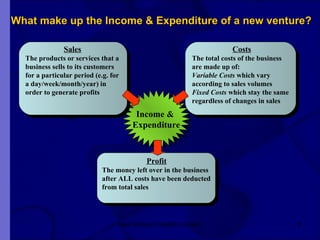
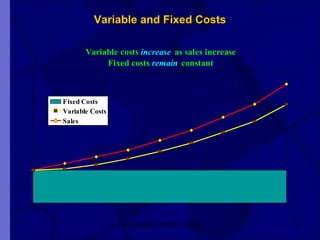
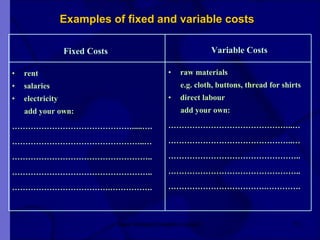
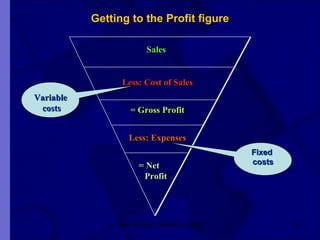
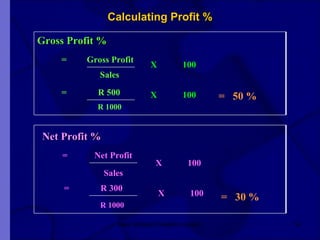
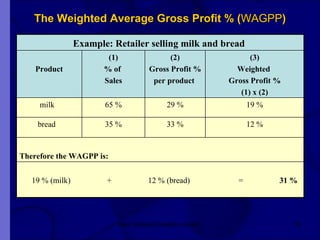
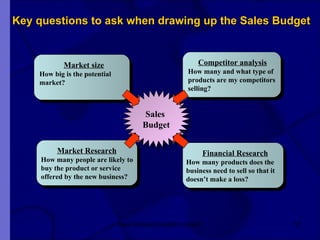
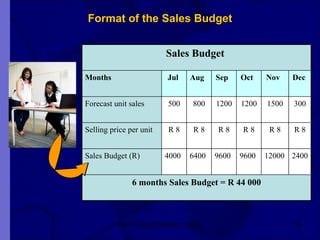
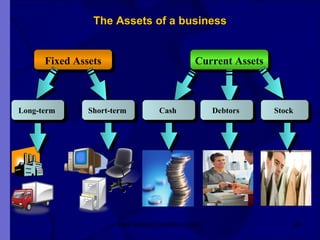
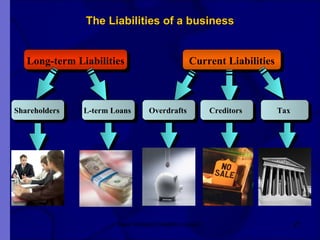
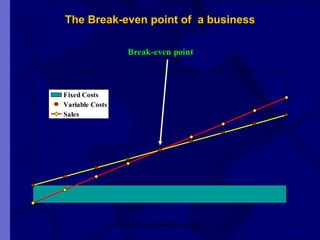
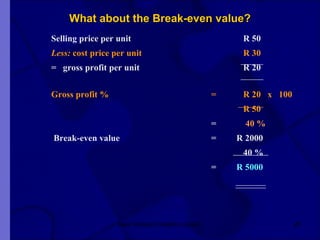
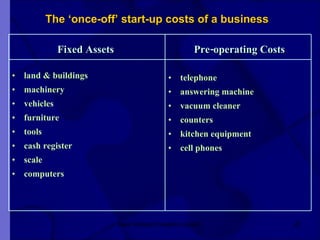
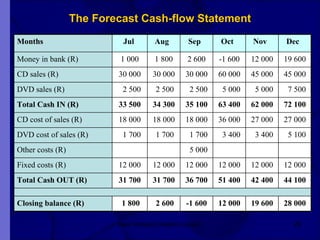
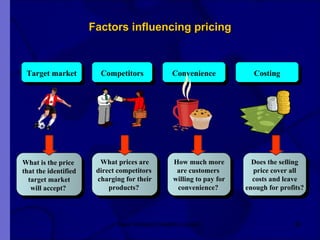
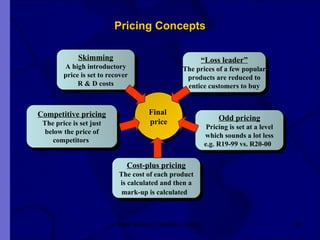
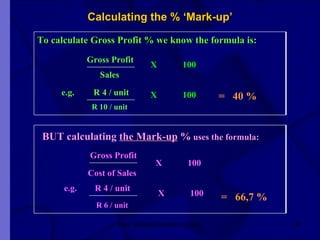
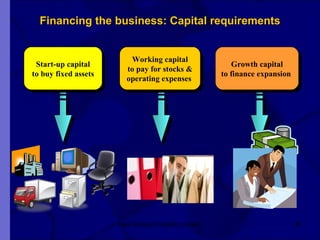
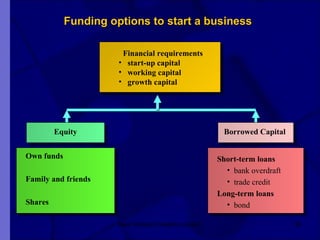
The document covers financial requirements for new venture creation, including how to assess income and expenditures, determine financial needs, pricing strategies, and break-even analysis. It emphasizes understanding costs, budgeting, and cash flow management for establishing a profitable business. Additionally, it outlines financing options and the significance of maintaining accurate financial records.