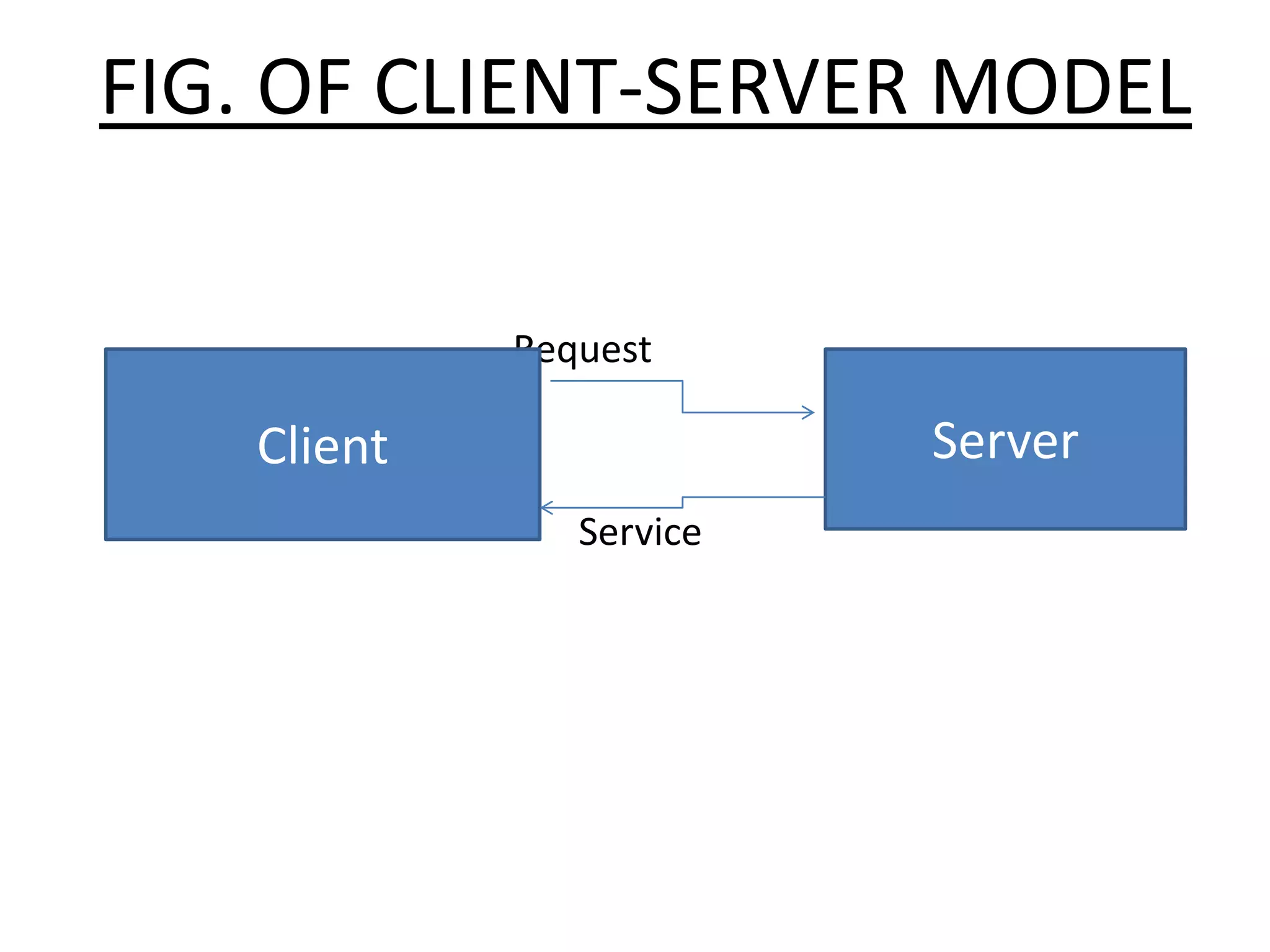
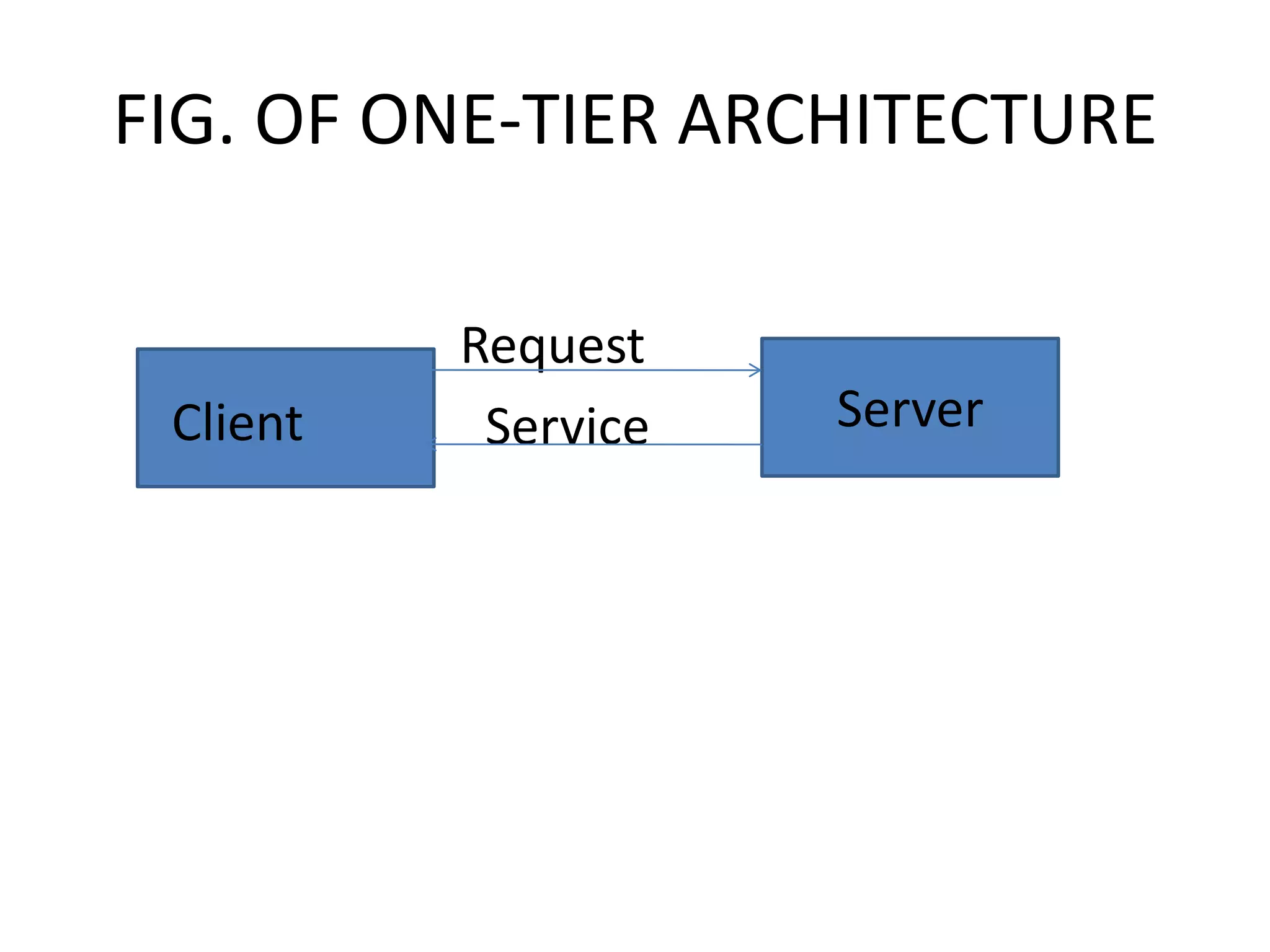
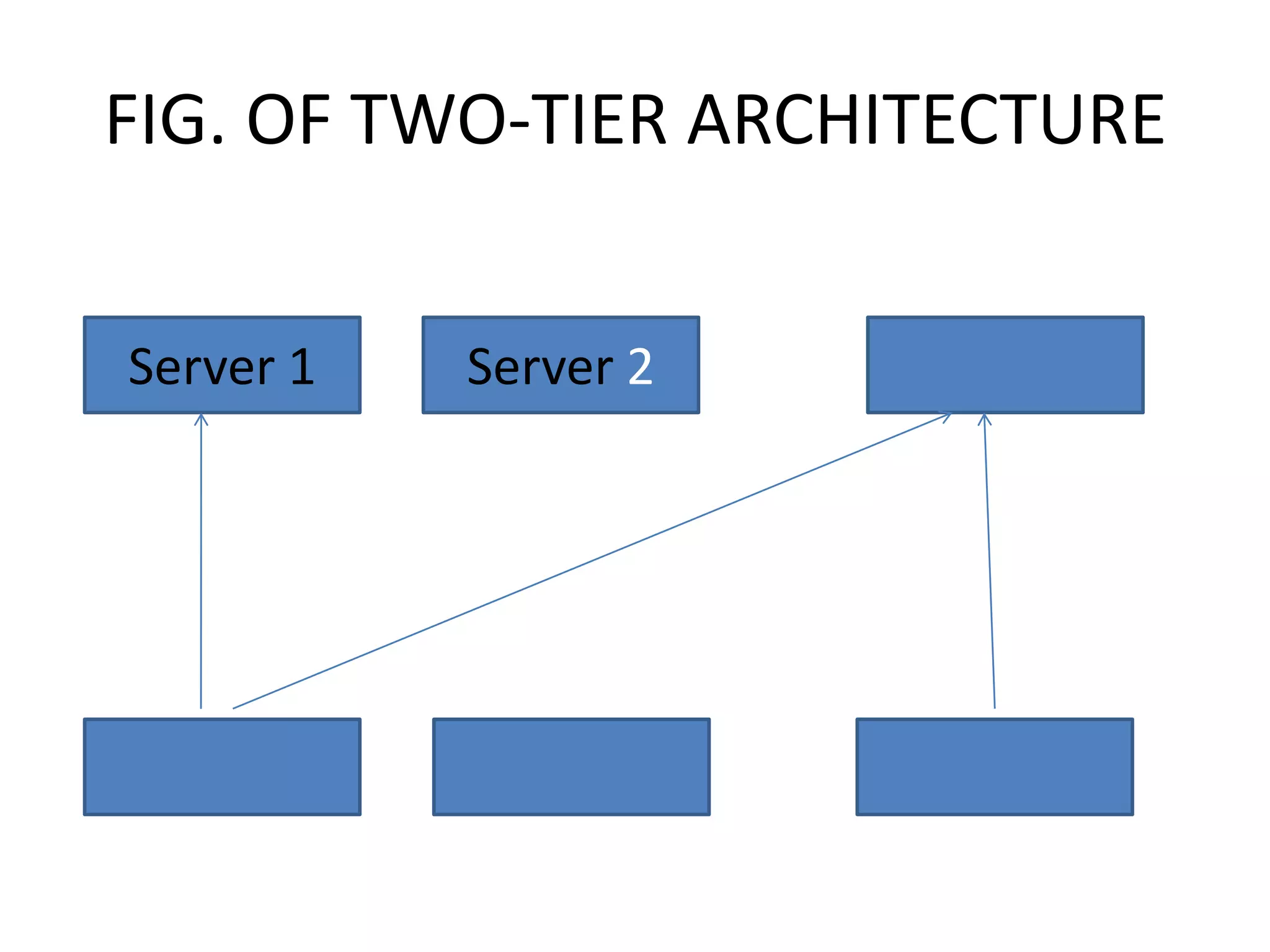
Client-server architecture separates programs into two parts - clients, which make requests, and servers, which fulfill requests. A client-server model has three main components: clients, servers, and communication middleware. Clients are front-end applications that users interact with to make requests. Servers are back-end applications that provide services to clients. Middleware facilitates communication between clients and servers. Common middleware standards are CORBA and COM/DCOM. Client-server systems can be organized as one-tier, two-tier, or three-tier architectures depending on how functionality is divided between clients and servers.