This document provides an introduction to network devices, addressing schemes, and the basic elements of a network. It discusses:
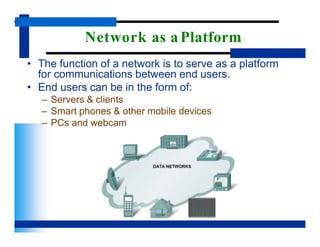
- The basic function of a network is to enable communication between end users such as servers, clients, mobile devices, and PCs.
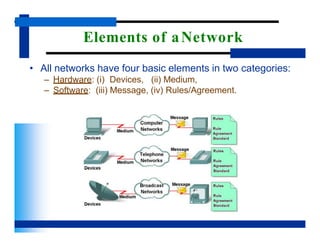
- All networks have four basic elements - hardware devices and medium, and software messages and rules/agreements. It describes examples of each element.
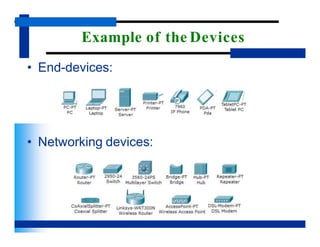
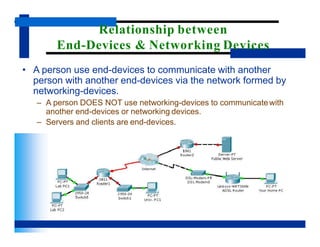
- It differentiates between end devices that users directly interact with, and networking devices that help facilitate communication between end devices. Common examples of each type of device are given.
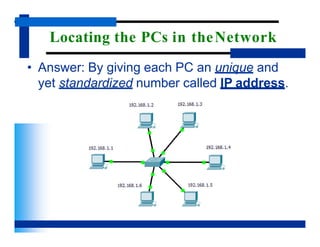
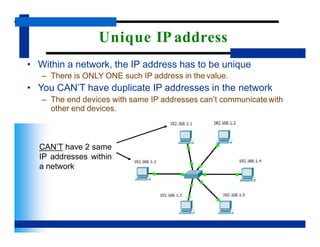
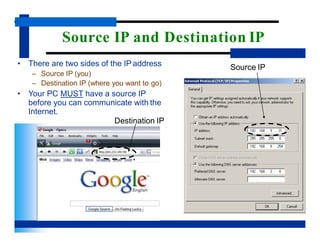
- There are three important addressing schemes that help identify locations and applications in a network - IP addresses identify individual devices, port numbers





























![Client Port numbers
• Client port numbers are not fixed.
• The value of client port number is not standardized
by IANA.
– It is normally larger than 1023
• Assigned by operating system randomly.
• Client ports are sometimes called connection ports
• The notation [IP:port_number] is called a socket.
• Socket can identify any network application/service
in the Internet.
– For example: 157.166.255.18:80 identify the web service
of www.cnn.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week22-220815234901-65e26b34/85/Introduction-to-Network-Devices-Addressing-Schemes-39-320.jpg)

![Example of [IP:port]
• 3 PCs are accessing the web server at the same time.
• At the server, it was detected that there are 3 connections
– 192.168.1.1:80, (IP: port number). Again, this notation is called a socket.
– Meaning the server IP is 192.168.1.1 and the port number is 80 (source port
number)
– Same service (web server application) is connected to three other applications
(web browser),.
– For example, 192.168.1.2 is having a application with a port number of 1029.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week22-220815234901-65e26b34/85/Introduction-to-Network-Devices-Addressing-Schemes-41-320.jpg)

![Example of [IP:port]
• Please notice that the servers’ web service will always
have a port number of 80
• The clients port numbers are rather random.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week22-220815234901-65e26b34/85/Introduction-to-Network-Devices-Addressing-Schemes-43-320.jpg)