Embed presentation
Downloaded 154 times

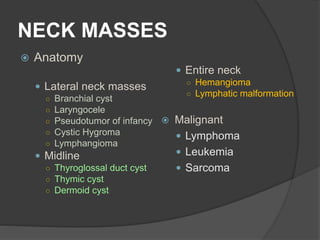
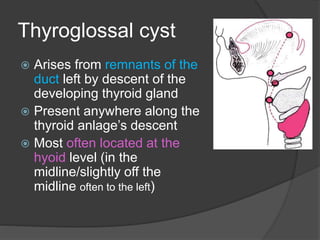

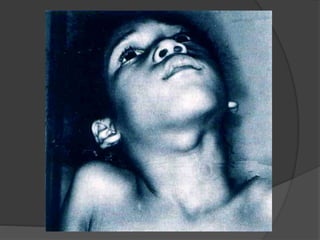

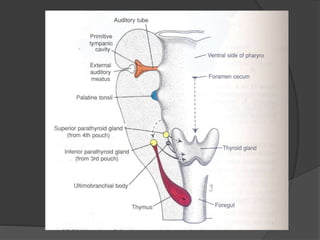


This document discusses different types of neck masses, including: - Lateral neck masses such as branchial cysts, laryngoceles, and lymphangiomas. - Midline masses like thyroglossal duct cysts, thymic cysts, and dermoid cysts. - Masses that can occur anywhere in the neck including hemangiomas and lymphatic malformations. - It provides more detail on thyroglossal duct cysts, thymic cysts, and sublingual dermoid cysts including their presentation, diagnosis, and treatment.







