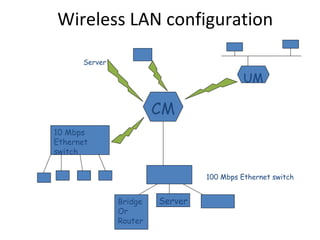
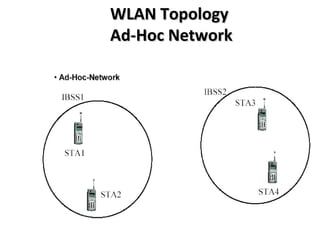
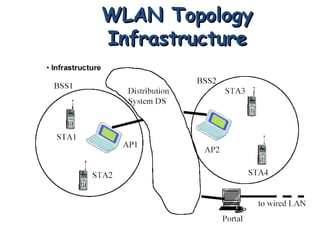
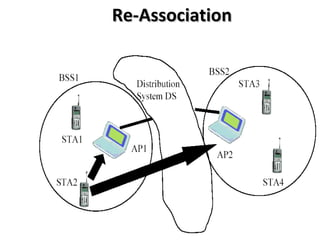
The document discusses wireless LAN (IEEE 802.11) standards. It describes how wireless LANs provide flexibility, portability and mobility by connecting devices using wireless transmission instead of physical wires. The key wireless LAN standard is IEEE 802.11, which was first published in 1997 and defines the physical and data link layer specifications. The standard provides benefits like interoperability, fast product development and support for future technologies. Common wireless LAN applications include use in medical facilities, schools, temporary situations and emergency response centers.