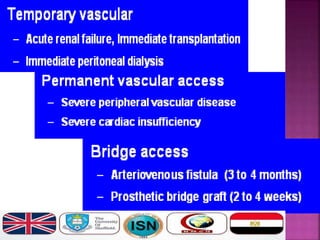
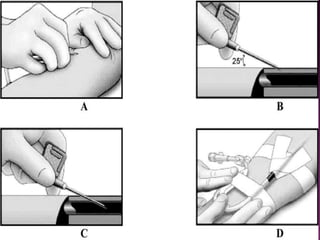
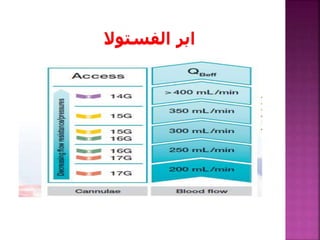
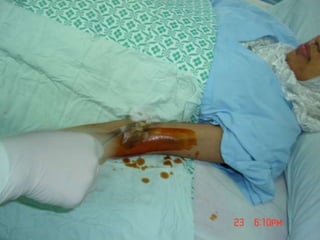
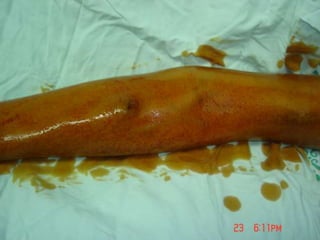
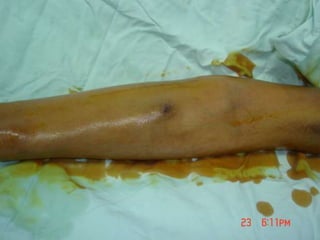
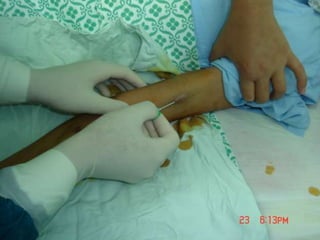
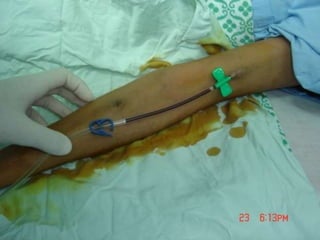
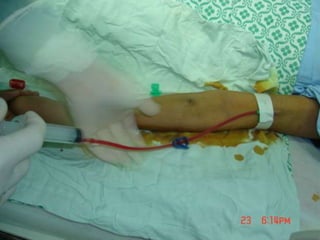
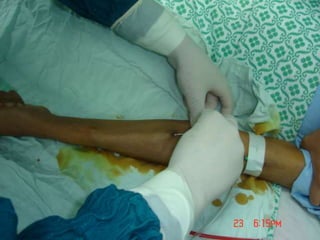
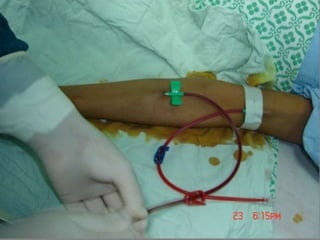
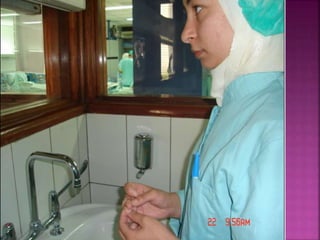
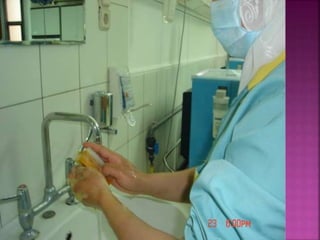
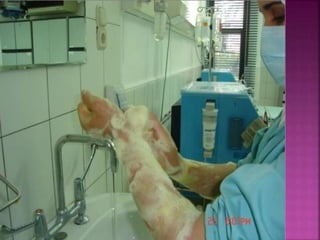
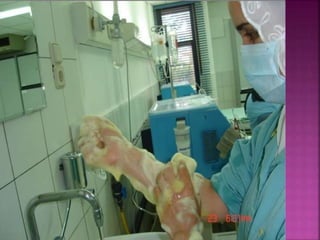
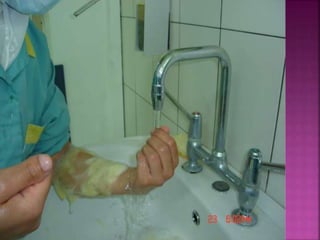
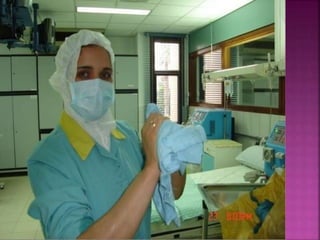
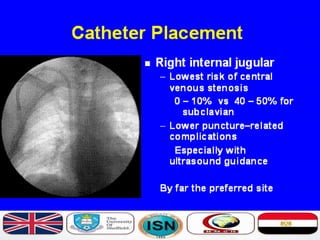
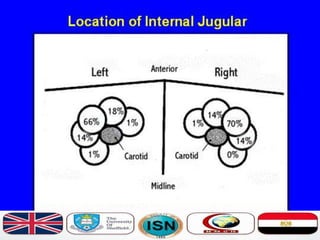
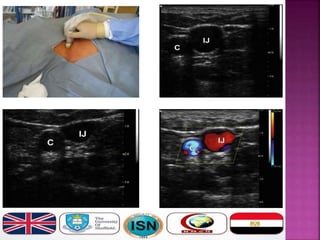
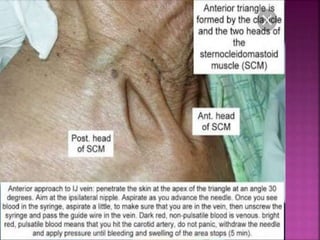
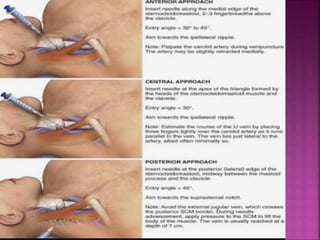
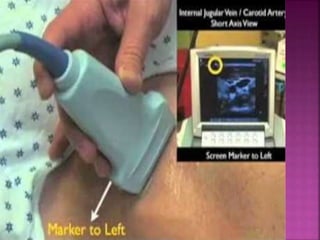
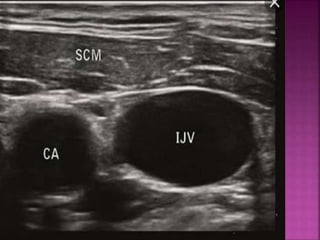
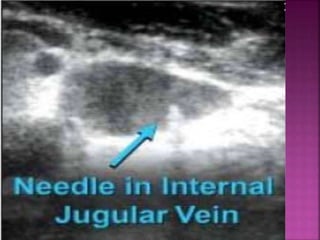
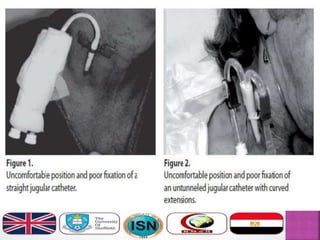
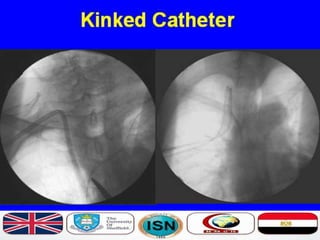
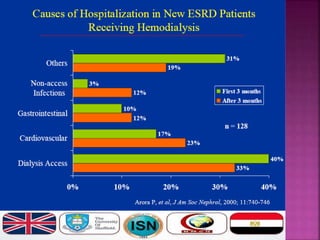
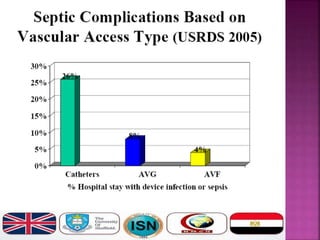
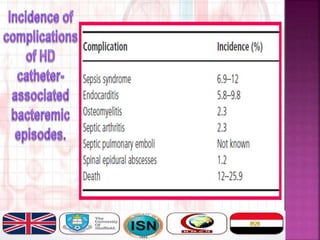
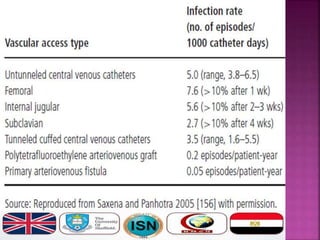
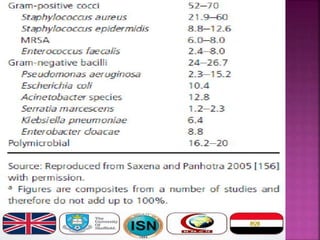
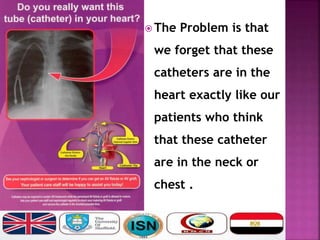
- Short-term catheters should only be used for acute dialysis or limited hospital use. Non-cuffed femoral catheters are only for bed-bound patients.
- Long-term catheters should be used with a plan for permanent access and prefer those capable of high flow rates. Choice depends on local experience and goals.
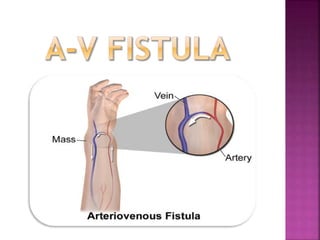
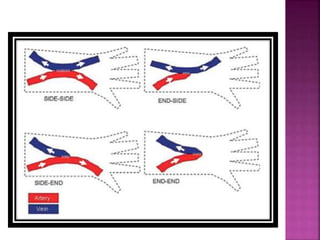
- Long-term catheters should avoid the same side as a maturing arteriovenous access, if possible.