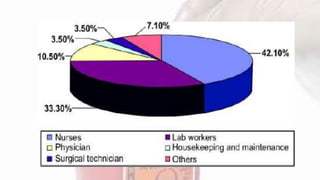
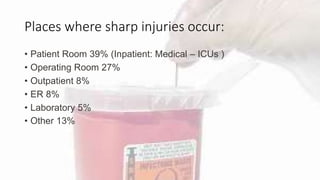
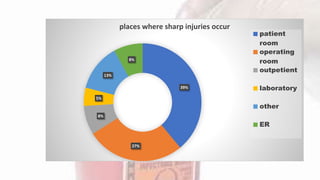
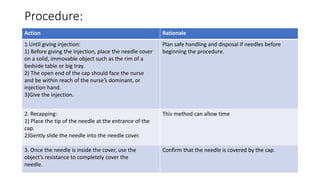
A needle stick injury is a puncture wound from a needle or other sharp object. Healthcare workers who frequently deal with blood, such as nurses, physicians, and laboratory technicians, are most at risk. Nearly 40% of needle stick injuries occur in patient rooms, and the most common devices involved are disposable syringes, suture needles, and intravenous catheters. To reduce risk, healthcare workers should avoid recapping needles, properly dispose of sharps in puncture-proof containers, and follow post-exposure procedures like washing and PEP if exposed. Proper needle disposal and a one-handed recapping technique can help prevent accidental needle sticks.