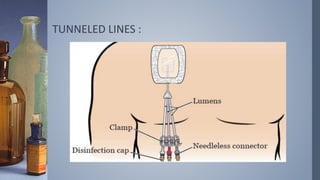
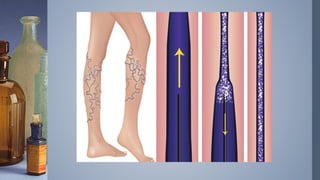
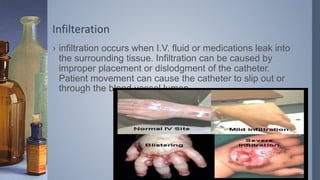
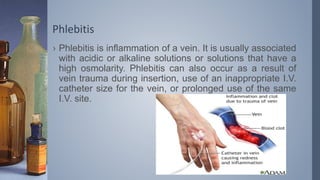
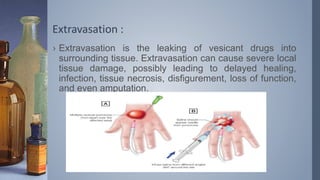
Intravenous (IV) therapy involves infusing fluids, nutrients, medications, or blood products directly into a vein. It has been used since the 1830s to treat conditions like cholera. IV therapy can deliver fluids, electrolytes, medications, and blood components to prevent or treat deficiencies via routes like IV, subcutaneous, intraosseous, or intrathecal. Common IV solutions include saline, dextrose, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. IV therapy requires devices like IV sets, tubing, catheters, and pumps to deliver fluids and medications safely and prevent complications like infection, infiltration of tissue, phlebitis, or extravasation.