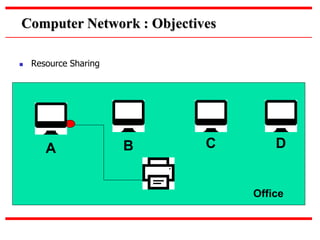
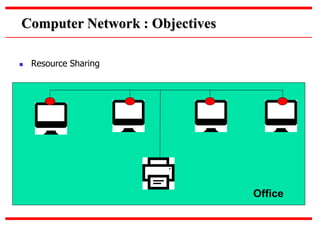
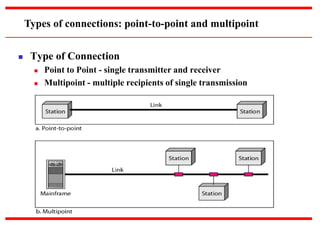
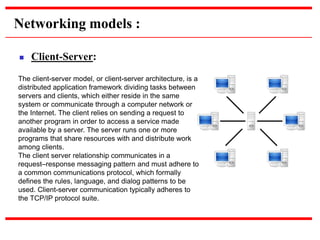
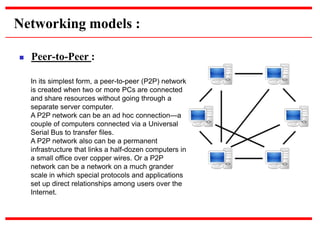
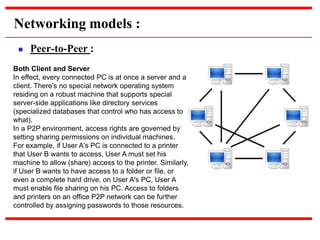
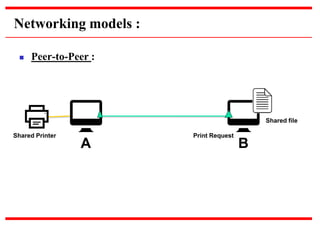
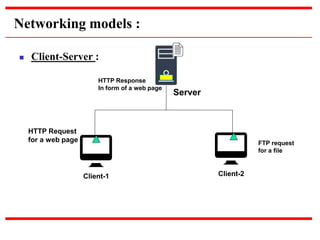
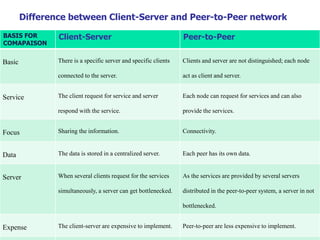
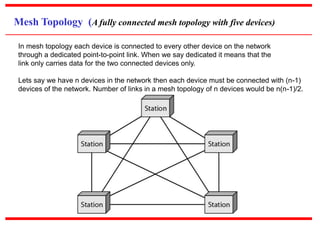
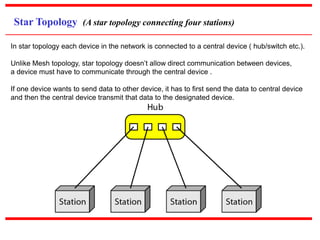
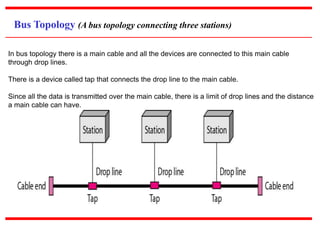
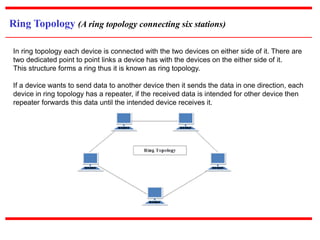
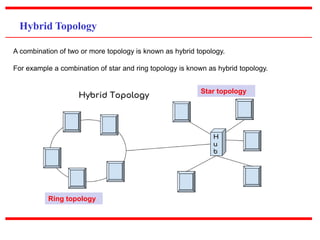
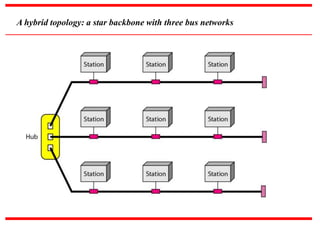
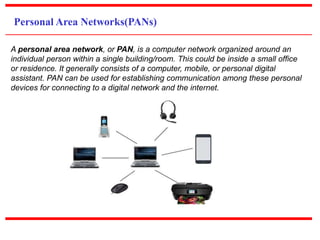
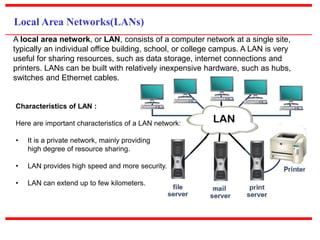
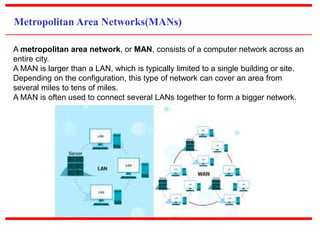
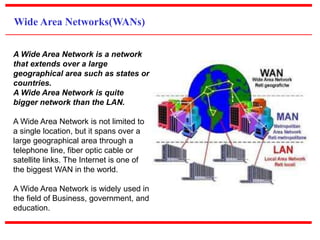
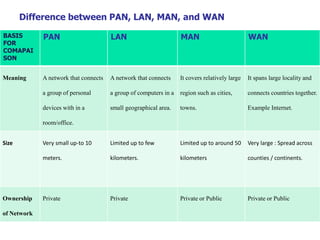
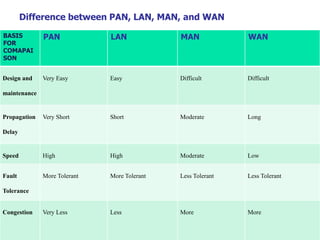
This document provides an overview of computer networks, detailing their definitions, types, objectives, and networking models. It covers key elements such as resource sharing, reliability, and security, and explains various network topologies including mesh, star, bus, and ring. Additionally, it categorizes networks based on size—from personal area networks (PANs) to wide area networks (WANs)—highlighting their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.