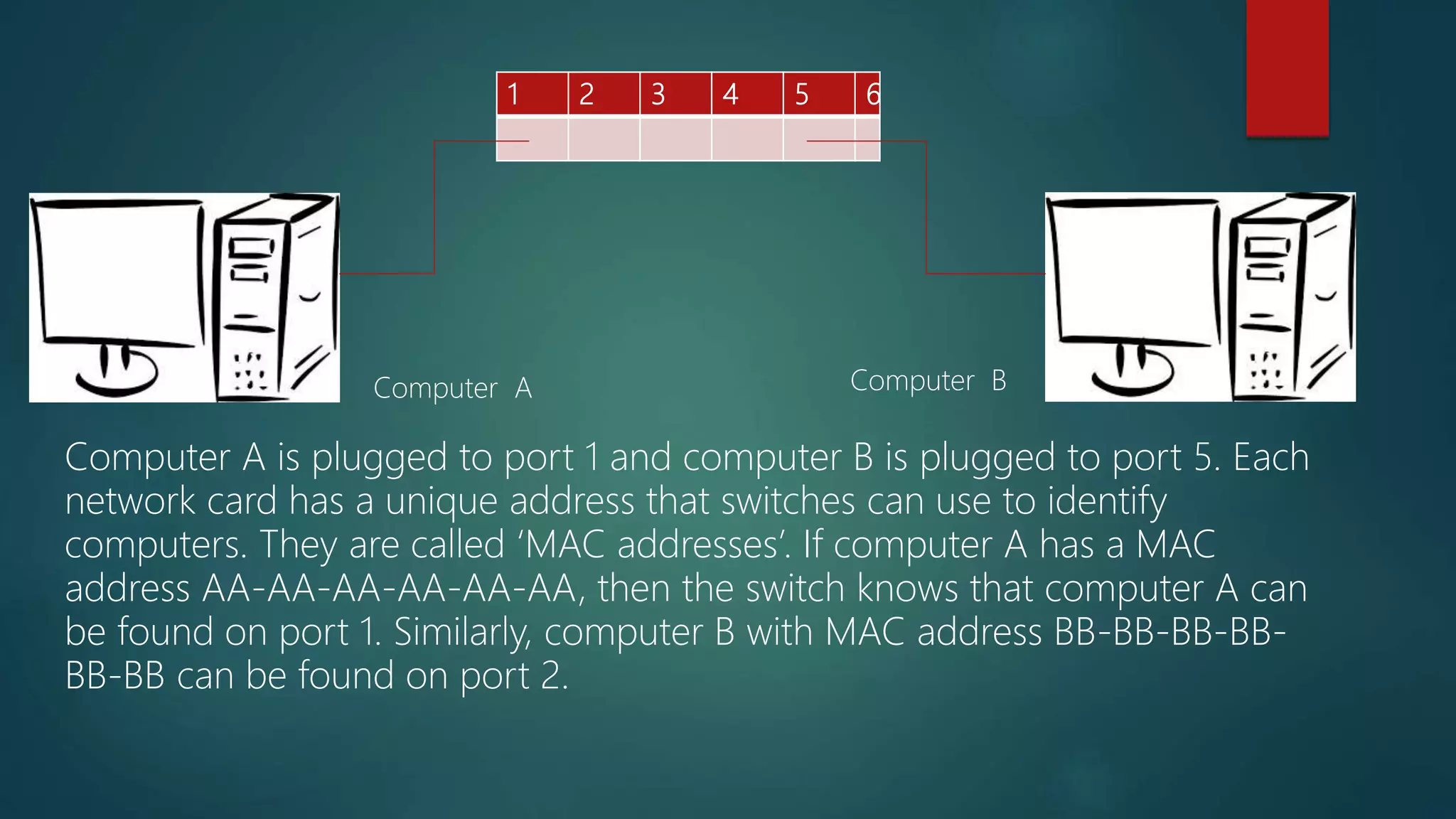
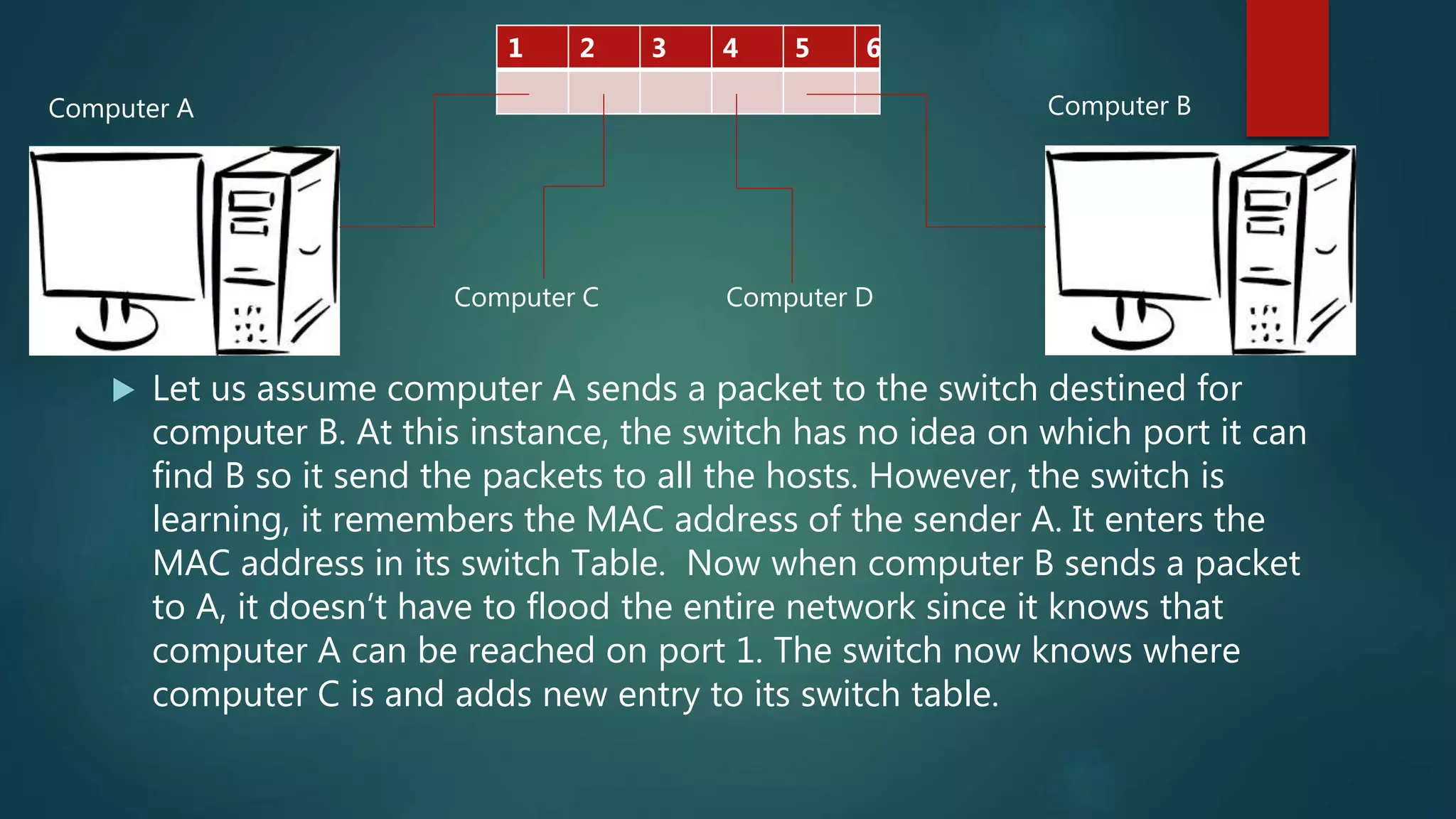
This document summarizes and compares common network devices: hubs, switches, and routers. It explains that hubs broadcast all data to all ports, wasting bandwidth, while switches learn MAC addresses to send data only to the targeted port. Routers connect different networks and route packets between them, allowing communication across the internet.