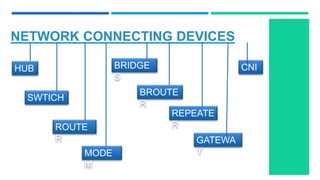
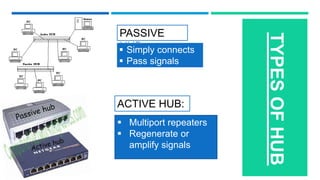
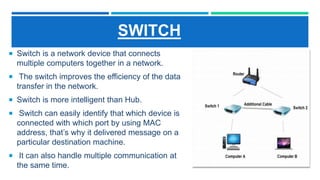
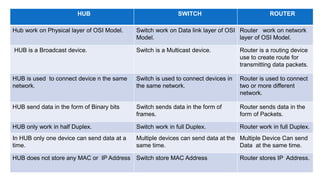
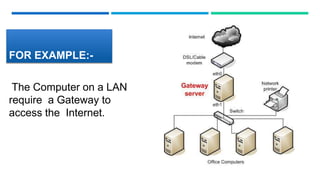
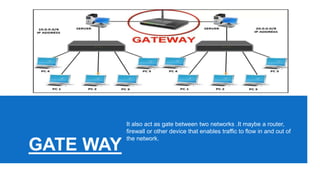
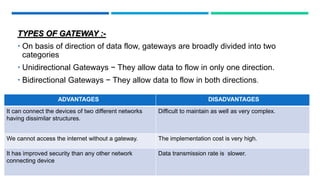
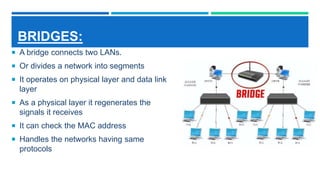
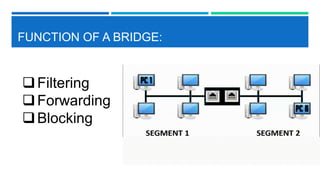
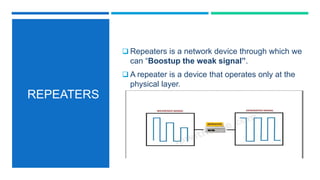
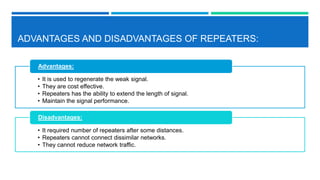
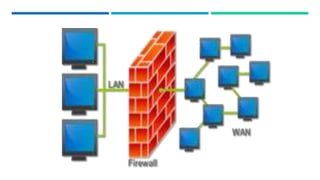
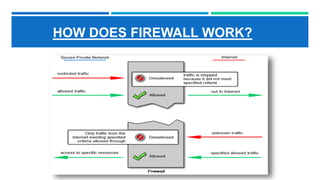
Networking devices such as hubs, switches, routers, and gateways are used to connect electronic devices and share files and resources over a local area network (LAN). Hubs connect multiple devices but do not filter traffic. Switches are more intelligent and can identify devices to deliver messages only to the intended recipient. Routers connect different networks and choose congestion-free paths. Gateways connect incompatible networks by translating between protocols. Other devices like bridges, brouters, repeaters, modems, access points, and network interface cards (NICs) help devices connect either via wired or wireless connections. Network security devices such as firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS