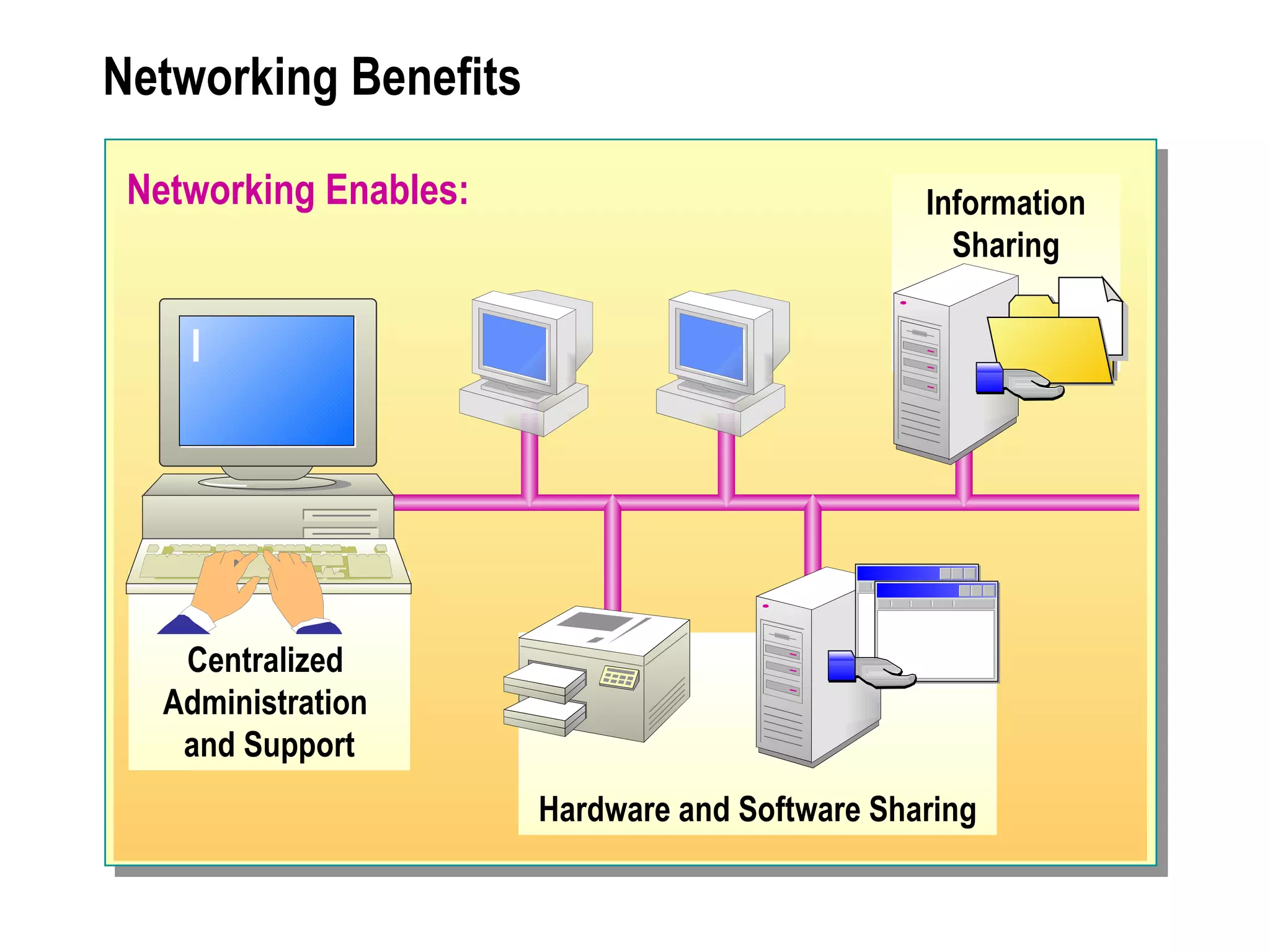
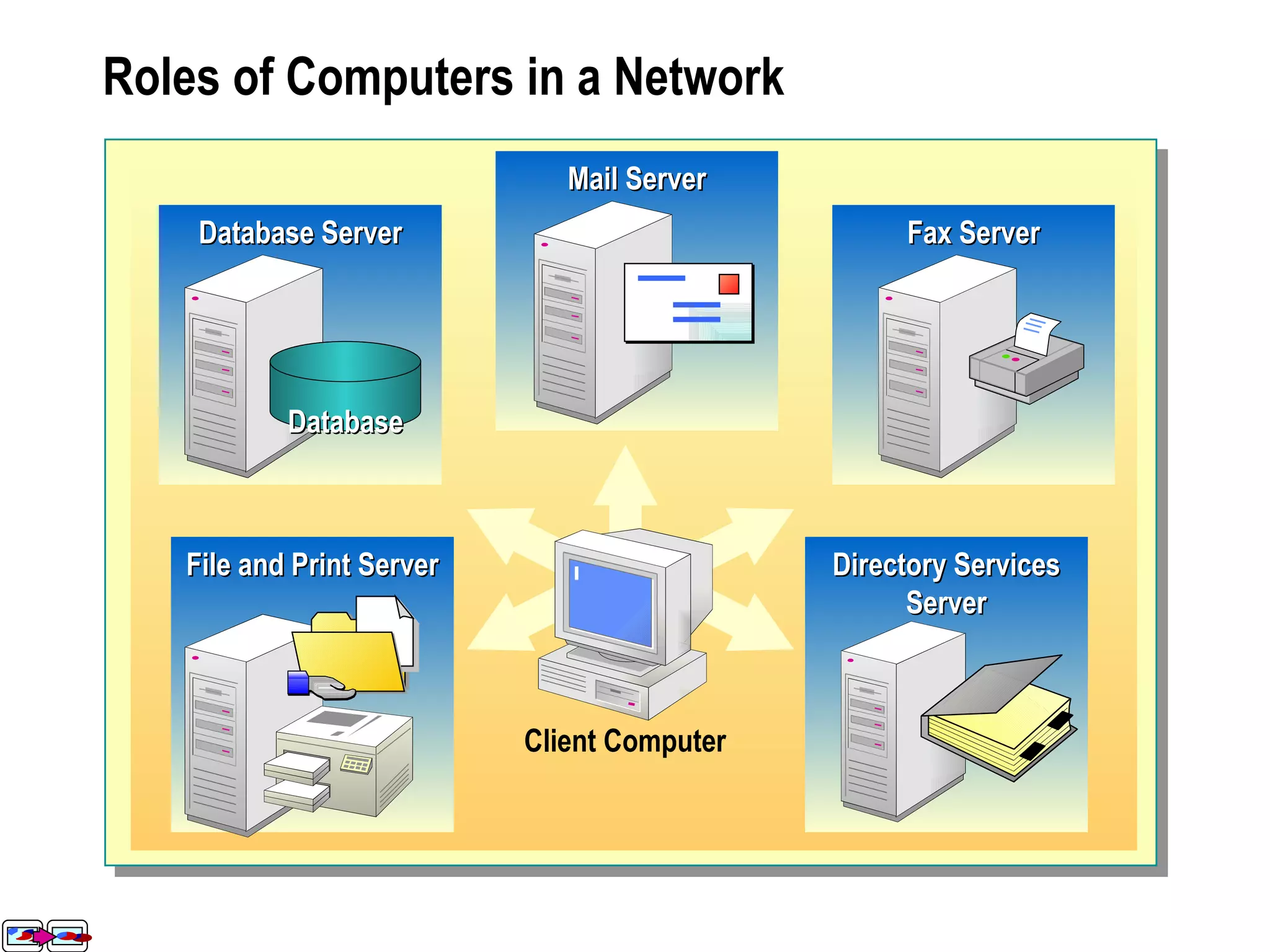
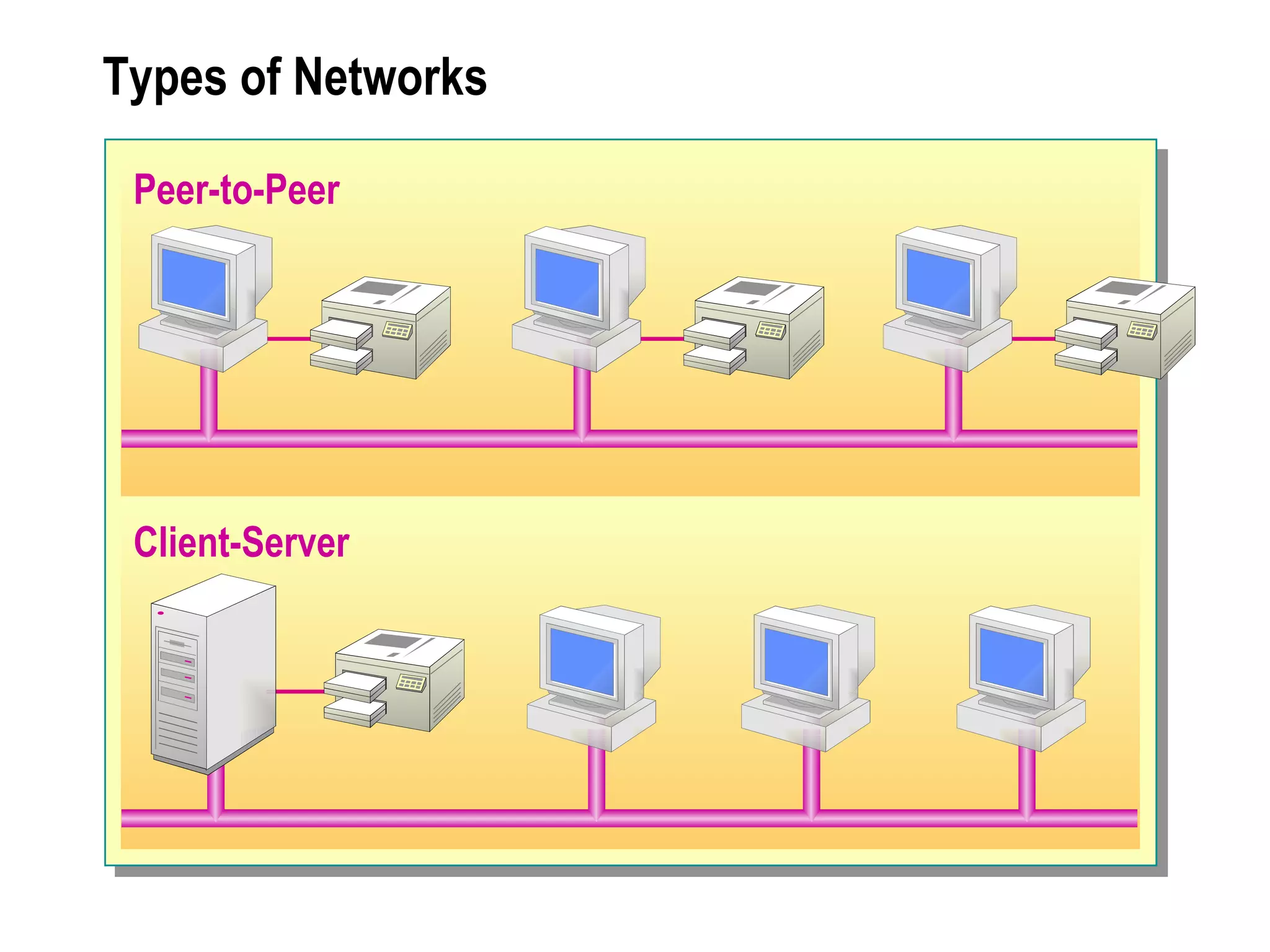
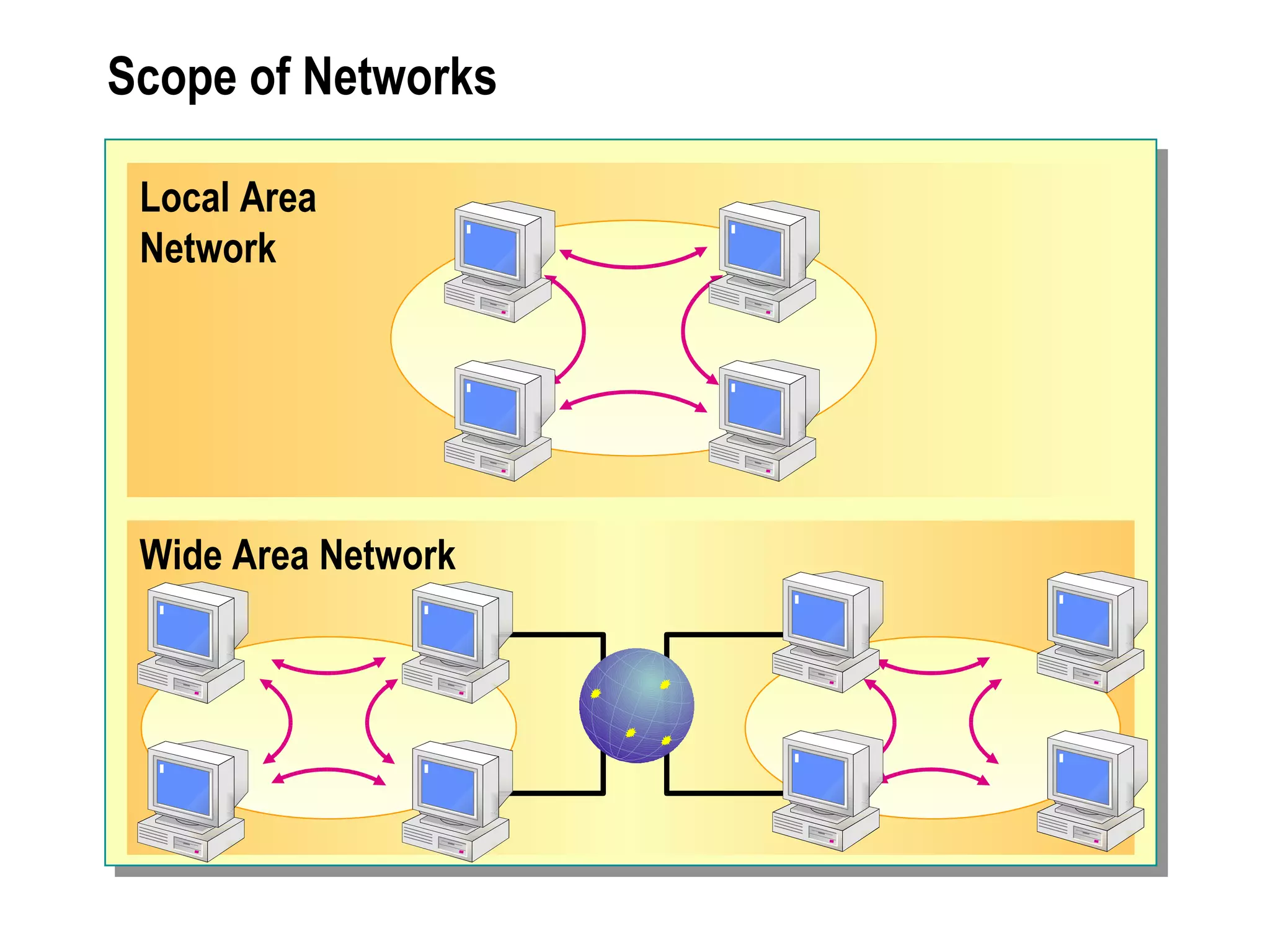
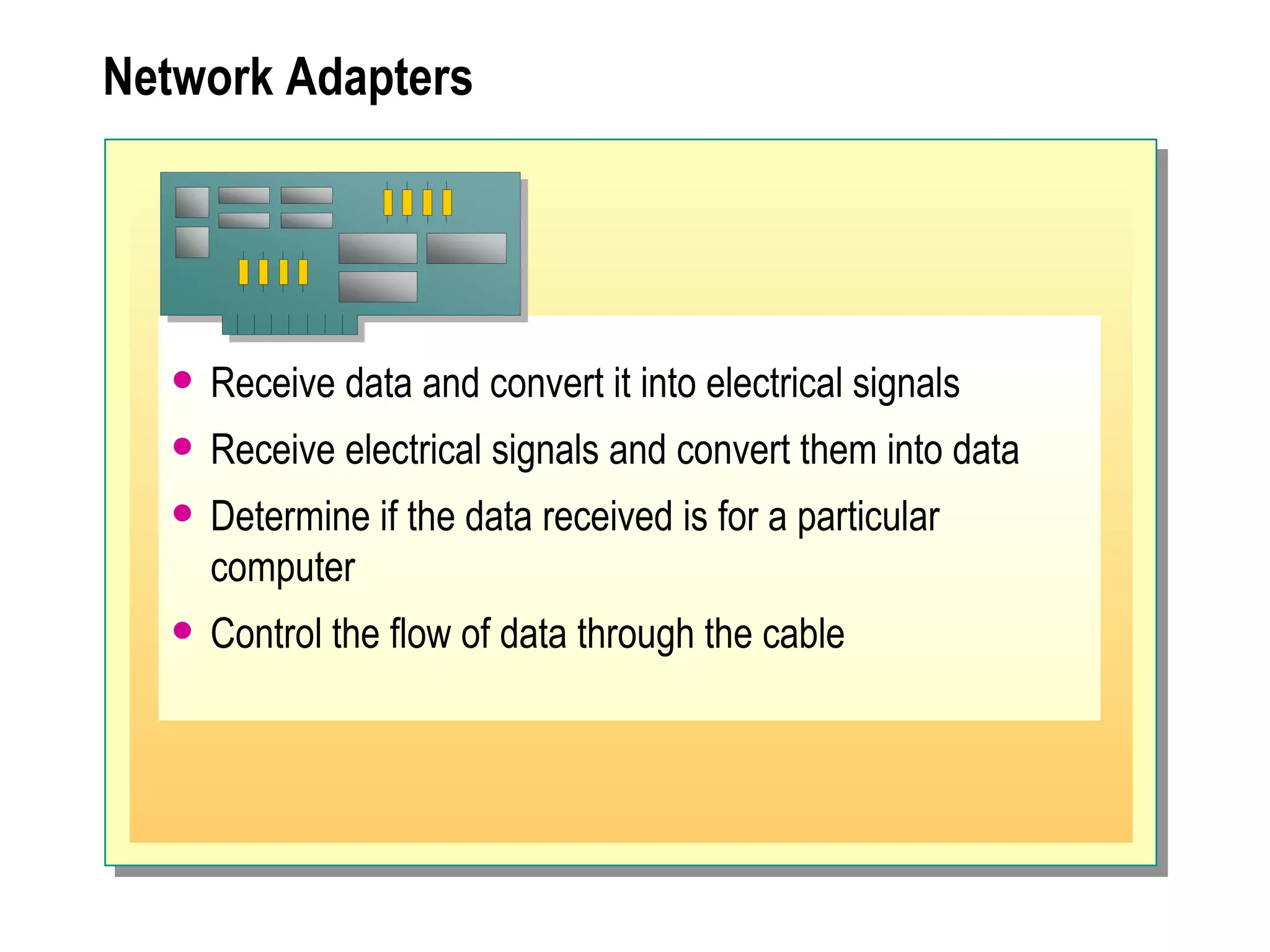
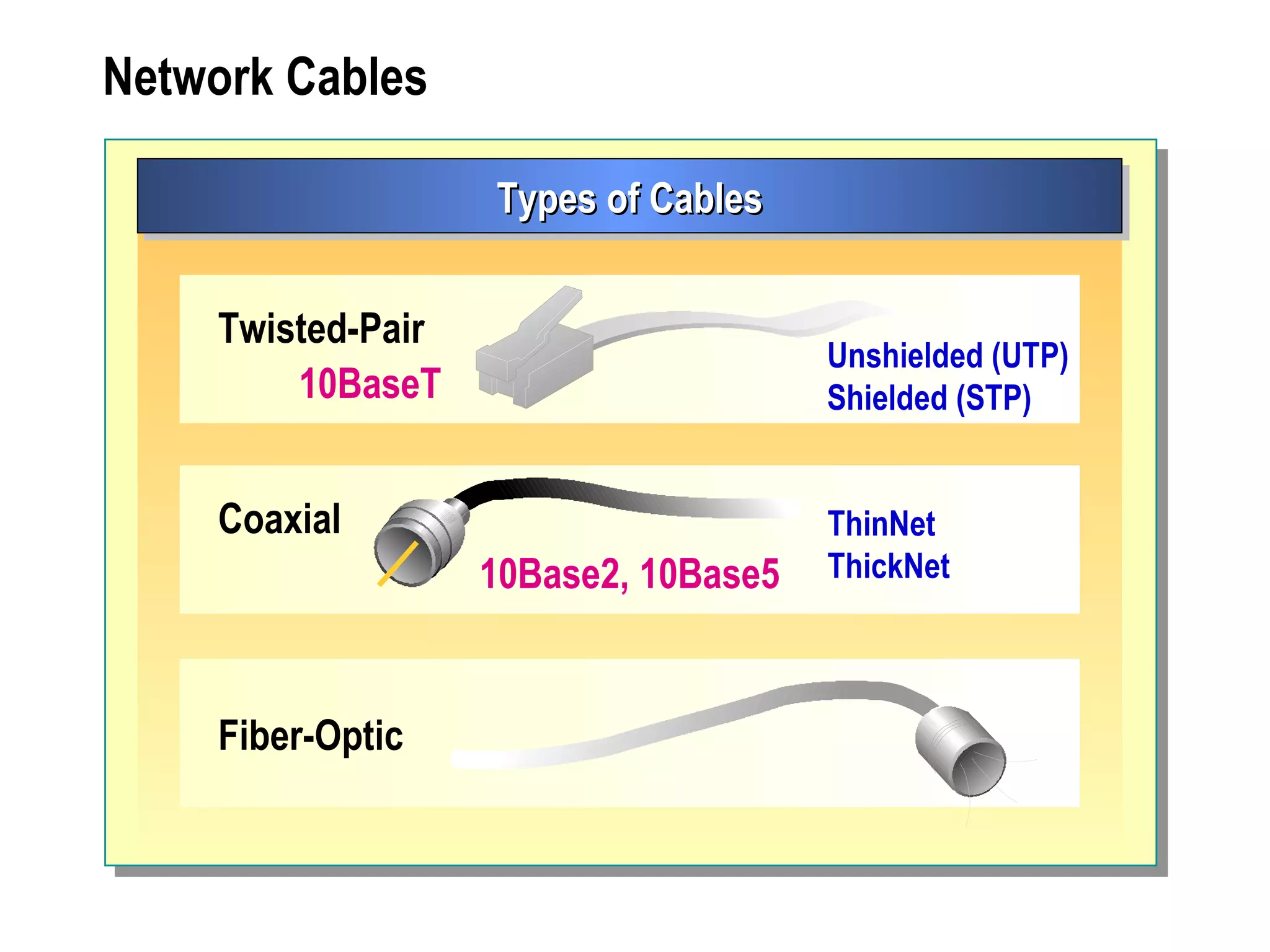
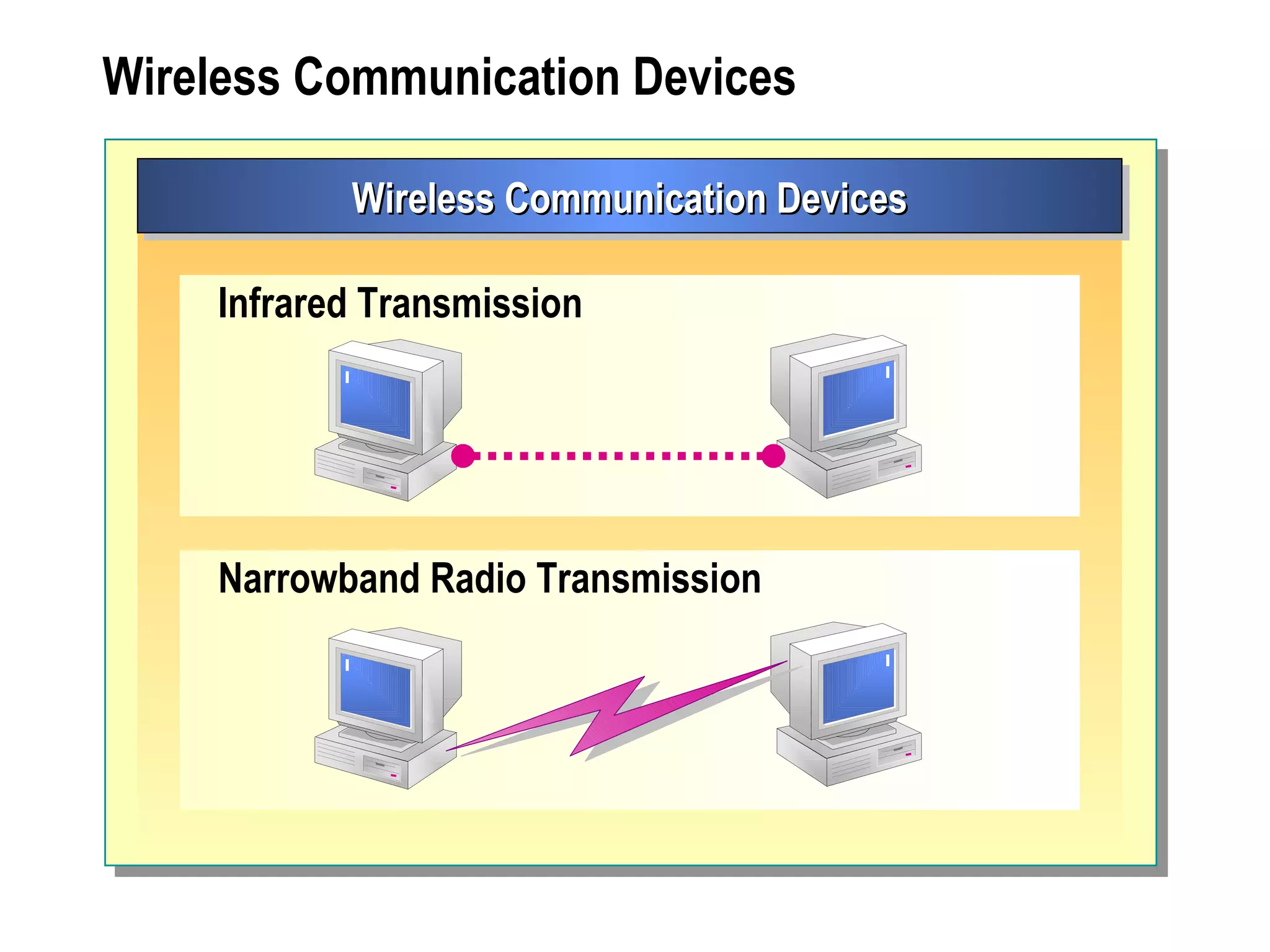
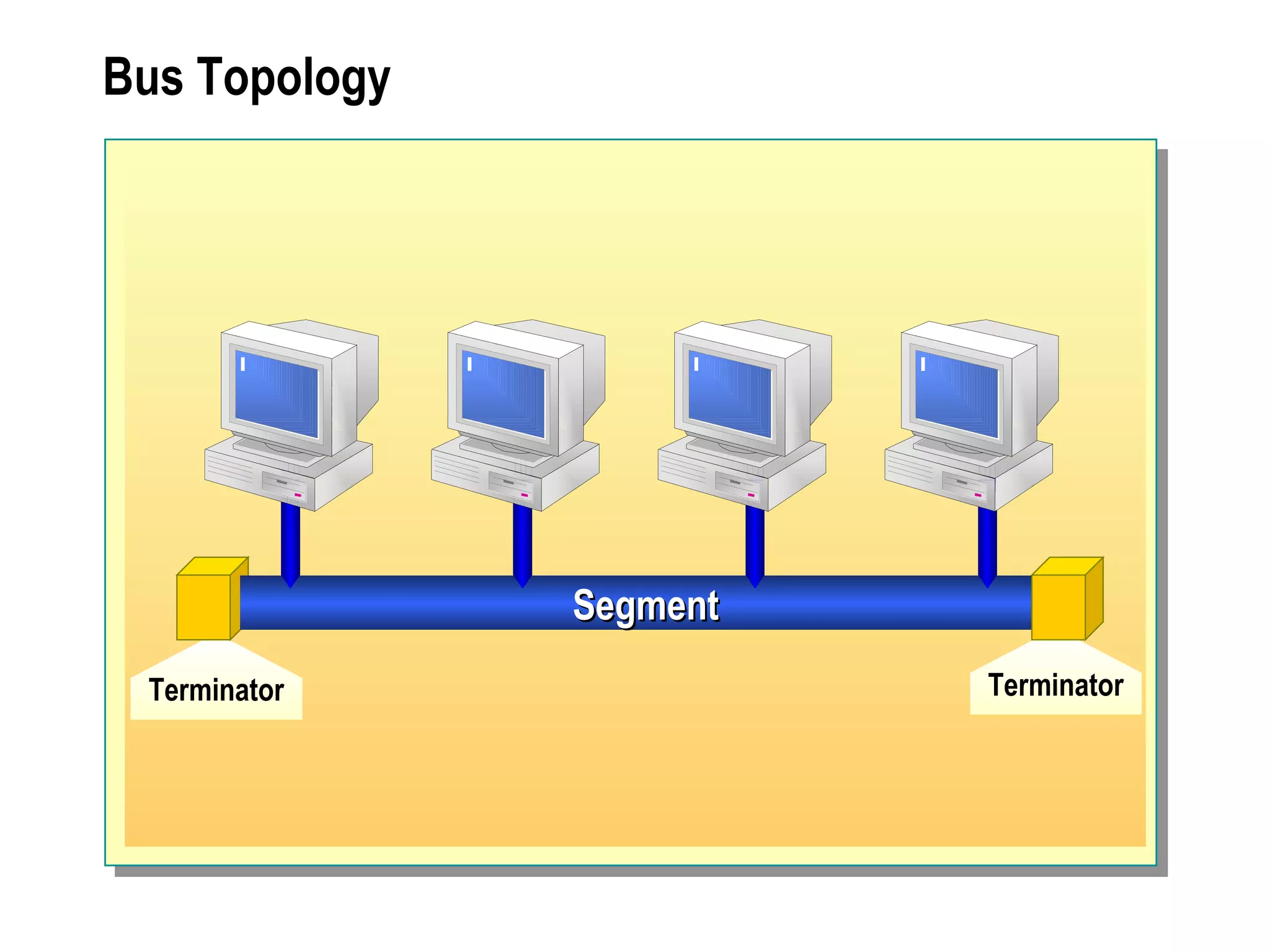
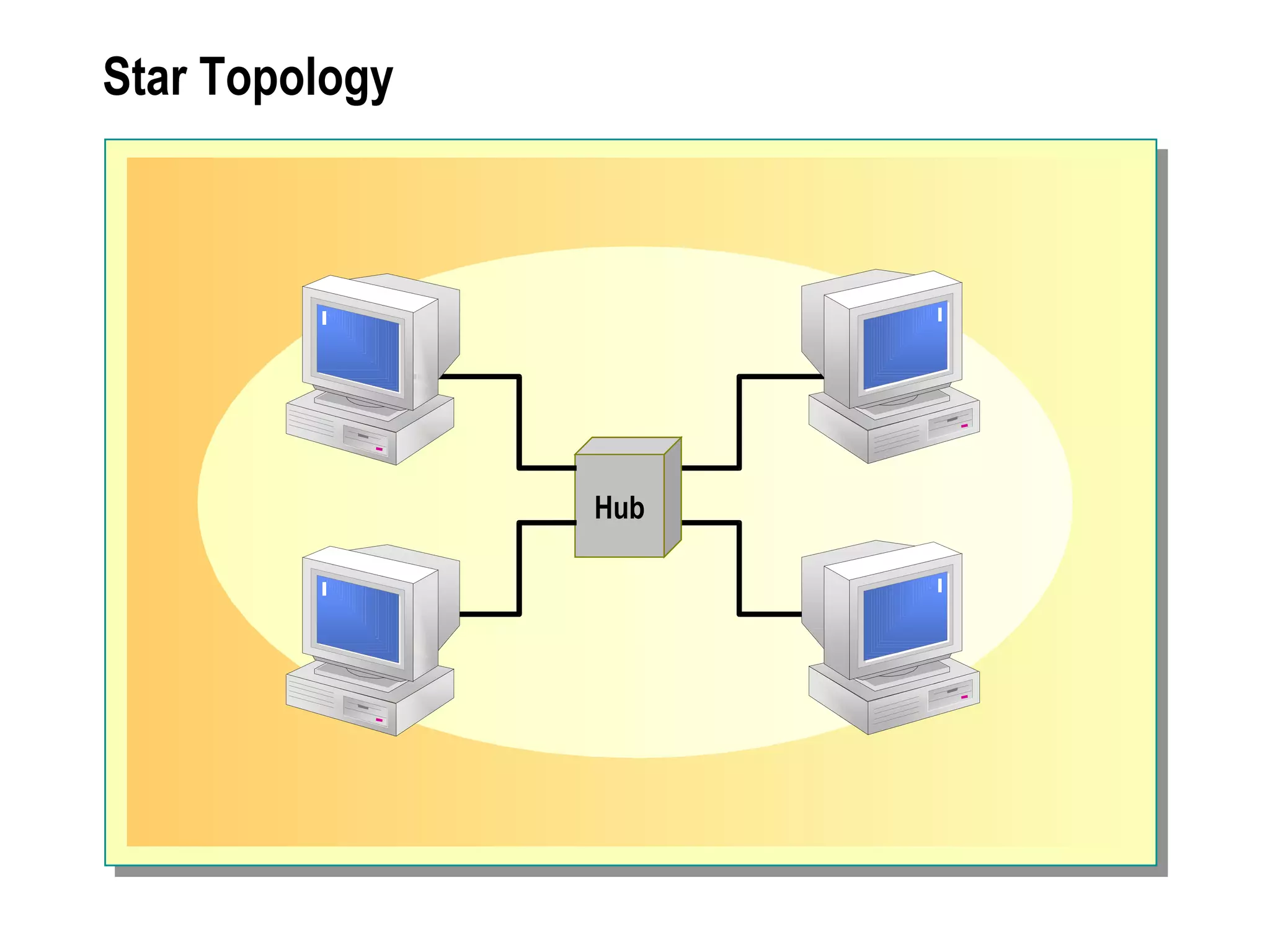
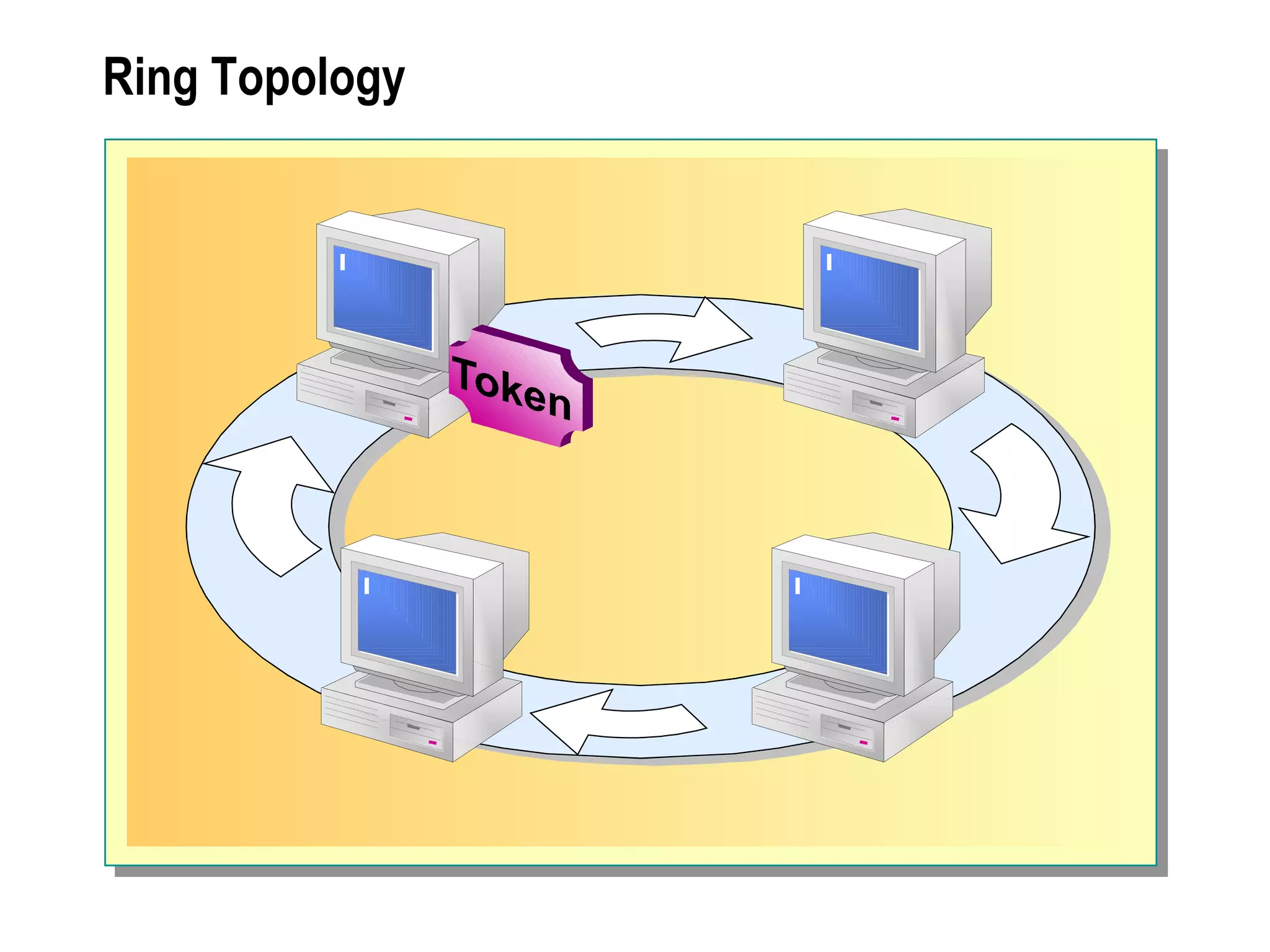
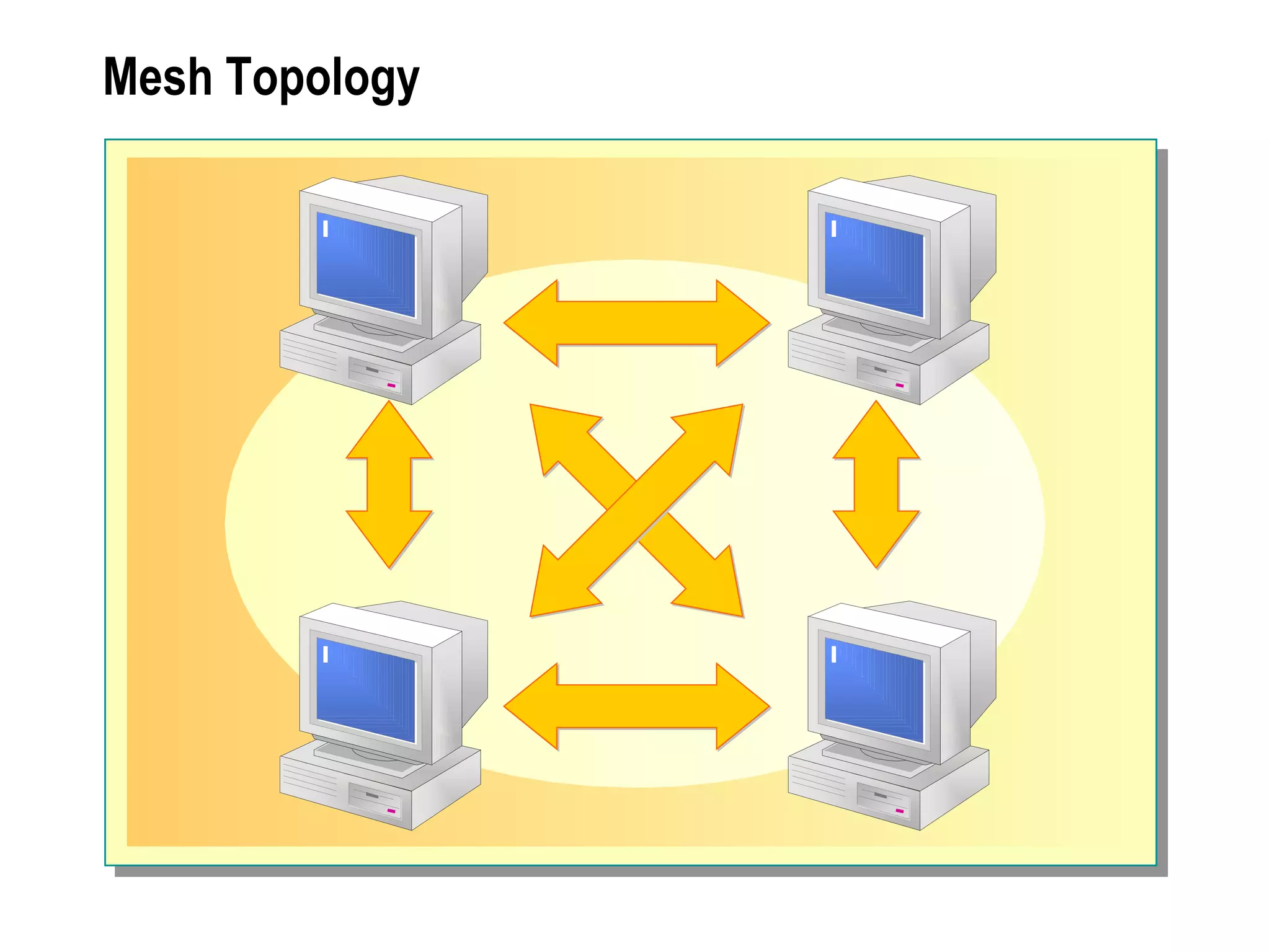
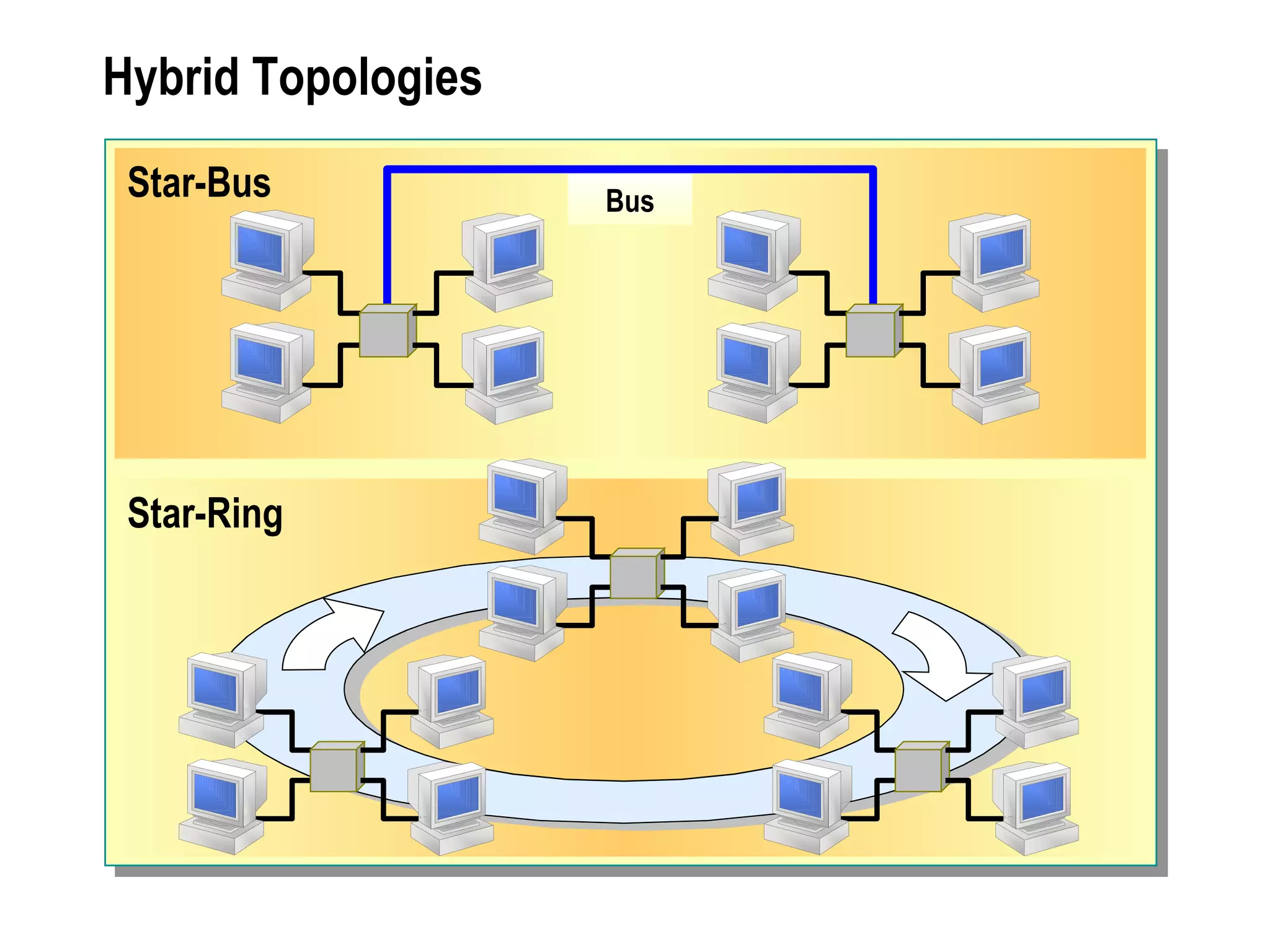
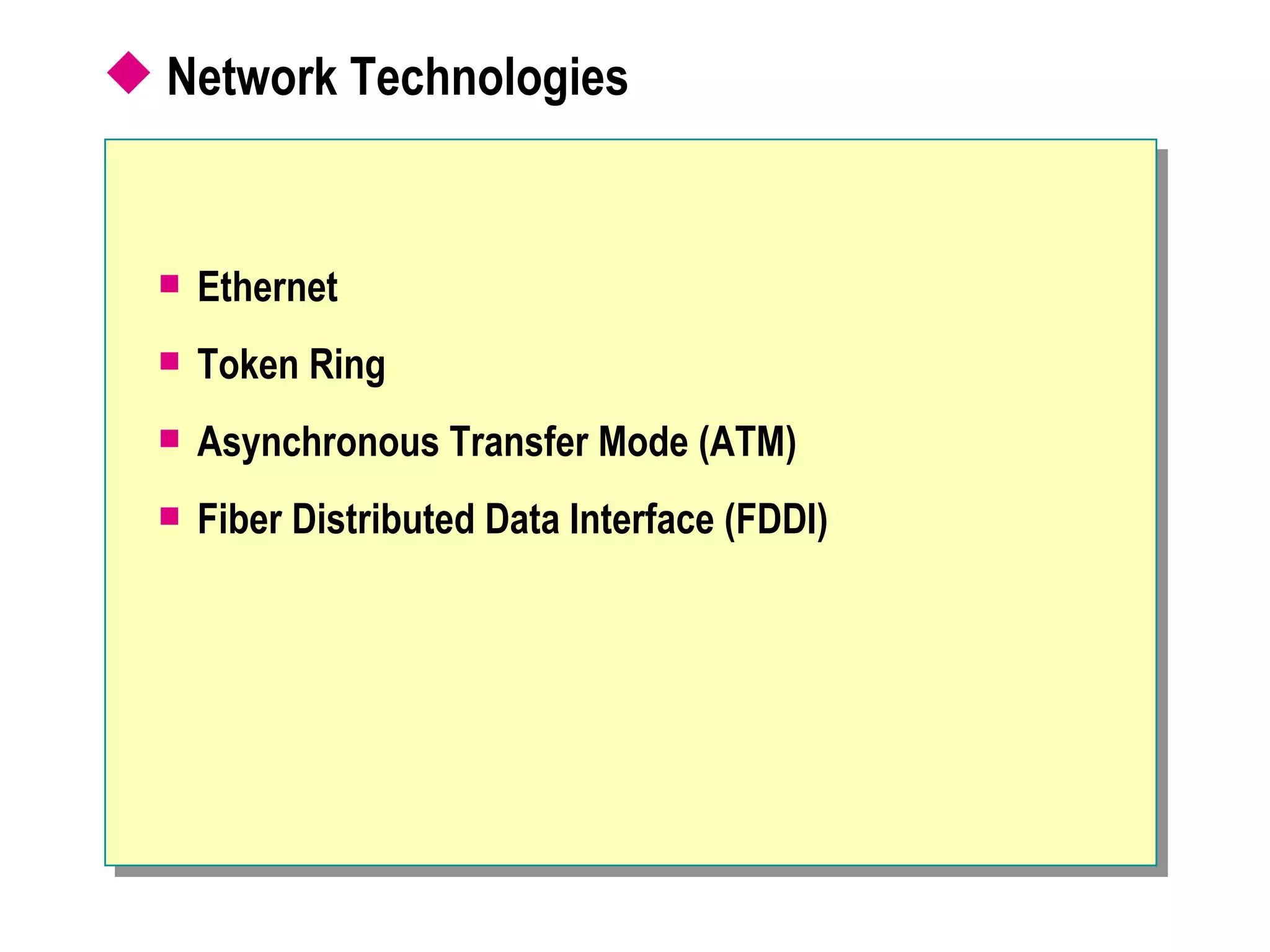
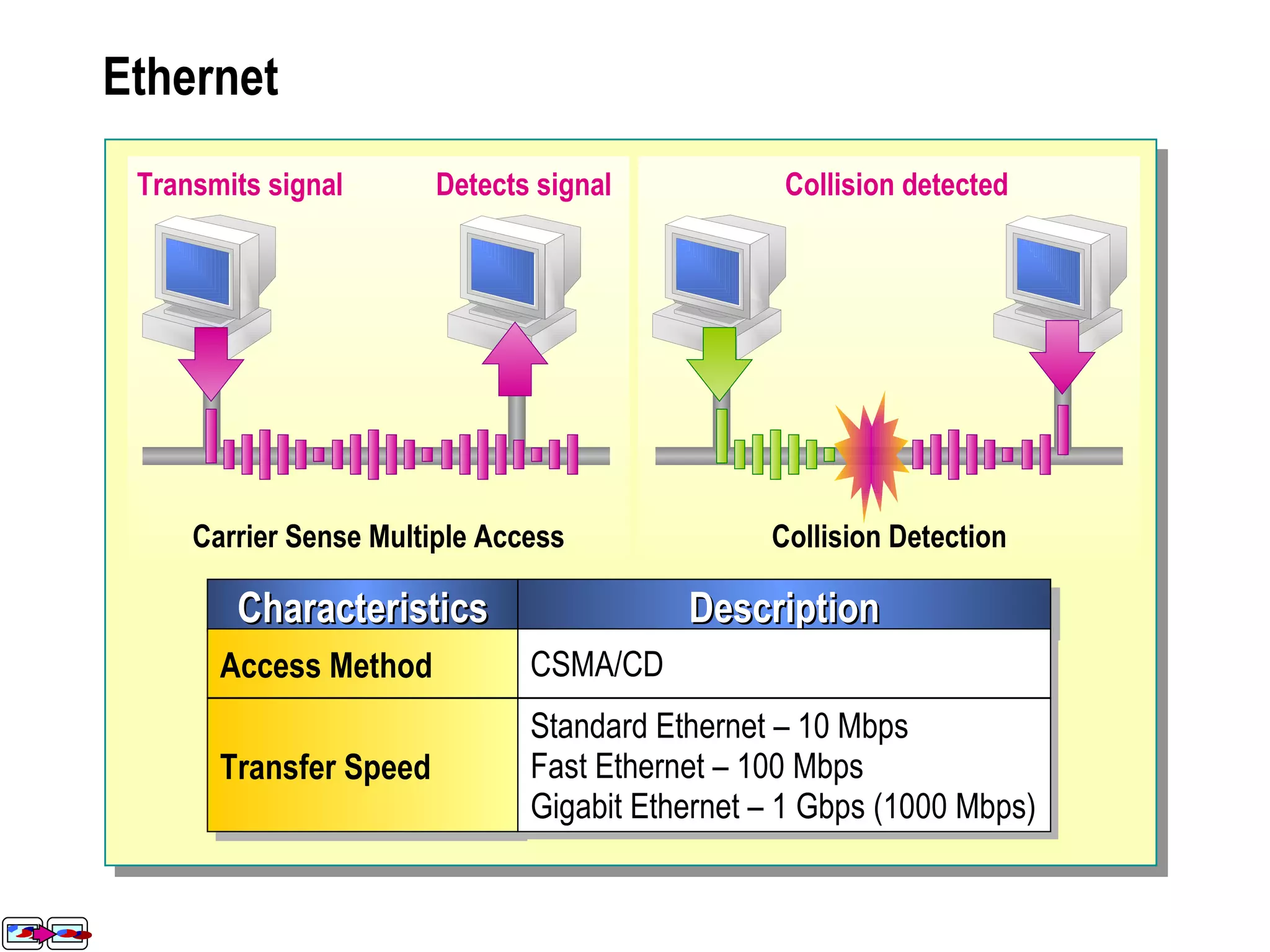
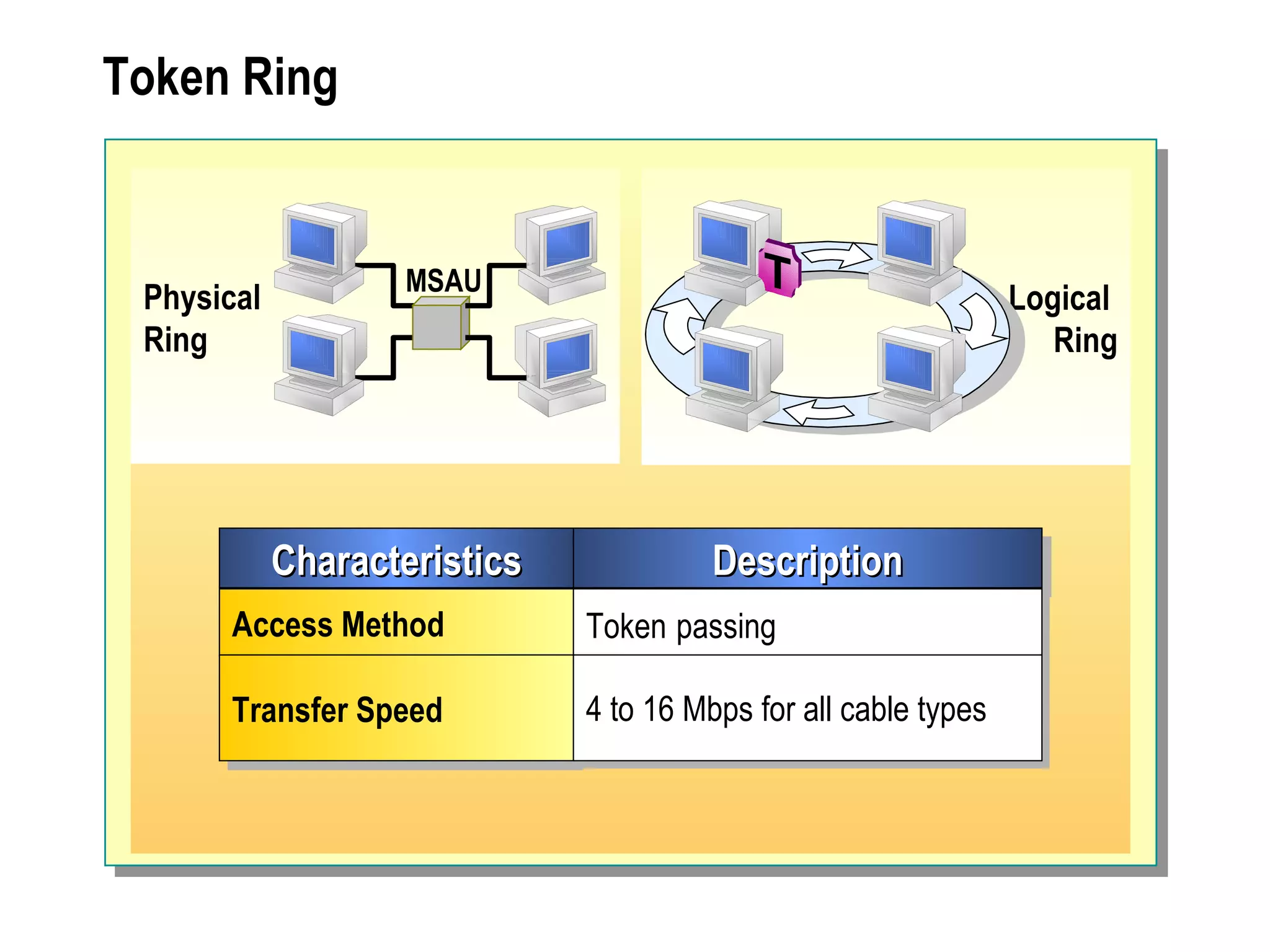
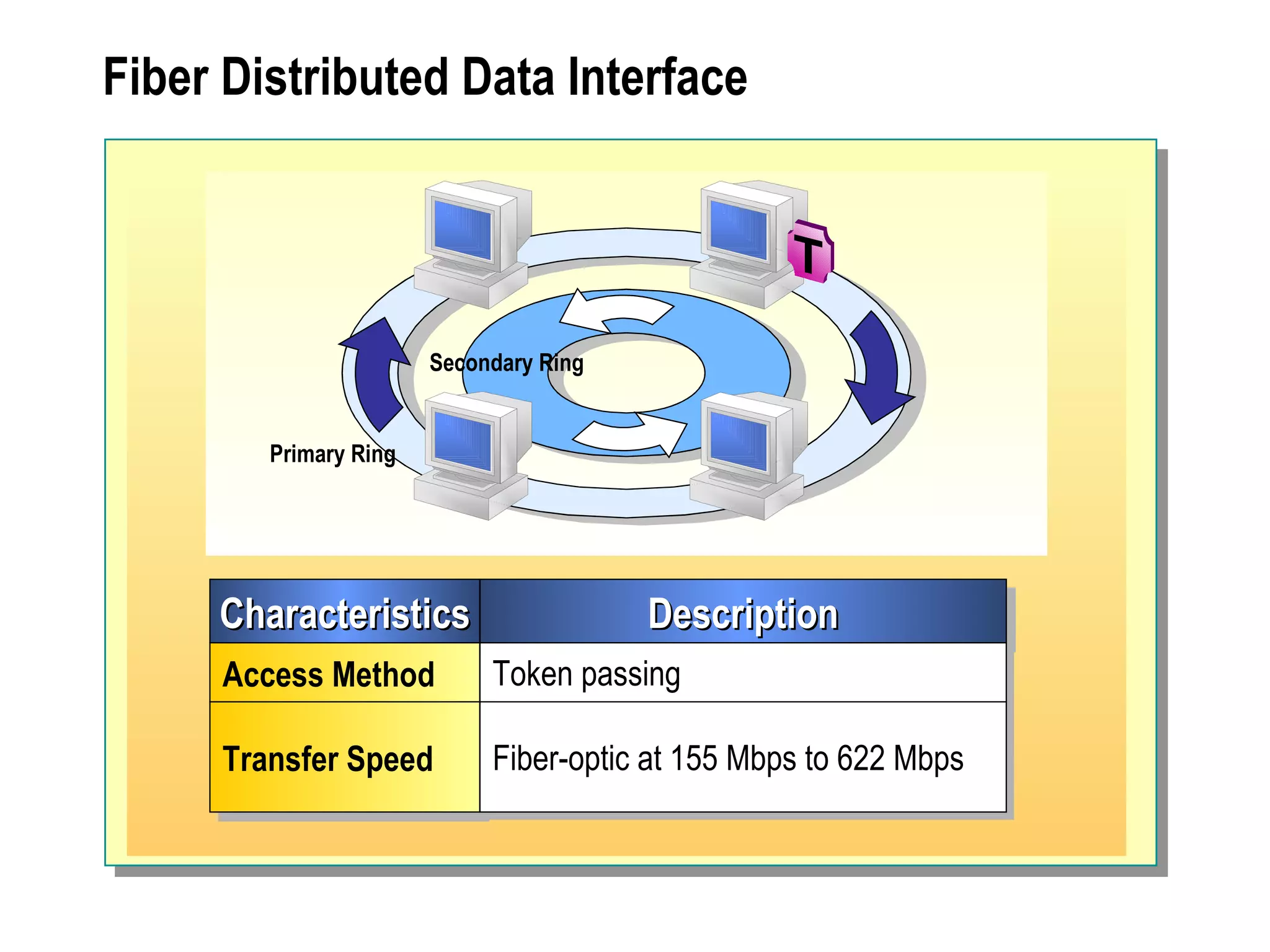
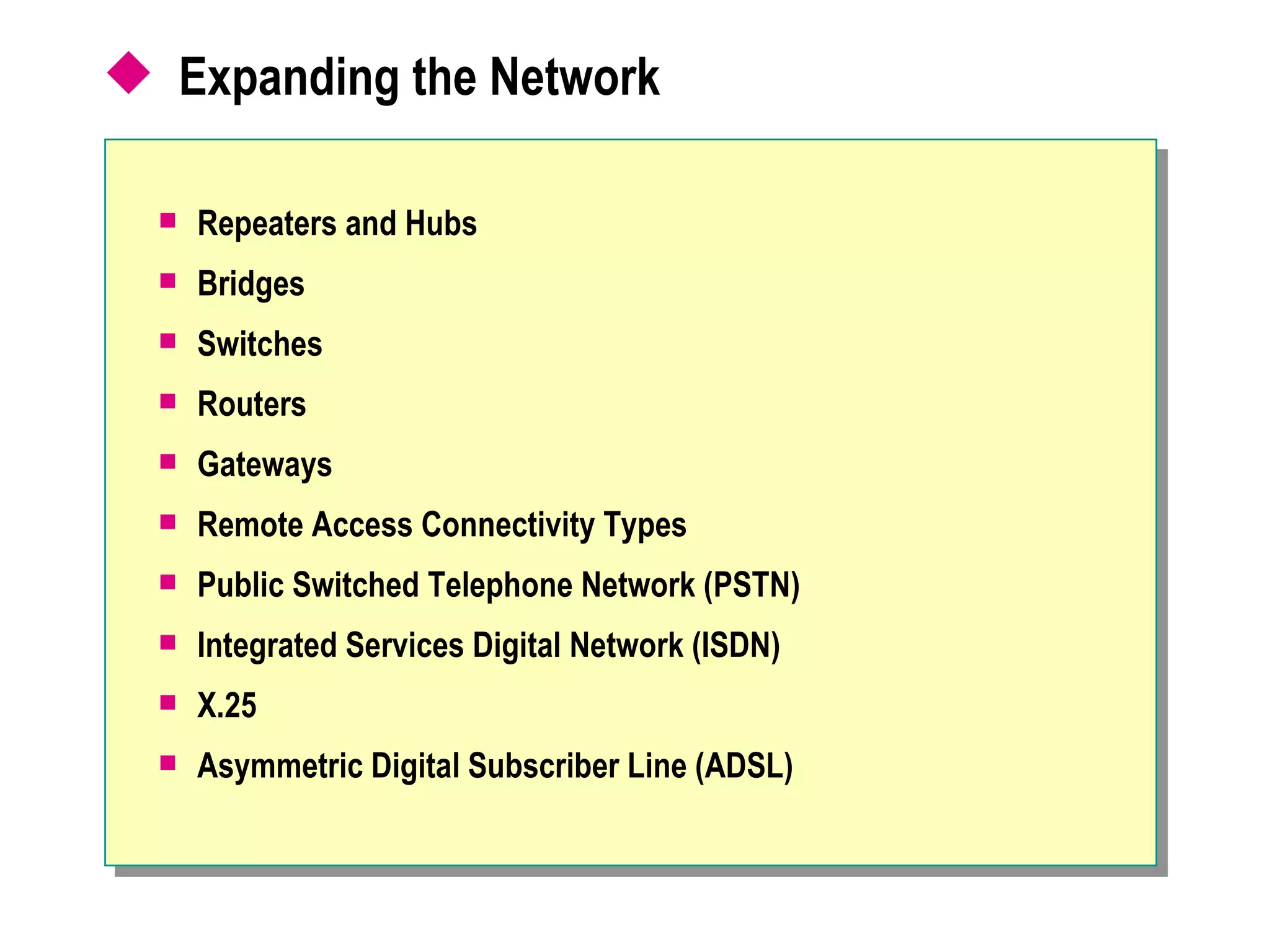
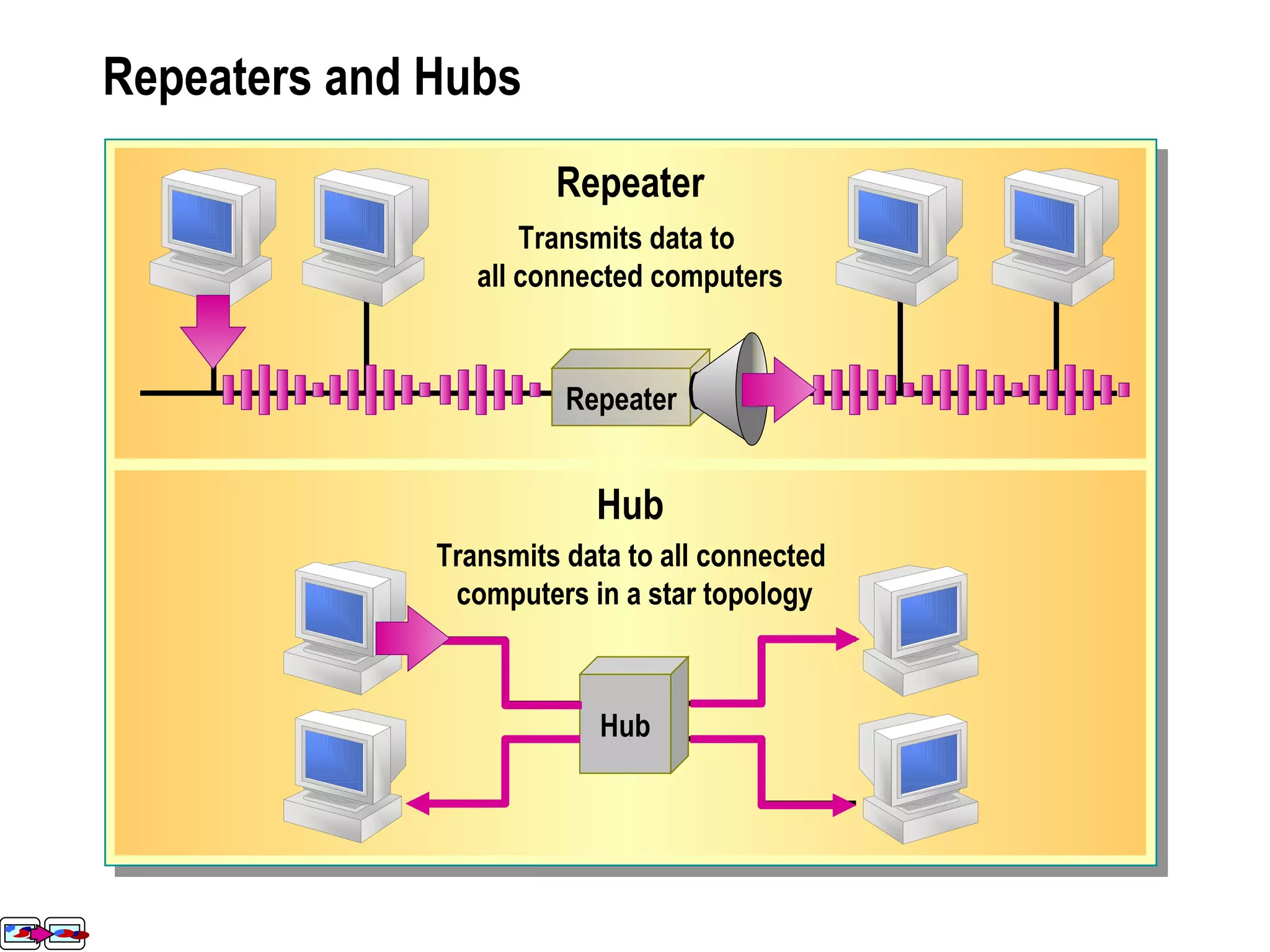
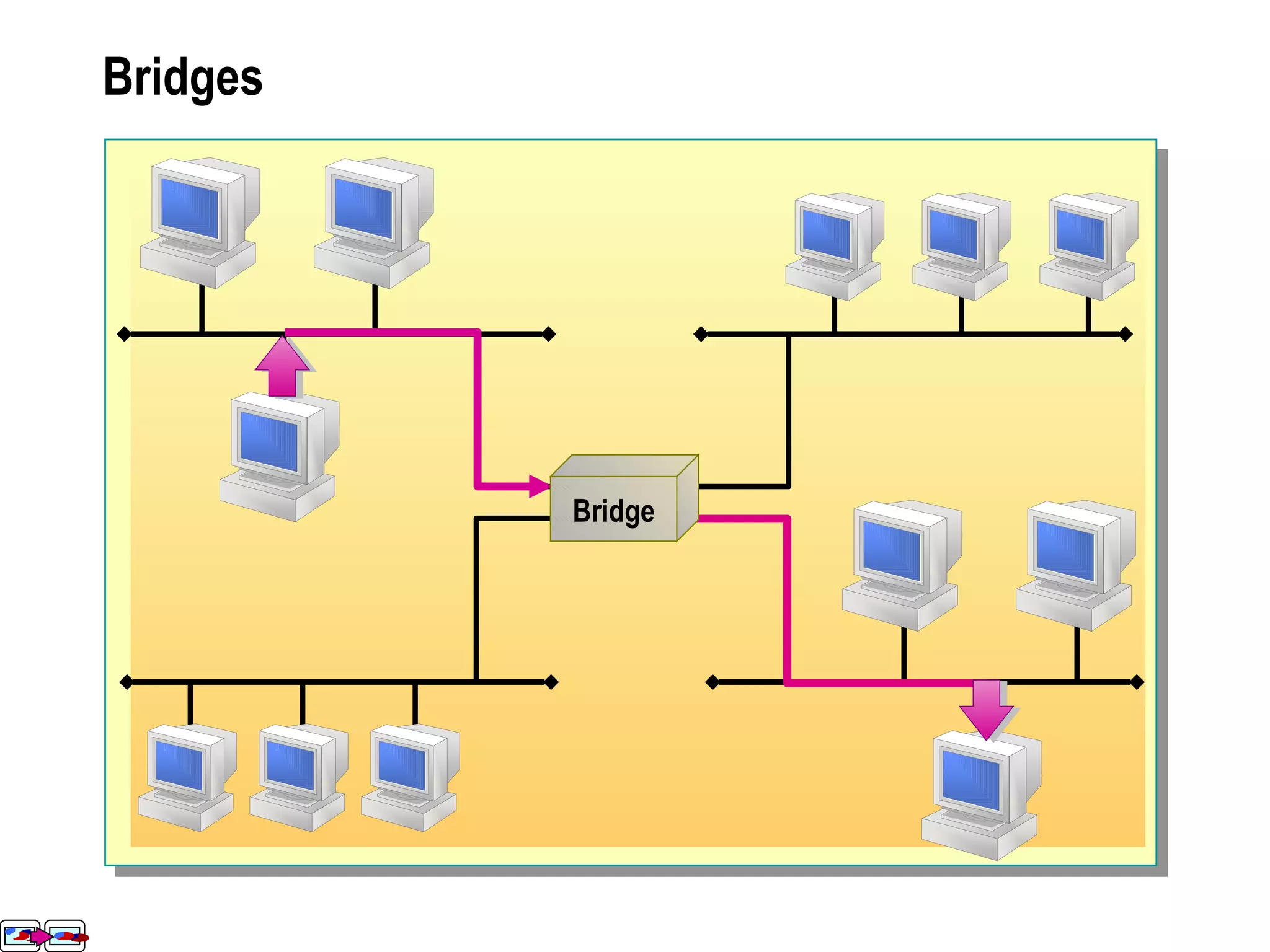
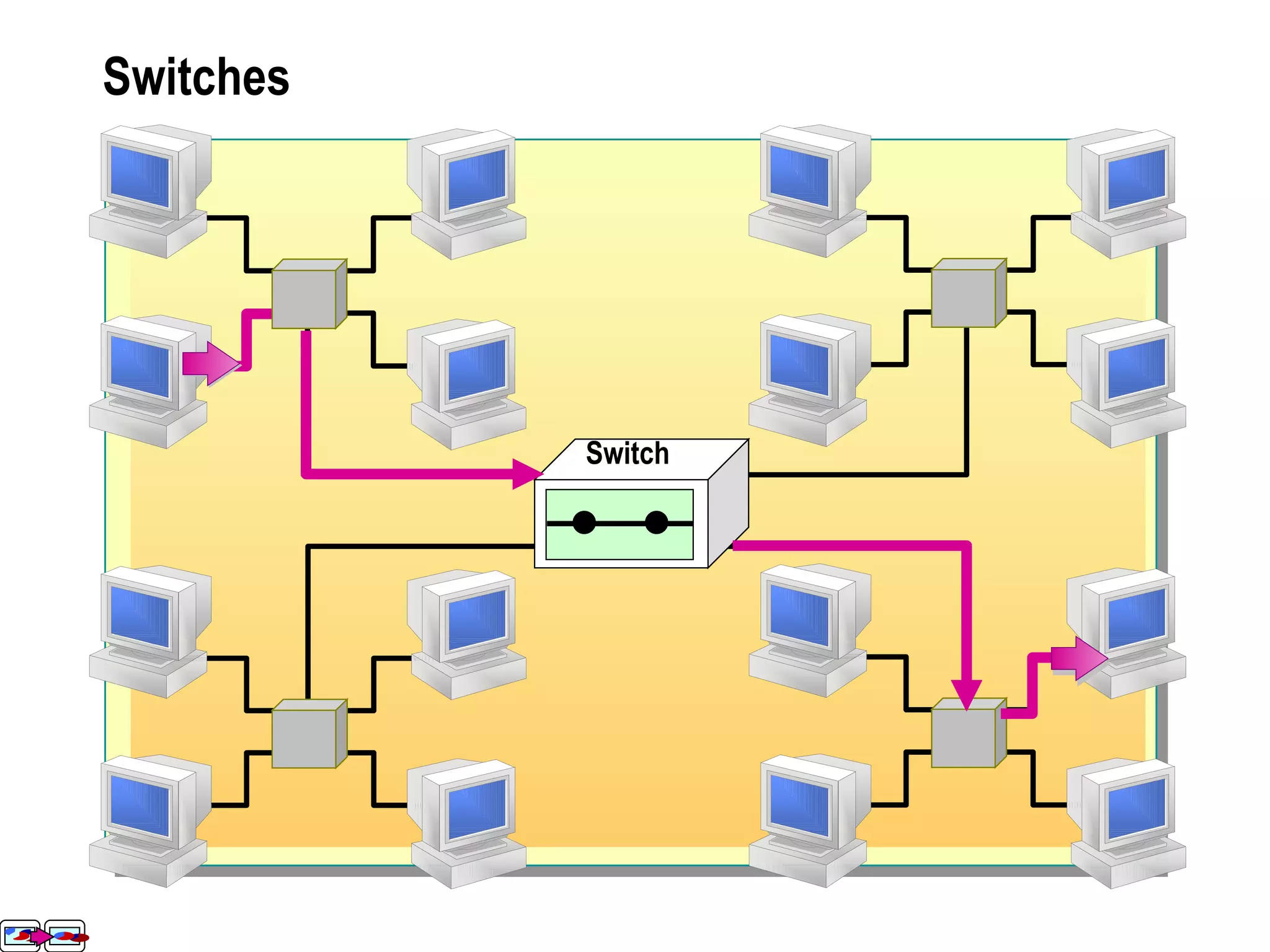
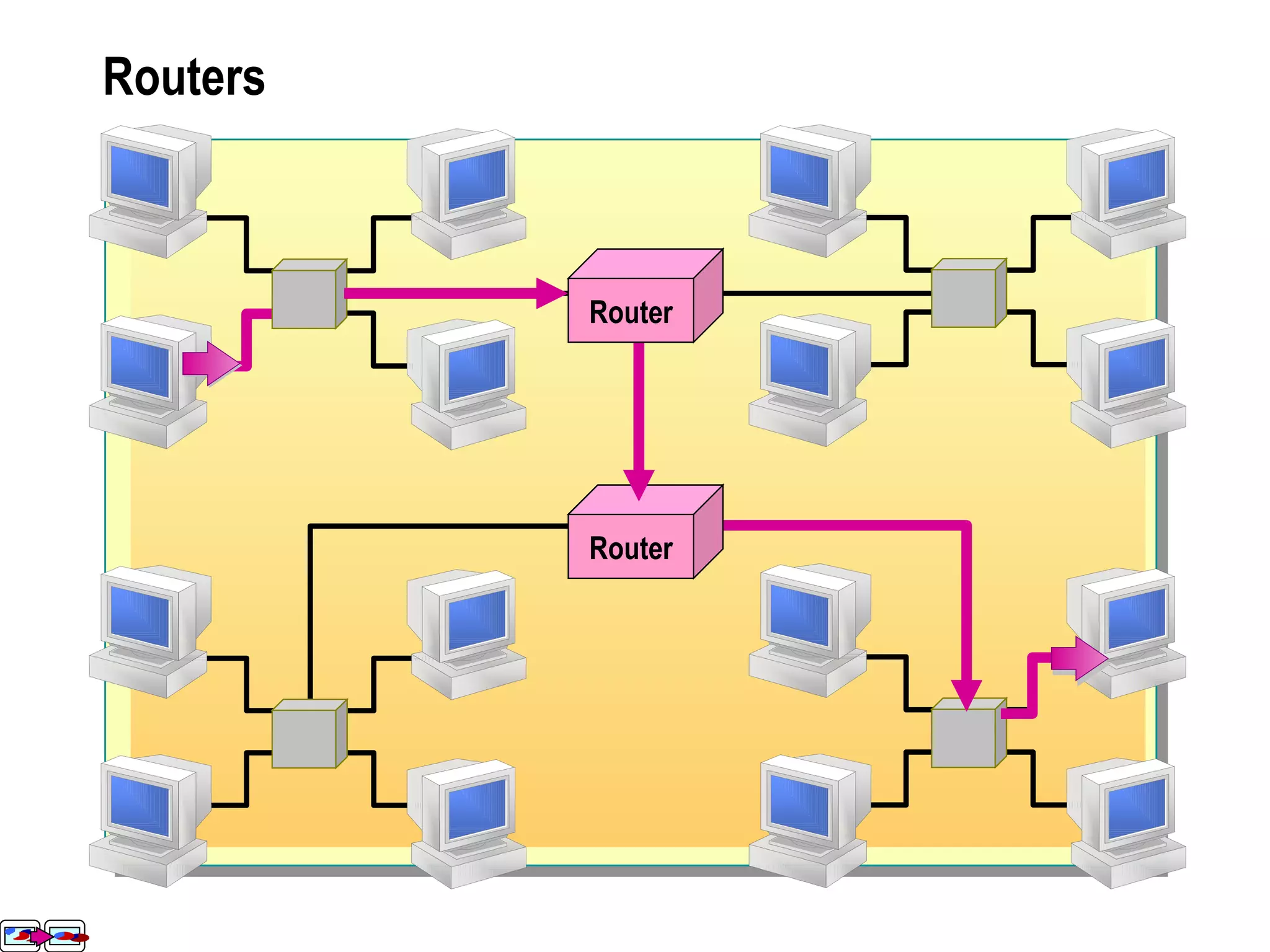
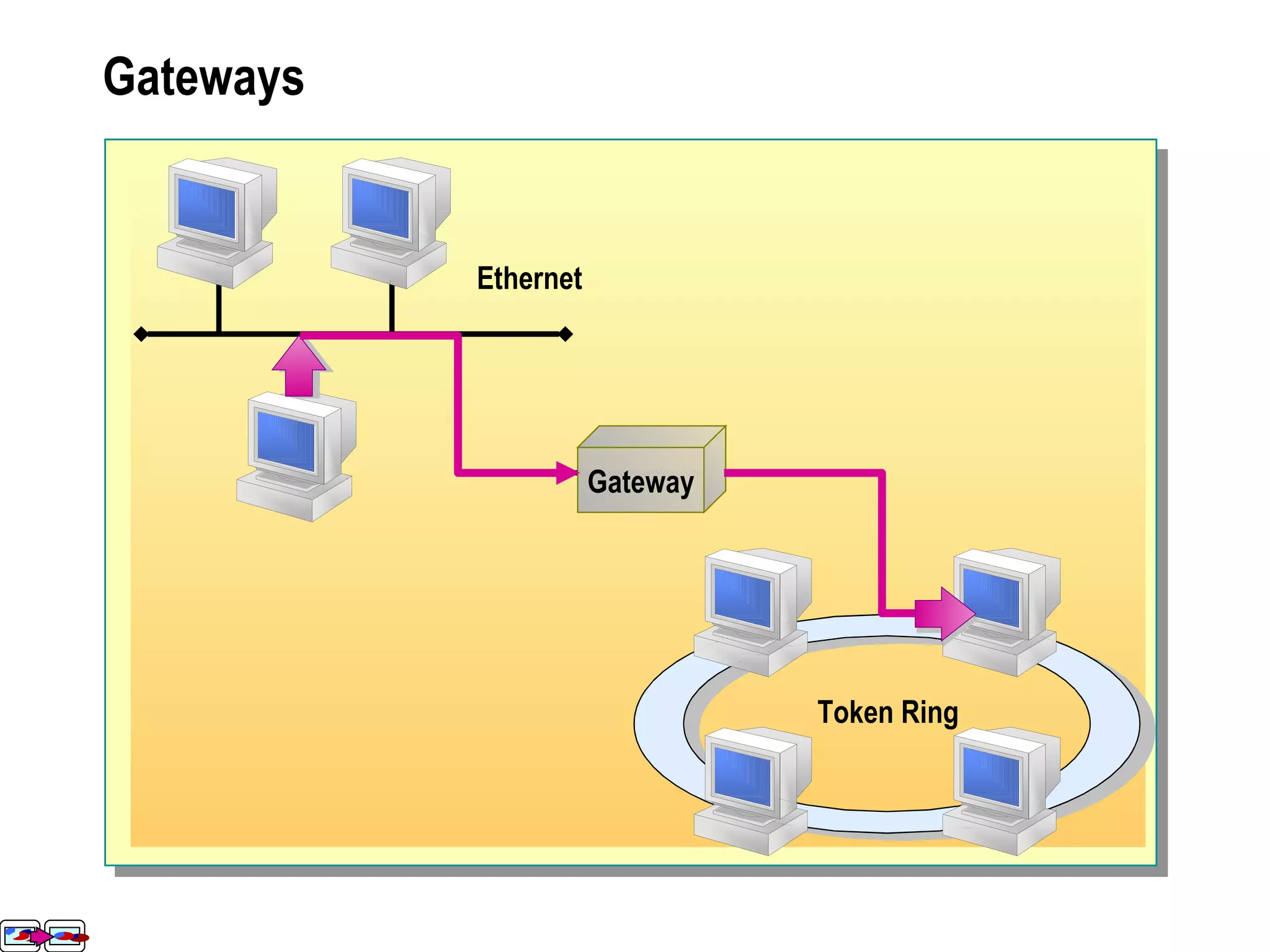
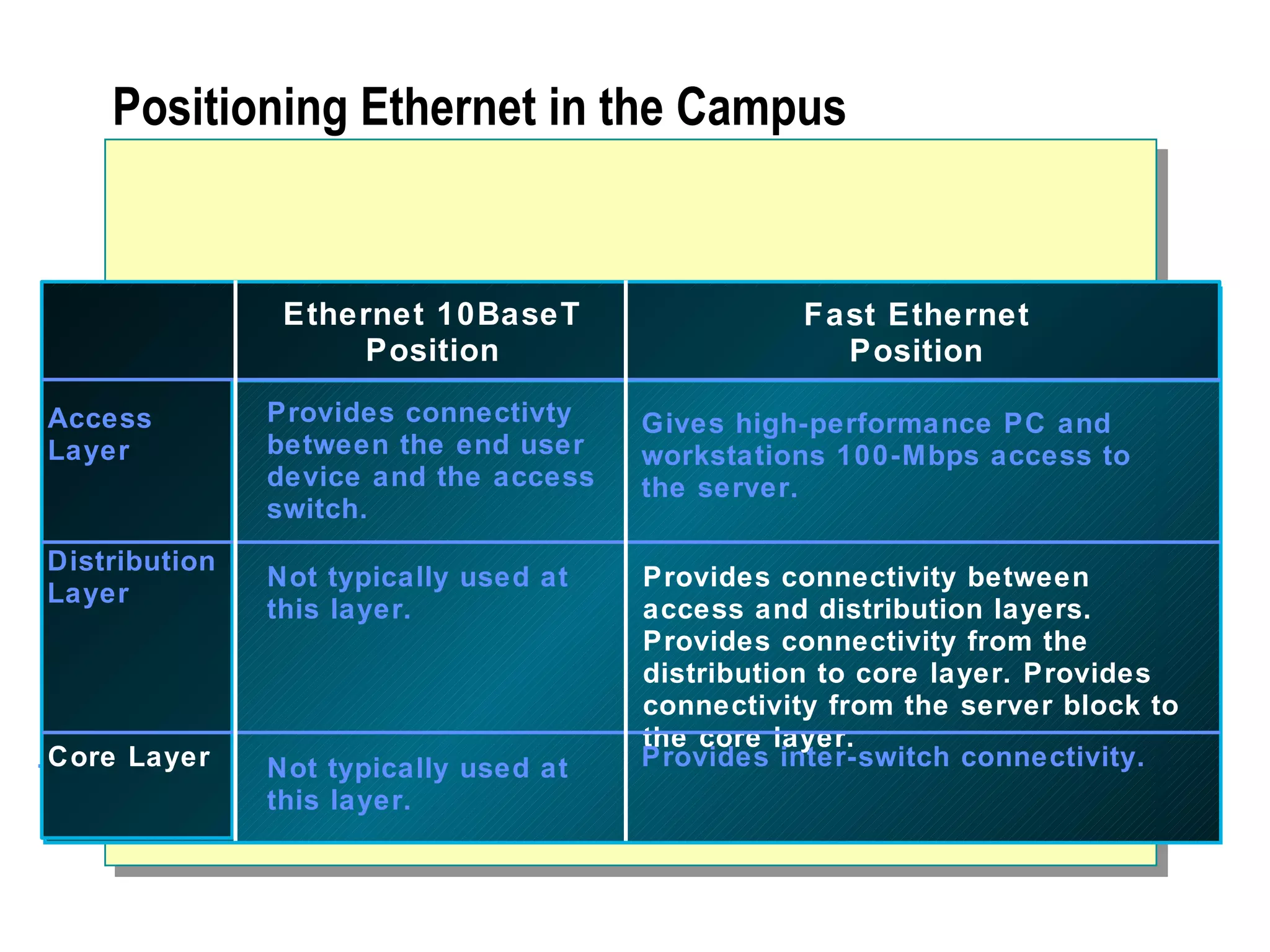
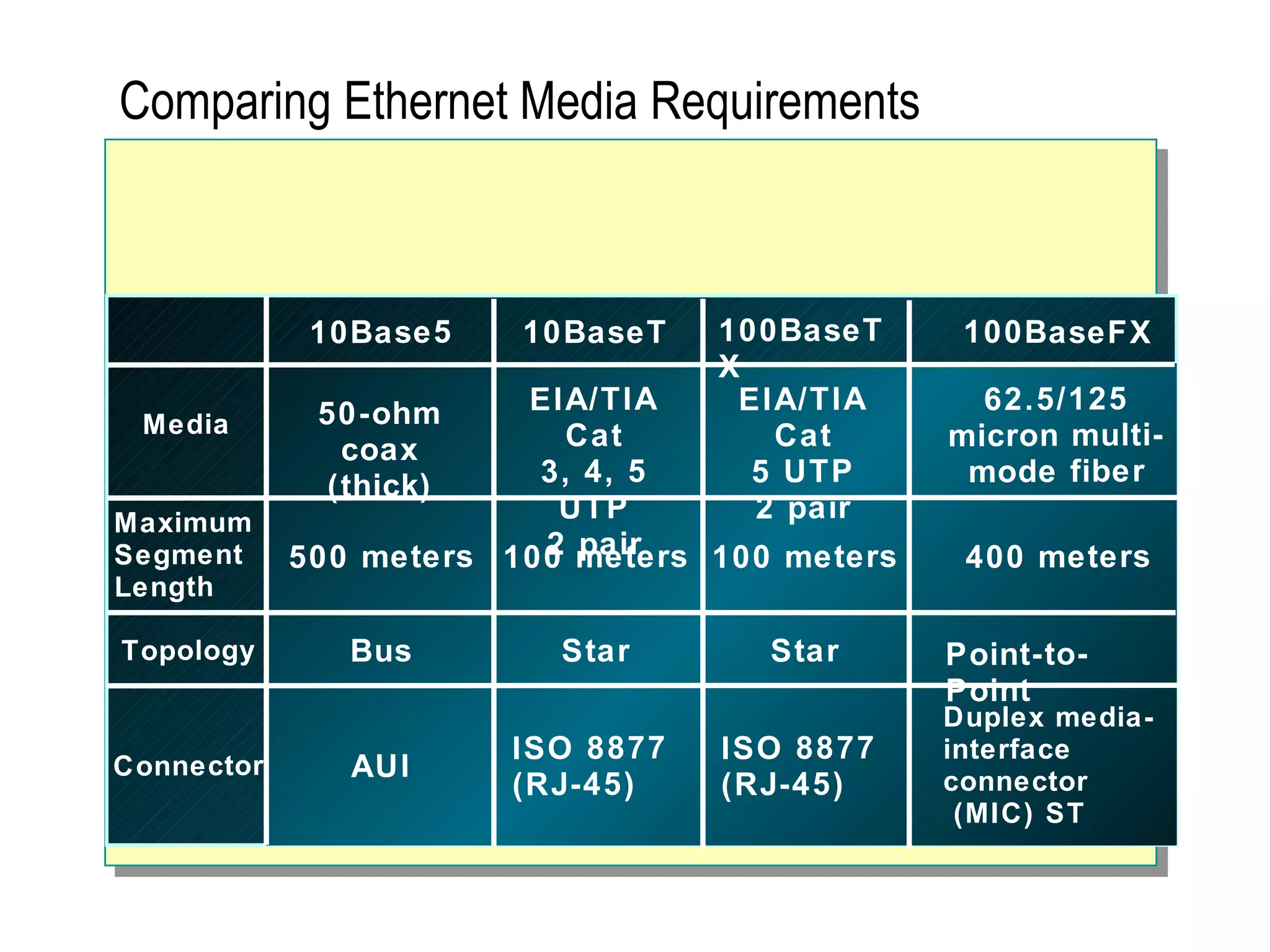
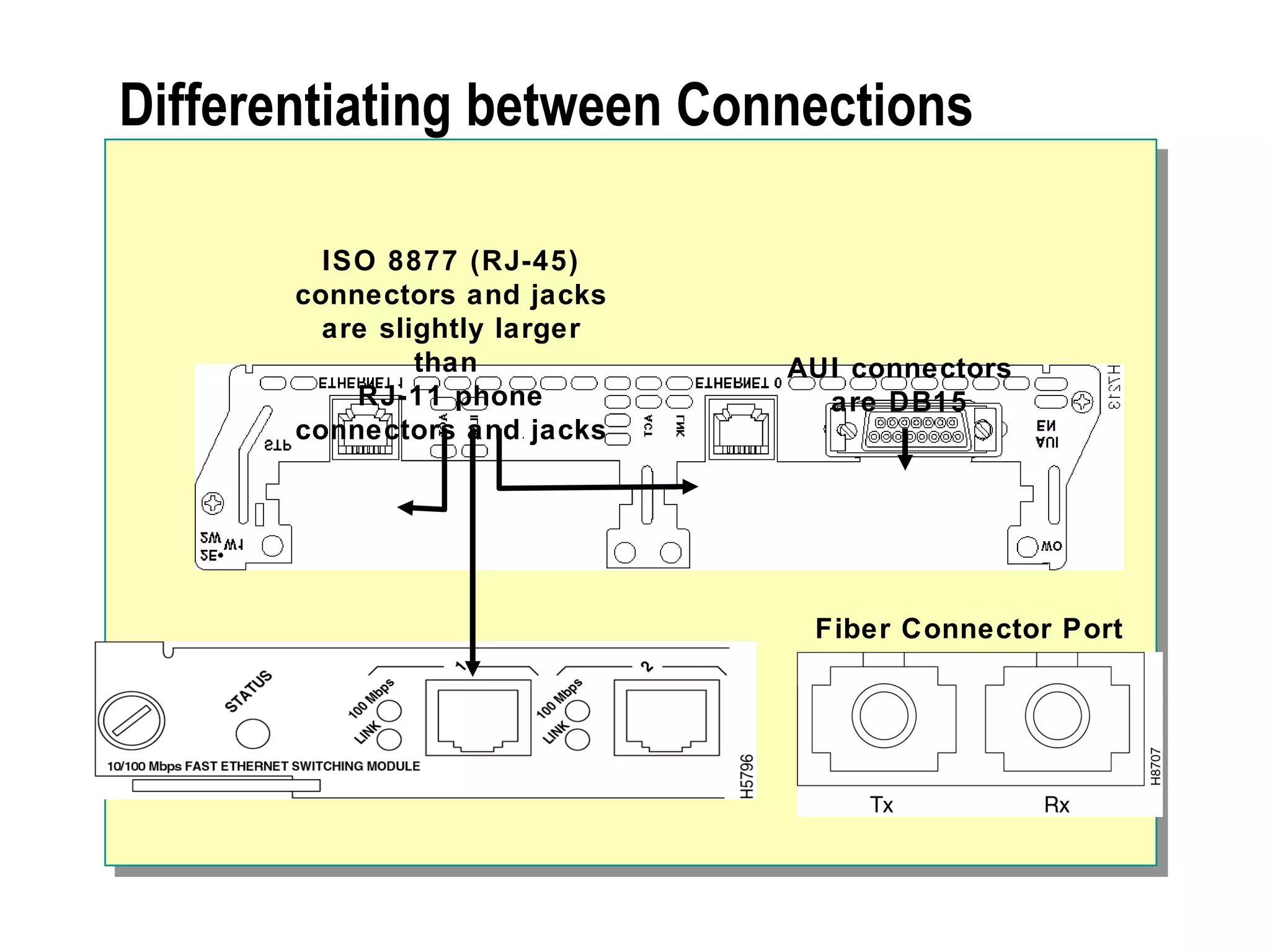
The document provides a comprehensive overview of networking essentials, including the benefits of networking, types of networks, roles of computers, and various components involved in network connectivity. It covers network topologies, technologies, and the functions of different hardware like adapters, cables, and devices such as routers and switches. Additionally, it details the specifications and methods of data transmission in both wired and wireless environments, emphasizing the importance of various Ethernet standards.