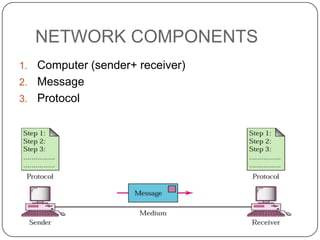
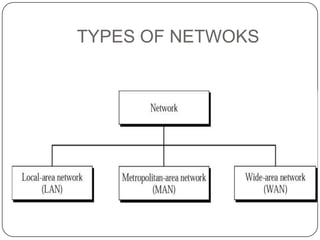
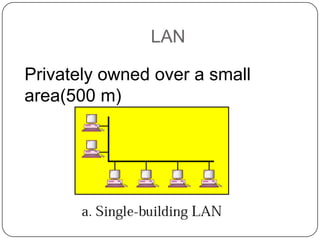
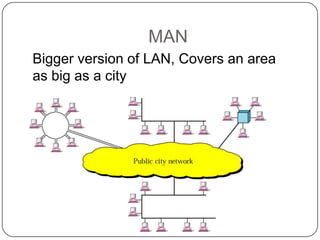
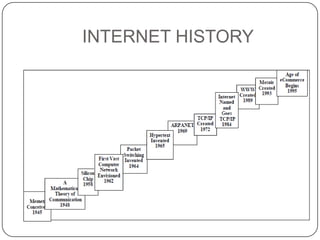
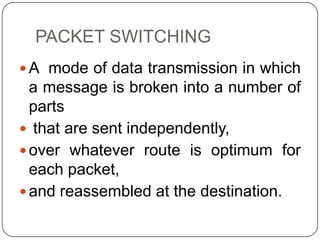
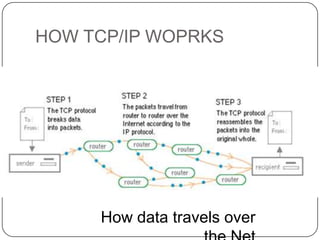
This document discusses networks, the Internet, and related topics. It defines a network as a set of connected devices that share resources and communicate through various media. The largest network is the Internet, which uses TCP/IP protocols and packet switching to transmit data over diverse communication systems on a global scale. The document also describes intranets, which are private internal networks, and extranets, which allow controlled external access. Key terms like Memex, Shannon's information theory, and the invention of the silicon chip provide historical context.