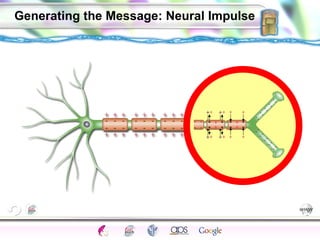
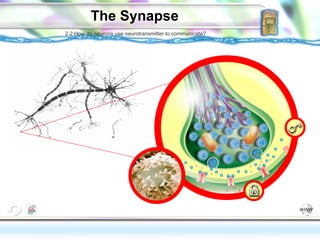
The document discusses the biological perspective and structure of the nervous system. It covers key topics like:
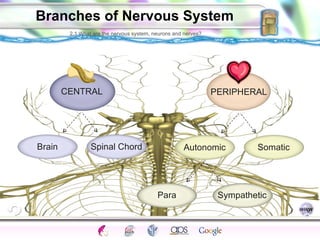
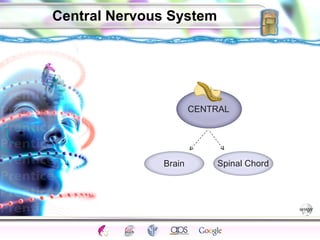
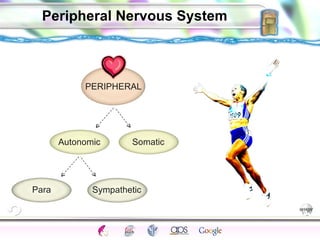
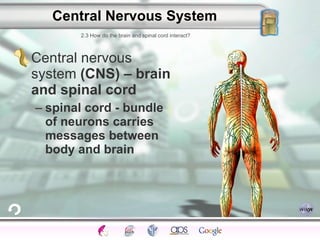
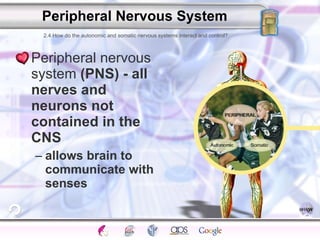
1. The central nervous system including the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system which connects the CNS to the senses and body.
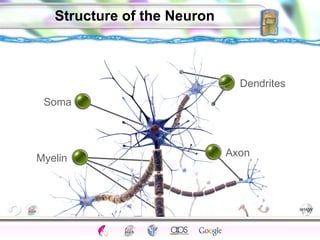
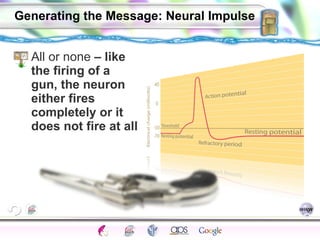
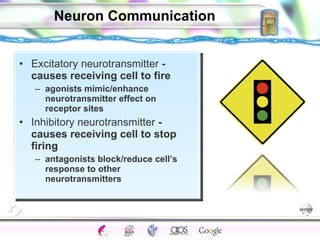
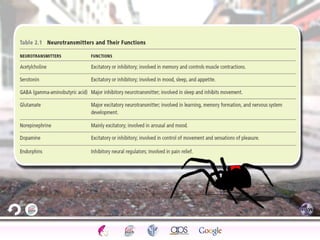
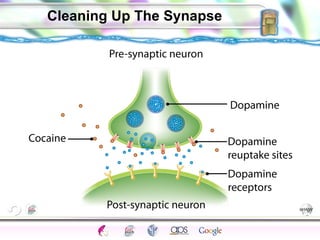
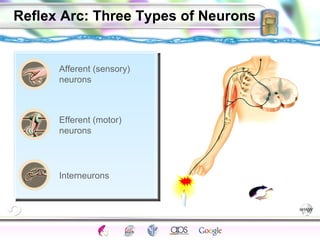
2. How neurons use neurotransmitters to communicate via synaptic transmission between neurons in either an excitatory or inhibitory manner.
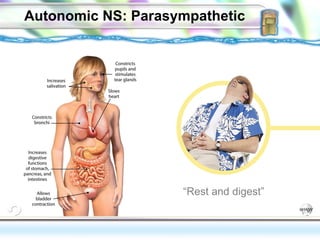
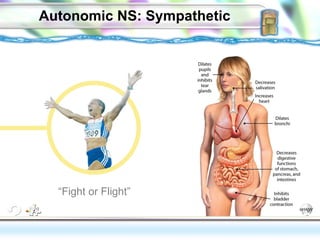
3. The autonomic nervous system which controls involuntary functions and is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems that work in opposition to activate the fight or flight response or rest and digest responses.