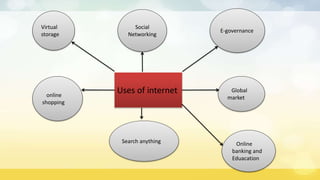
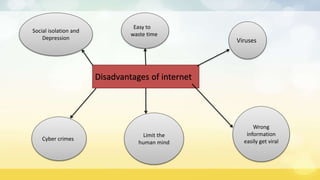
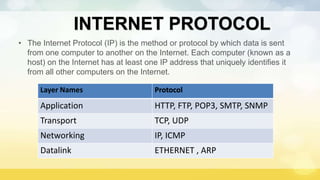
The document provides an overview of the internet including its origin, advantages, disadvantages, and how it works. It discusses that the internet originated from ARPANET, a network funded by the US military in the 1960s. It connects computers through telephone lines, cables, satellites, and wireless connections. Information is broken into packets and sent using TCP and IP protocols, then reassembled at its destination. The internet provides advantages like online shopping, education and banking but also disadvantages such as viruses, cyber crimes, and wasting time.