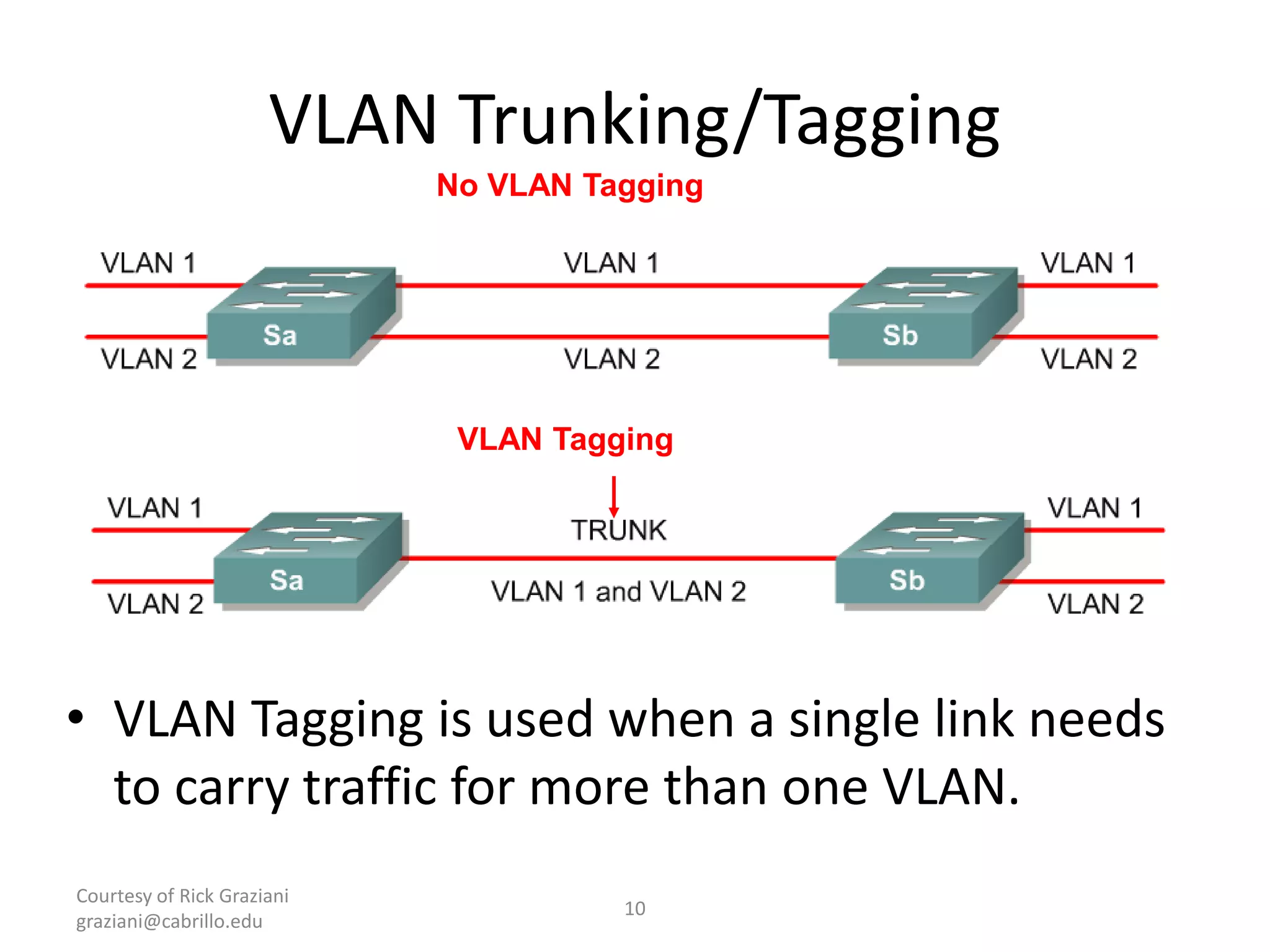
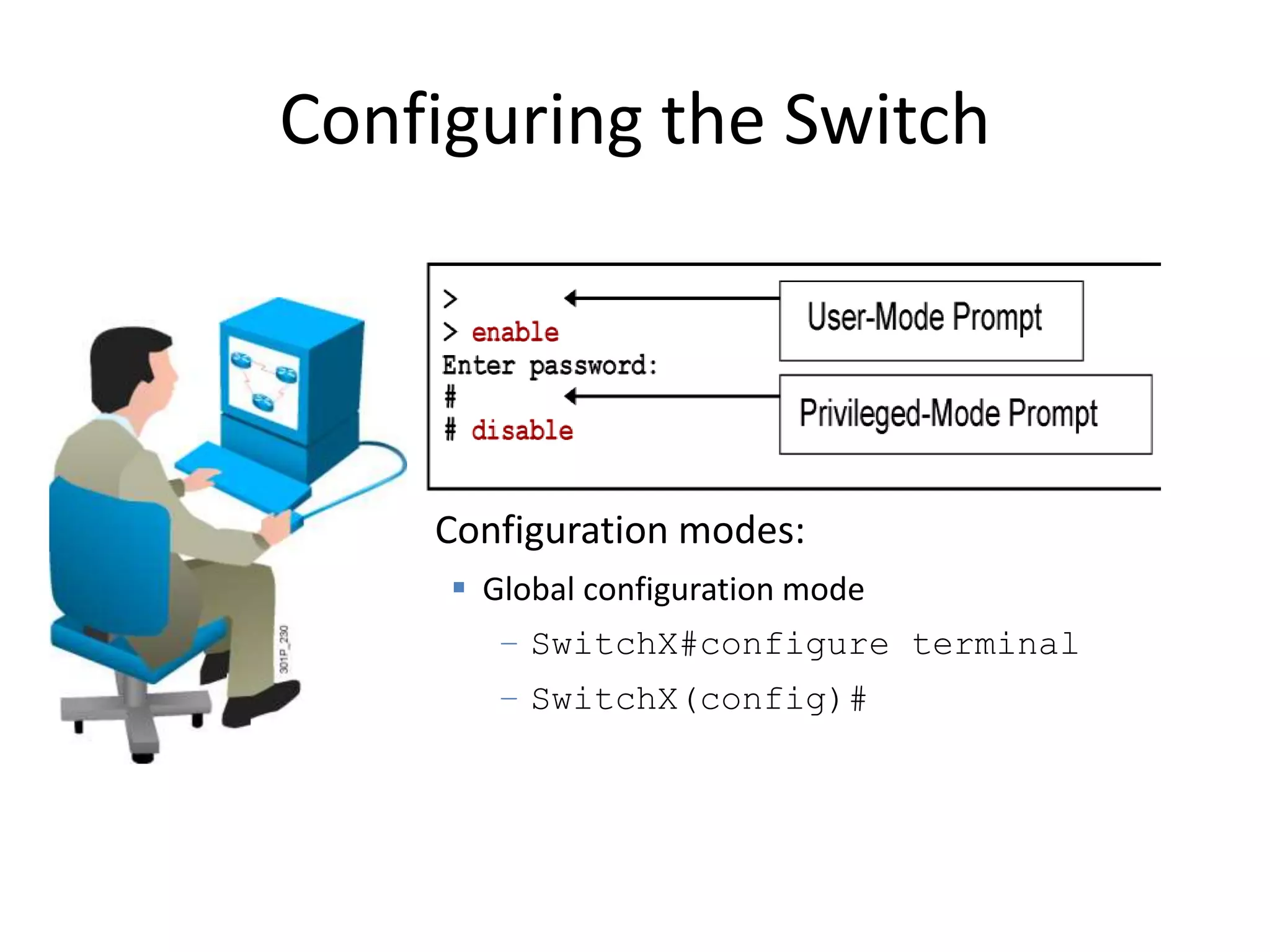
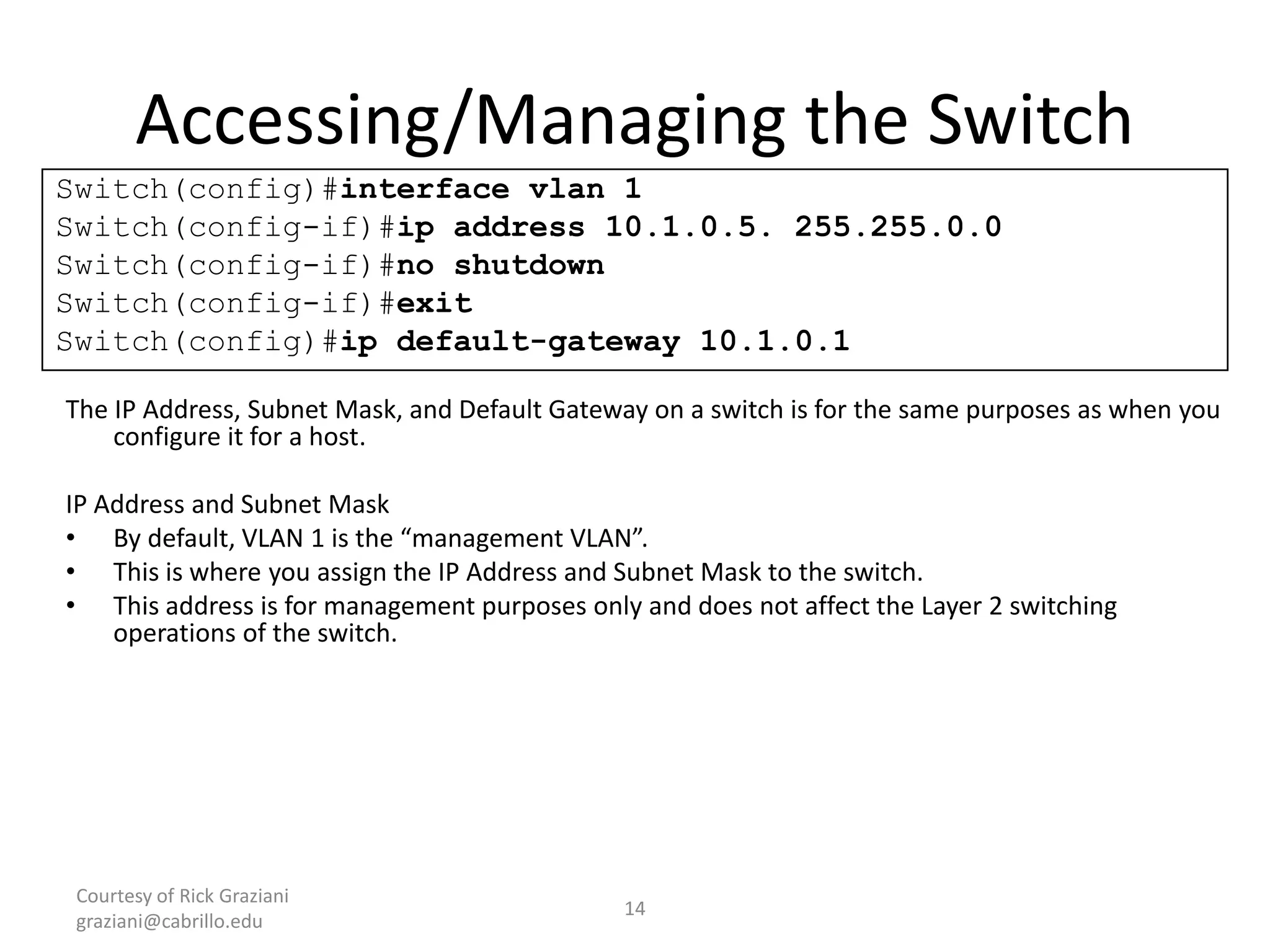
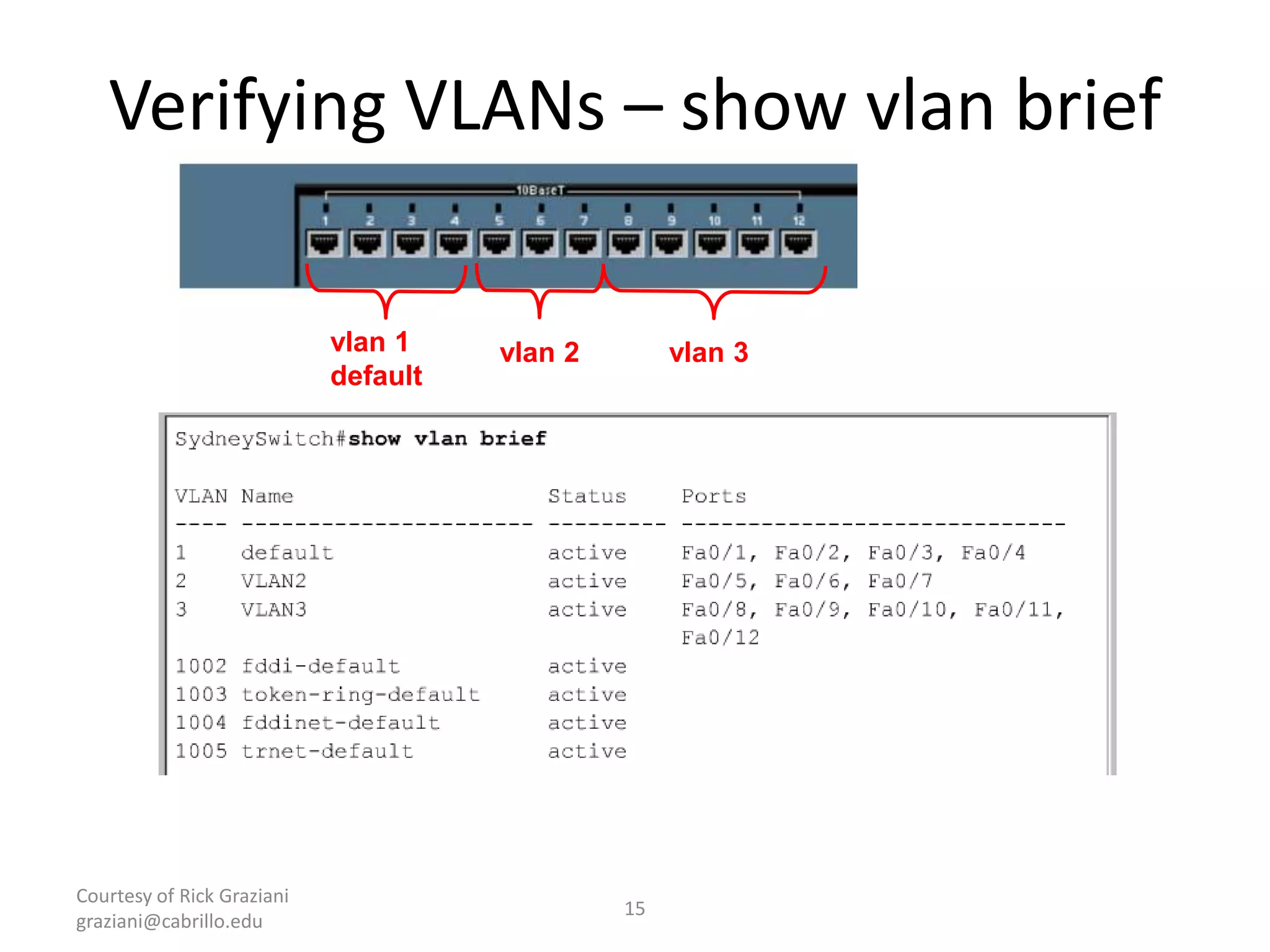
The document provides an overview of Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), explaining their definition, benefits, and operations, including static and dynamic memberships. It highlights VLANs' roles in enhancing security, flexibility, segmentation, and cost-effectiveness within network management. Additionally, the document discusses VLAN trunking and configurations using Cisco switches.