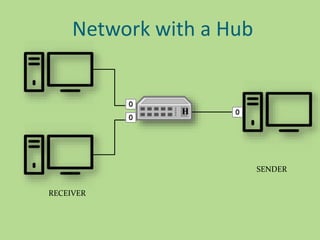
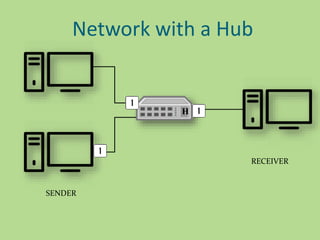
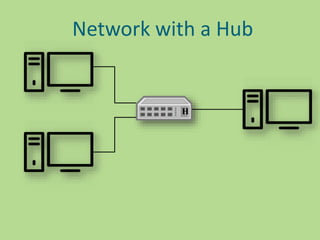
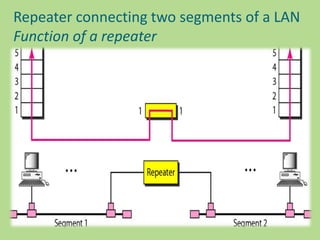
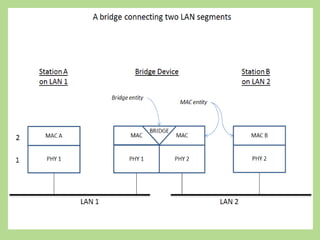
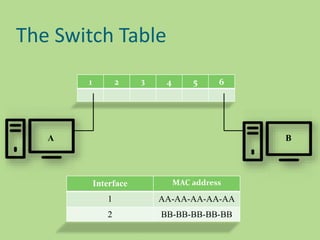
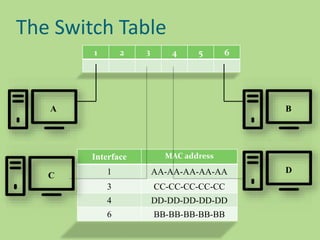
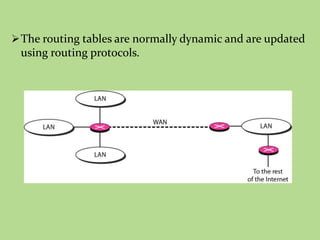
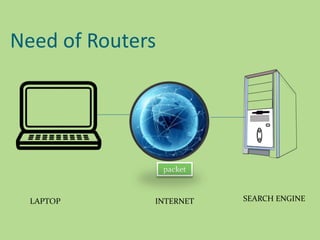
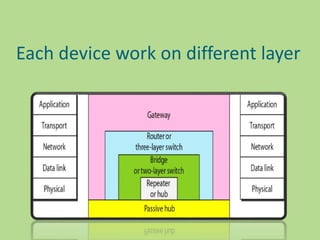
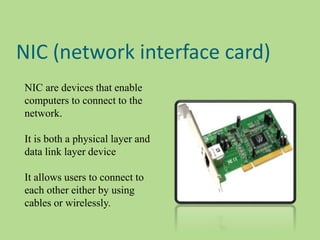
This document discusses several common networking devices and their functions. It describes hubs, switches, bridges, routers, gateways, CSU/DSUs, NICs, ISDN adapters, modems, and firewalls. Hubs broadcast traffic to all ports, wasting bandwidth, while switches only forward frames to their destination port. Bridges operate at the data link layer and routers at the network layer. Gateways perform protocol translation. NICs connect devices to the network. Modems convert digital to analog signals for transmission over phone lines. Firewalls control network access for security.