Embed presentation
Downloaded 116 times

![Formula NNI=2D (N/A) D : average distance between each point & its nearest neighbour ( ∑d/N ) [ d =each individual distance] N : number of studied points A : size of the studied area ! SAME UNITS! _ _](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nearest-neighbour-index-1234860740496933-3/85/Nearest-Neighbour-Index-3-320.jpg)
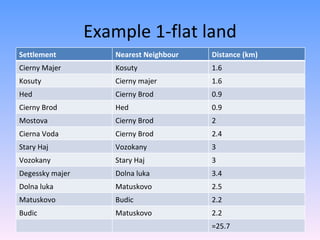

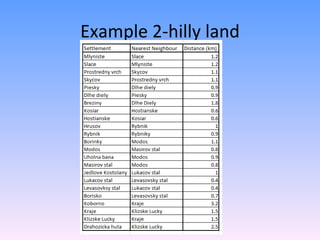



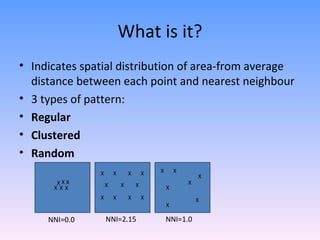
The Nearest Neighbour Index (NNI) is used to quantify the spatial distribution patterns of points on a map as either regular, random, or clustered. It is calculated by taking the average distance between each point and its nearest neighbour, divided by the expected average distance if the points were randomly distributed over the area. Values closer to 0 indicate clustering, near 1 indicate randomness, and greater than 1 indicate regular spacing between points. The document provides examples of calculating the NNI to classify settlement patterns in different landscapes as either regular or clustered.


![Formula NNI=2D (N/A) D : average distance between each point & its nearest neighbour ( ∑d/N ) [ d =each individual distance] N : number of studied points A : size of the studied area ! SAME UNITS! _ _](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nearest-neighbour-index-1234860740496933-3/85/Nearest-Neighbour-Index-3-320.jpg)





