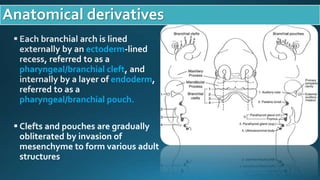
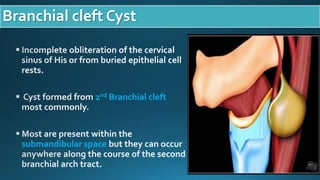
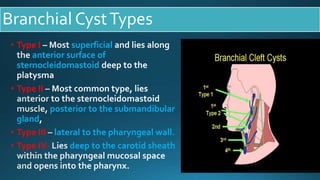
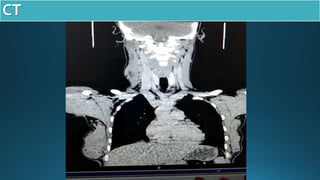
This document presents a case study of a 23-year-old patient who presented with a right neck cyst. Imaging including ultrasound, CT, and MRI revealed a cystic mass posterior to the mandibular ramus. Differential diagnoses included thyroglossal duct cyst, cystic hygroma/lymphangioma, and dermoid cyst. However, based on location and imaging features such as extension between the carotid arteries, it was determined to be a second branchial cleft cyst. The document discusses branchial arch embryology and anomalies that can result from incomplete obliteration of clefts, including branchial cysts. Branchial cysts most commonly involve the second arch and present as painless swellings in