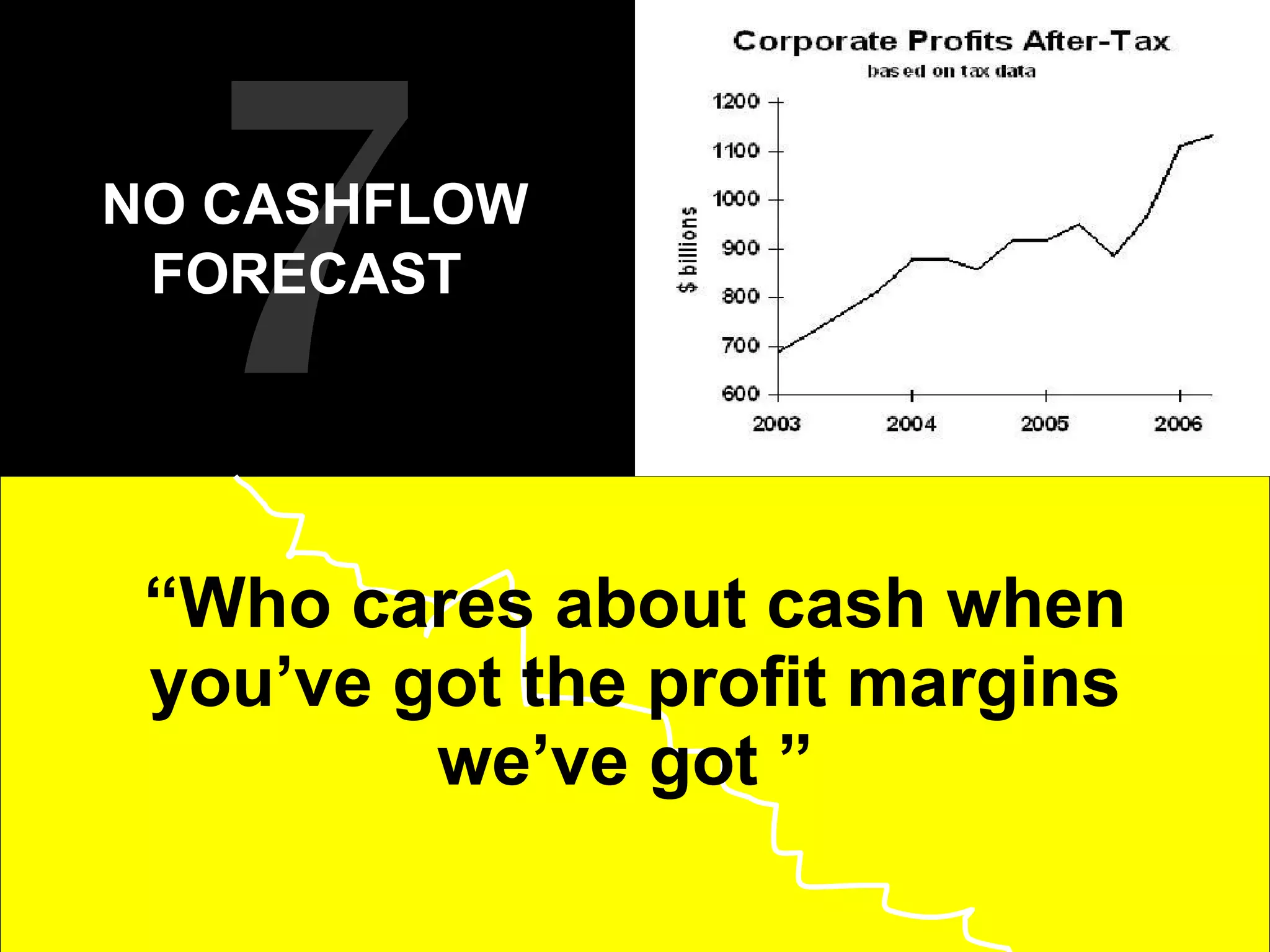
1. The document discusses 10 common mistakes that entrepreneurs make that can lead their startups to fail, such as having no real passion for the business, no understanding of the market, no differentiation from competitors, and no business model or cash flow forecast.
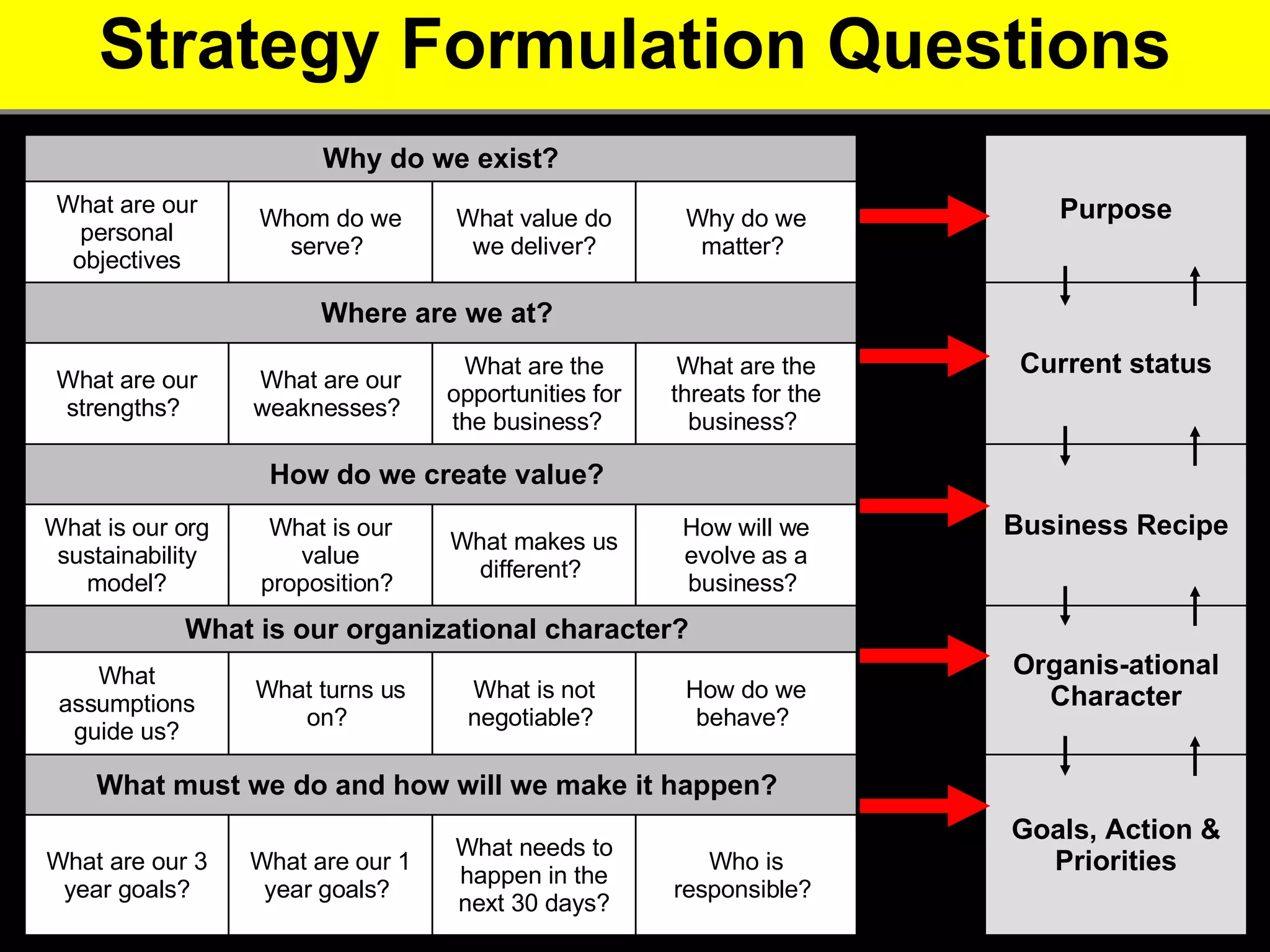
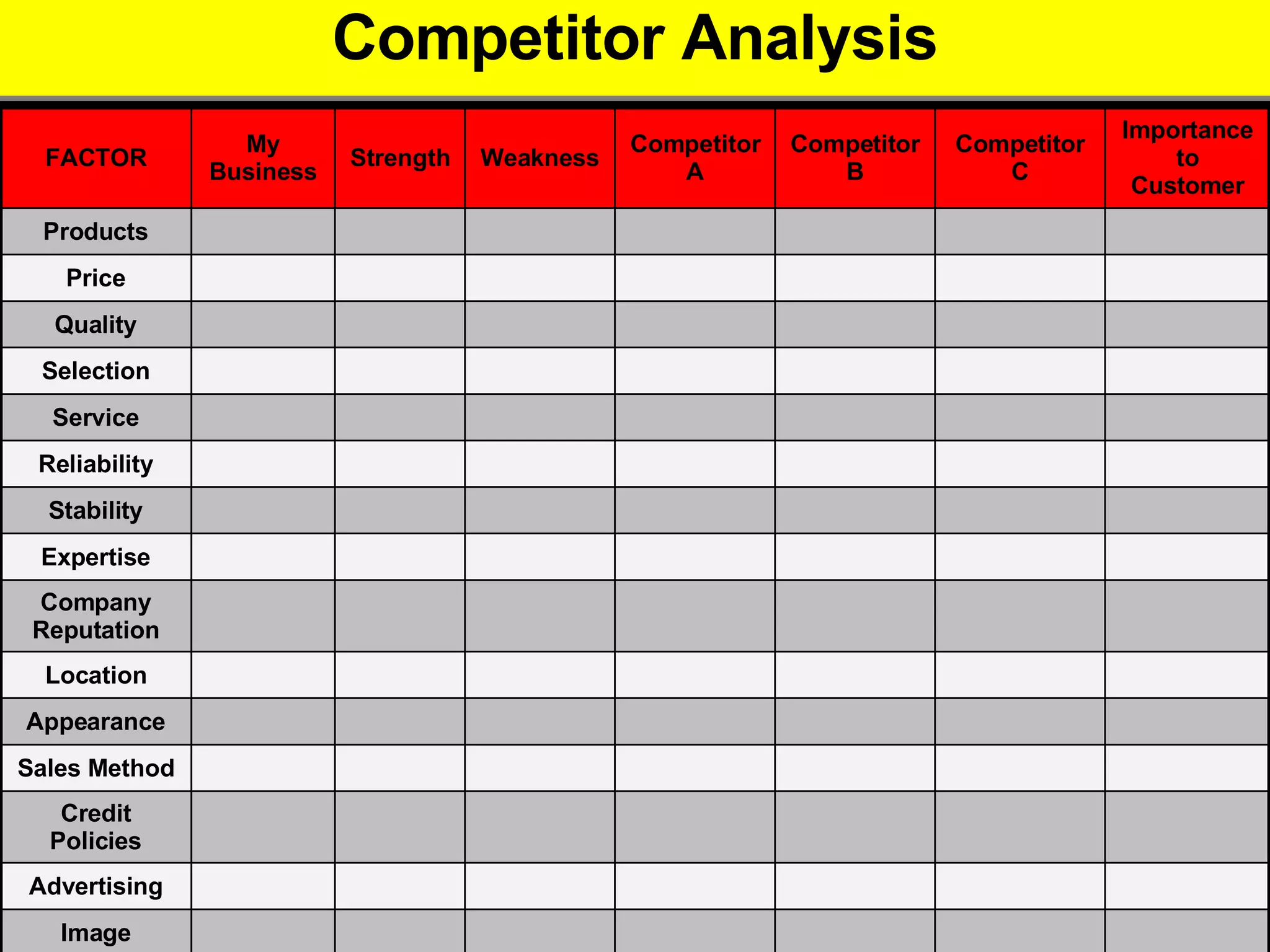
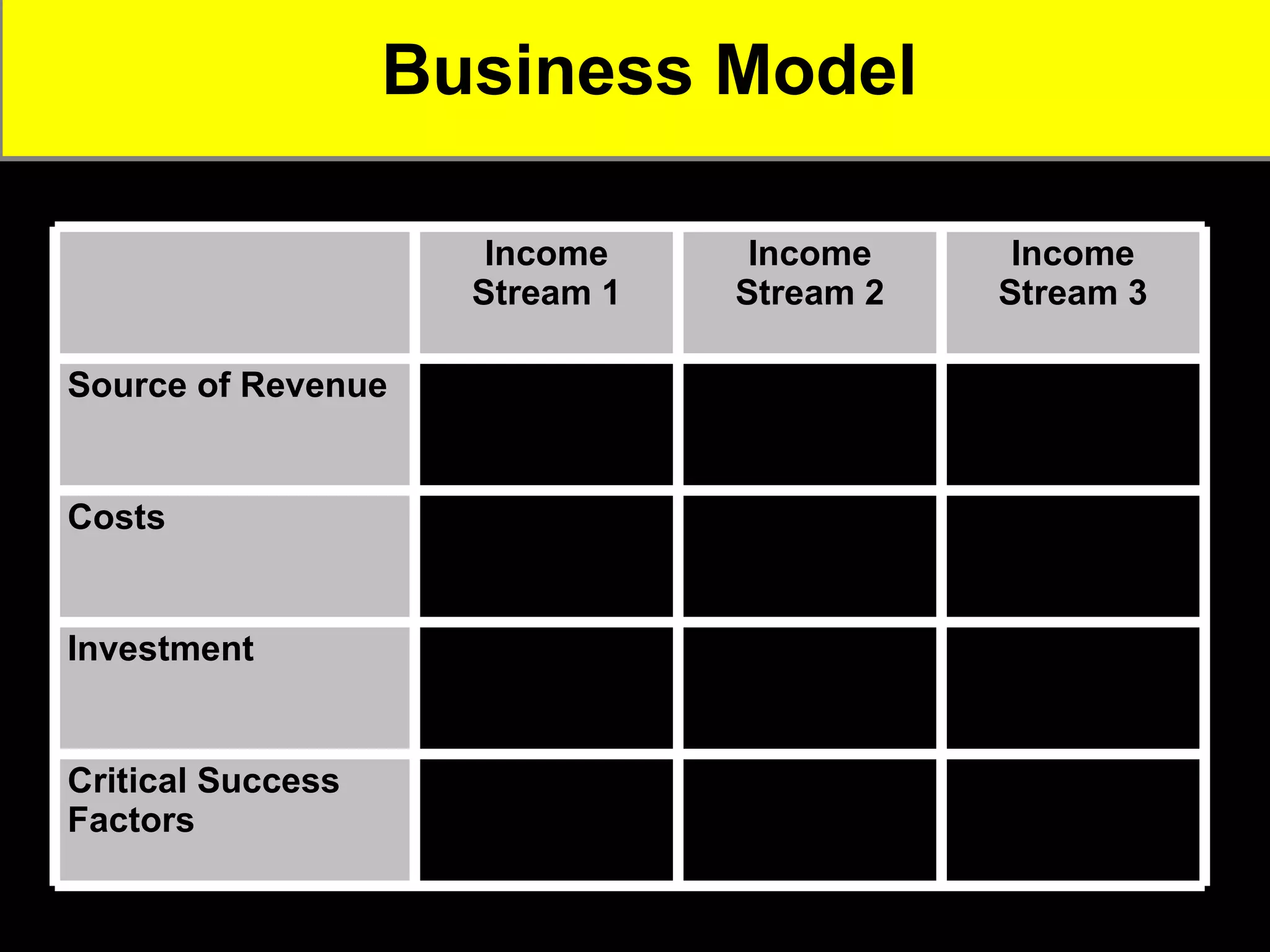
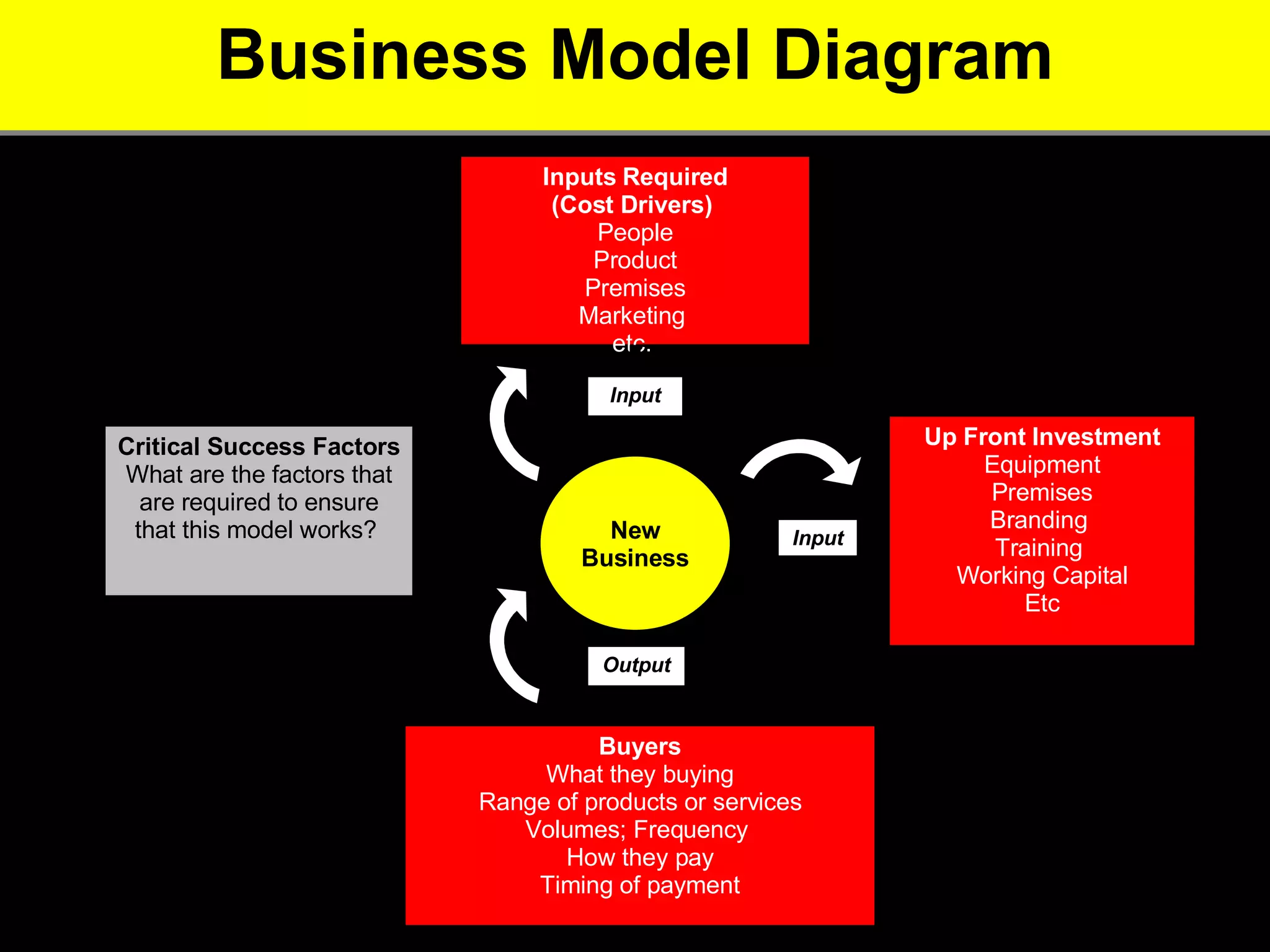
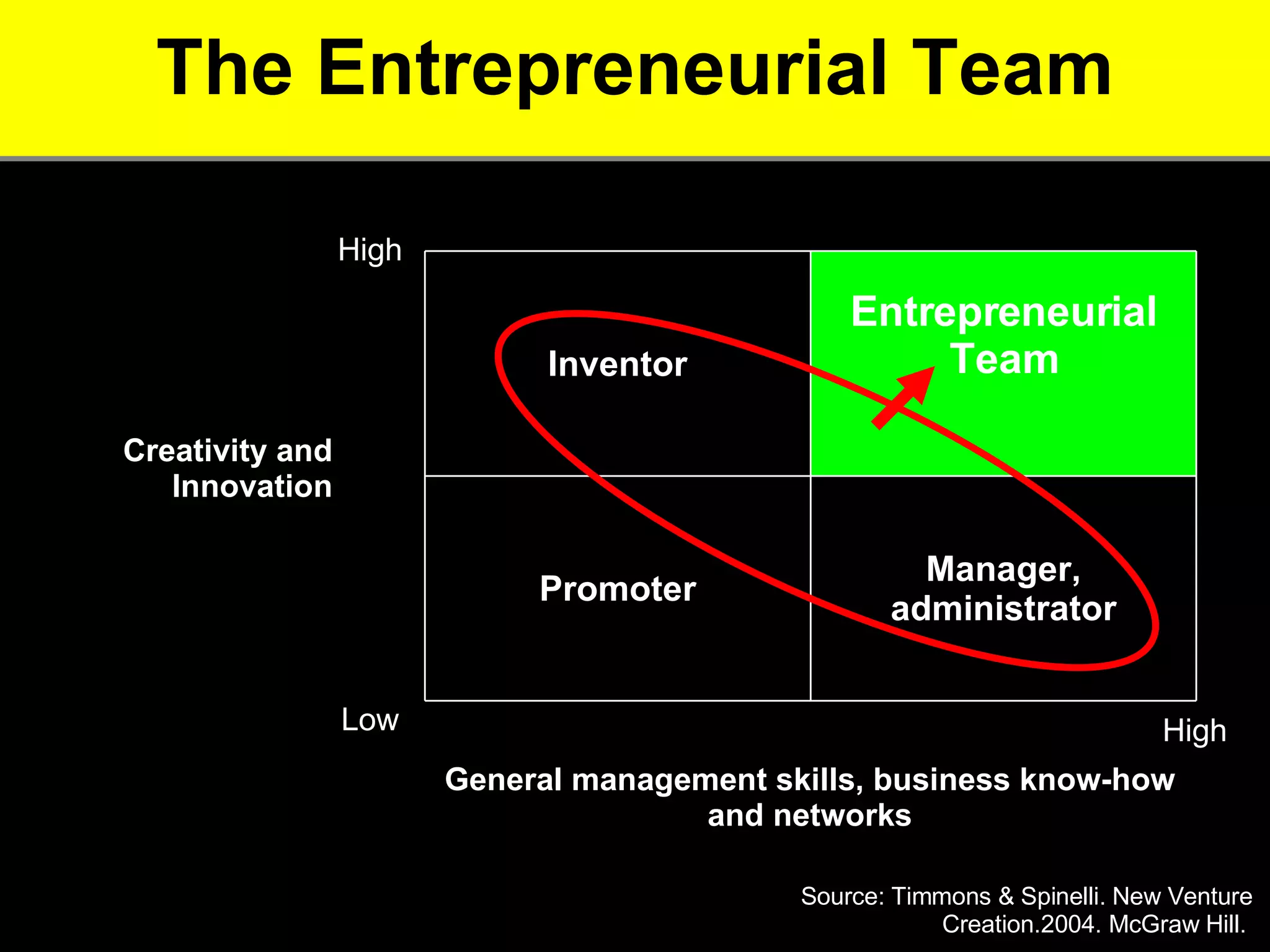
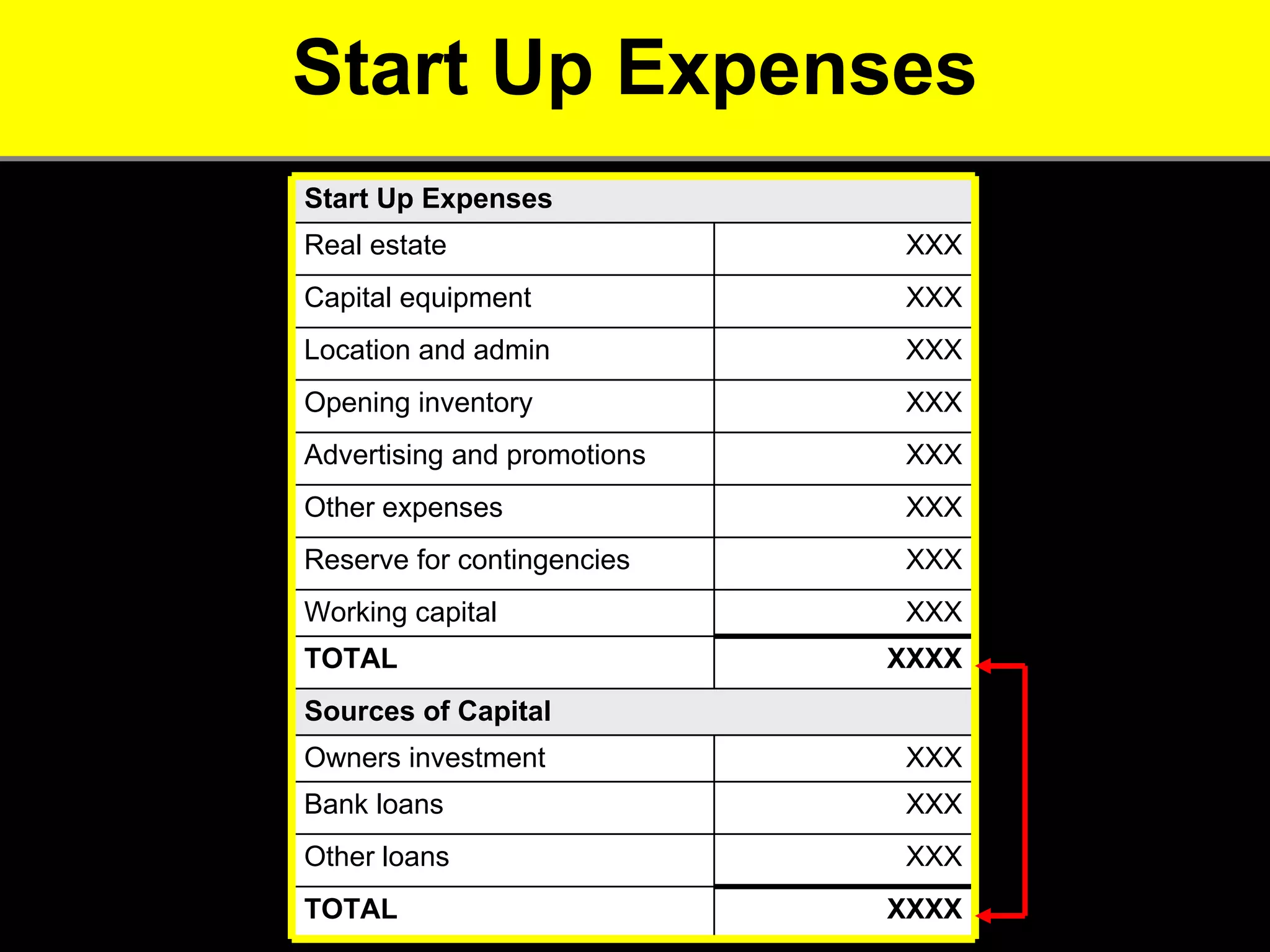
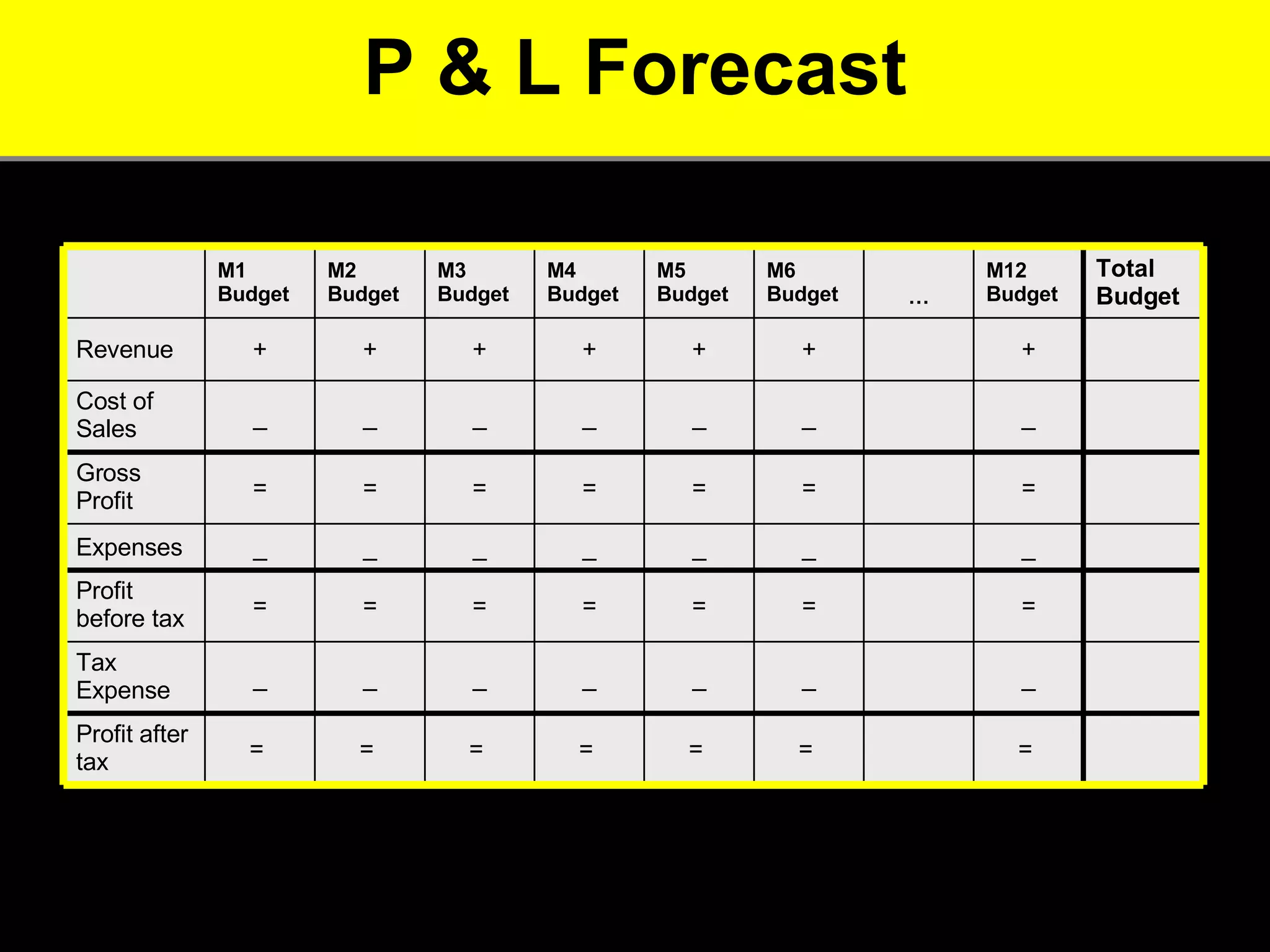
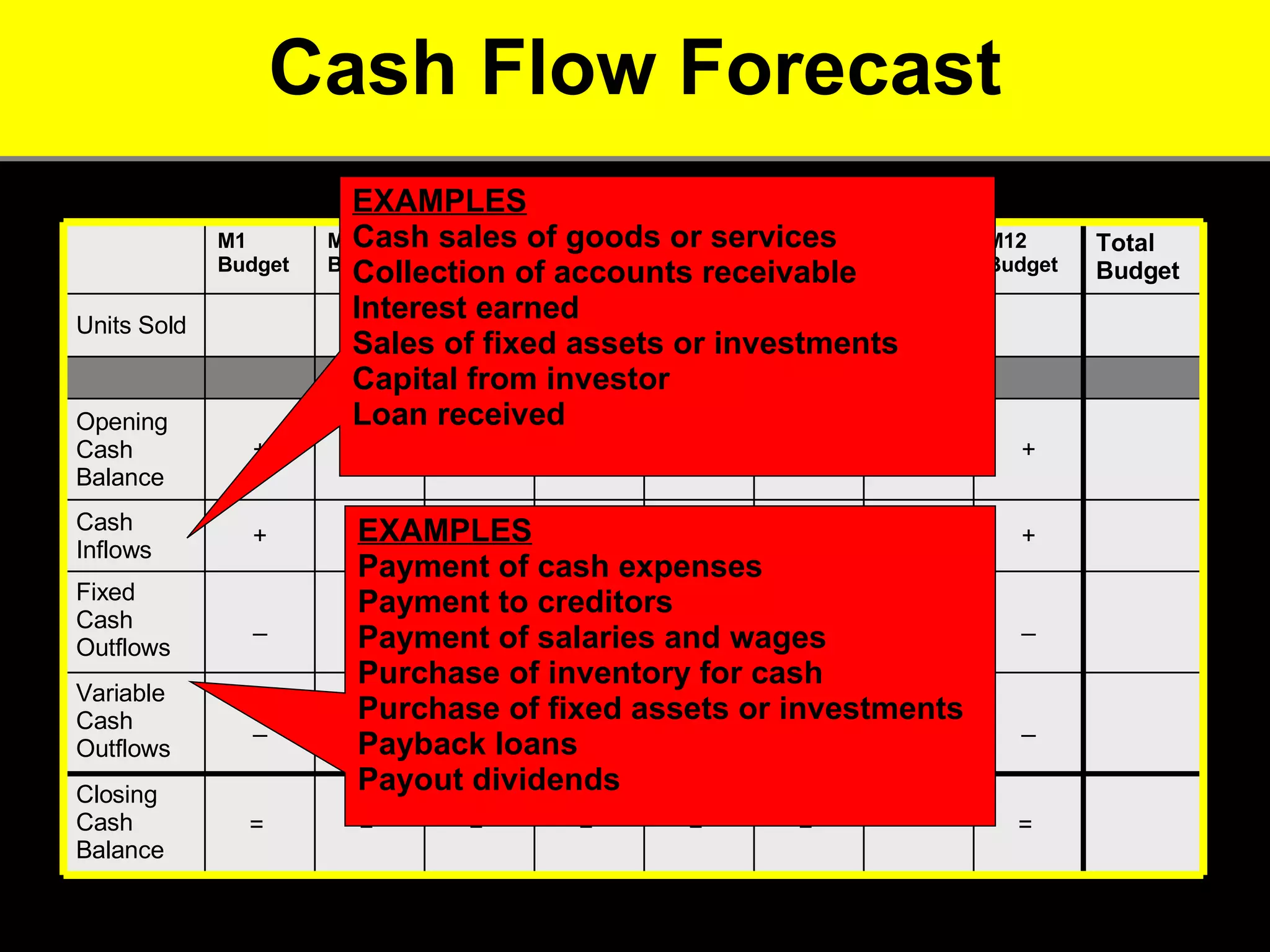
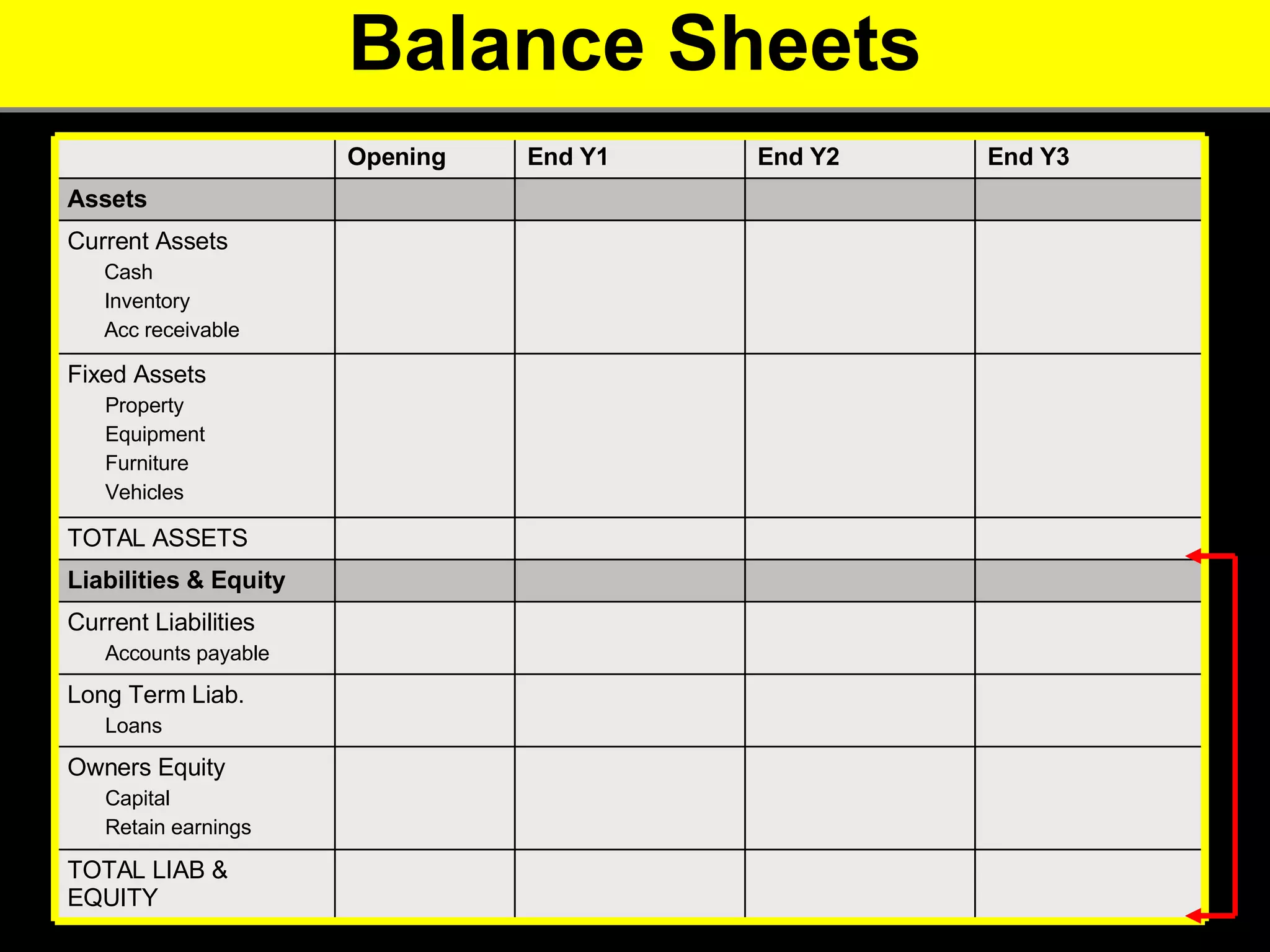
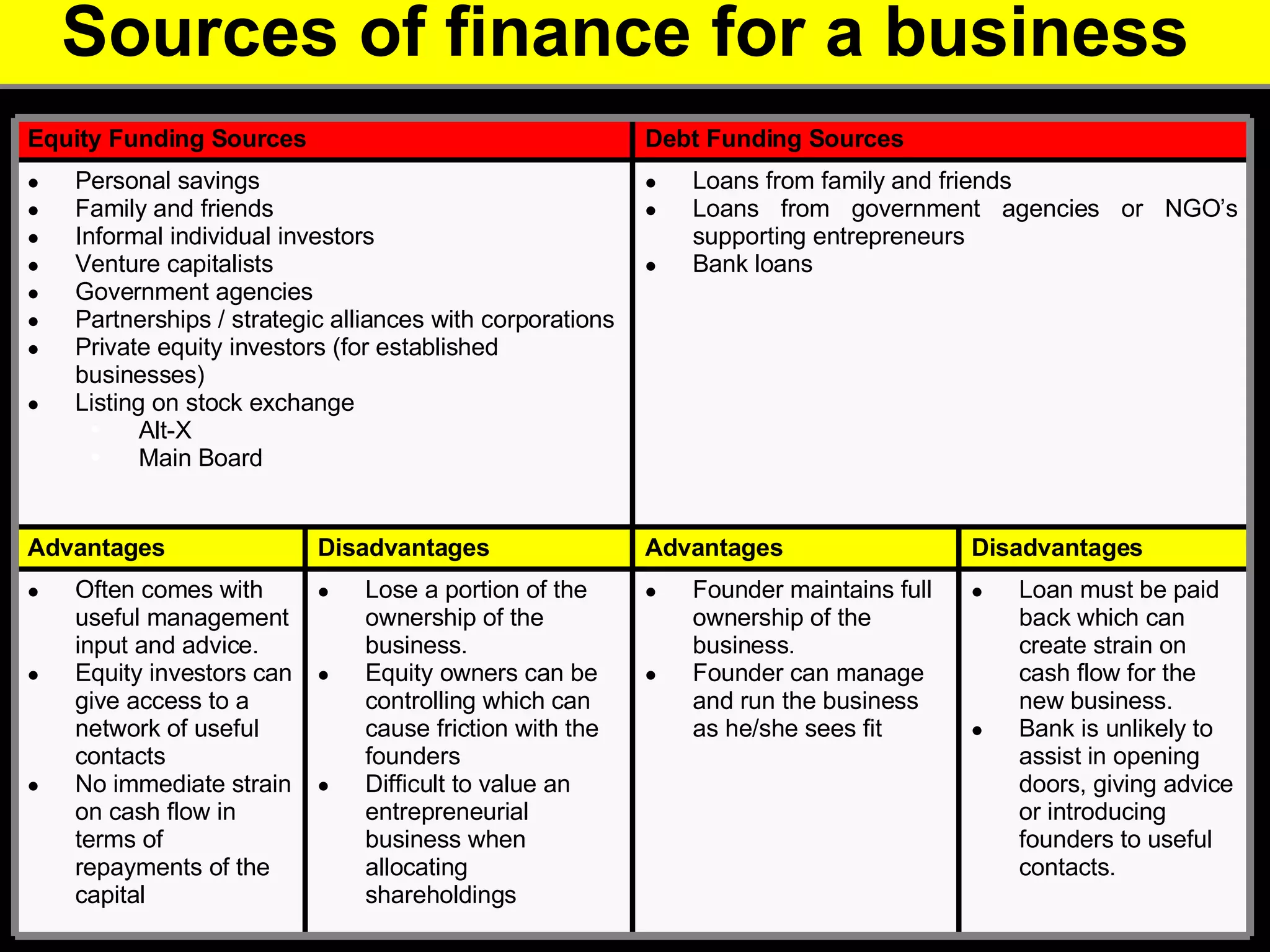
2. It provides tips for entrepreneurs to avoid these mistakes like conducting thorough market research, developing competitive advantages, creating a balanced founding team, and developing financial plans with sales forecasts and budgets.
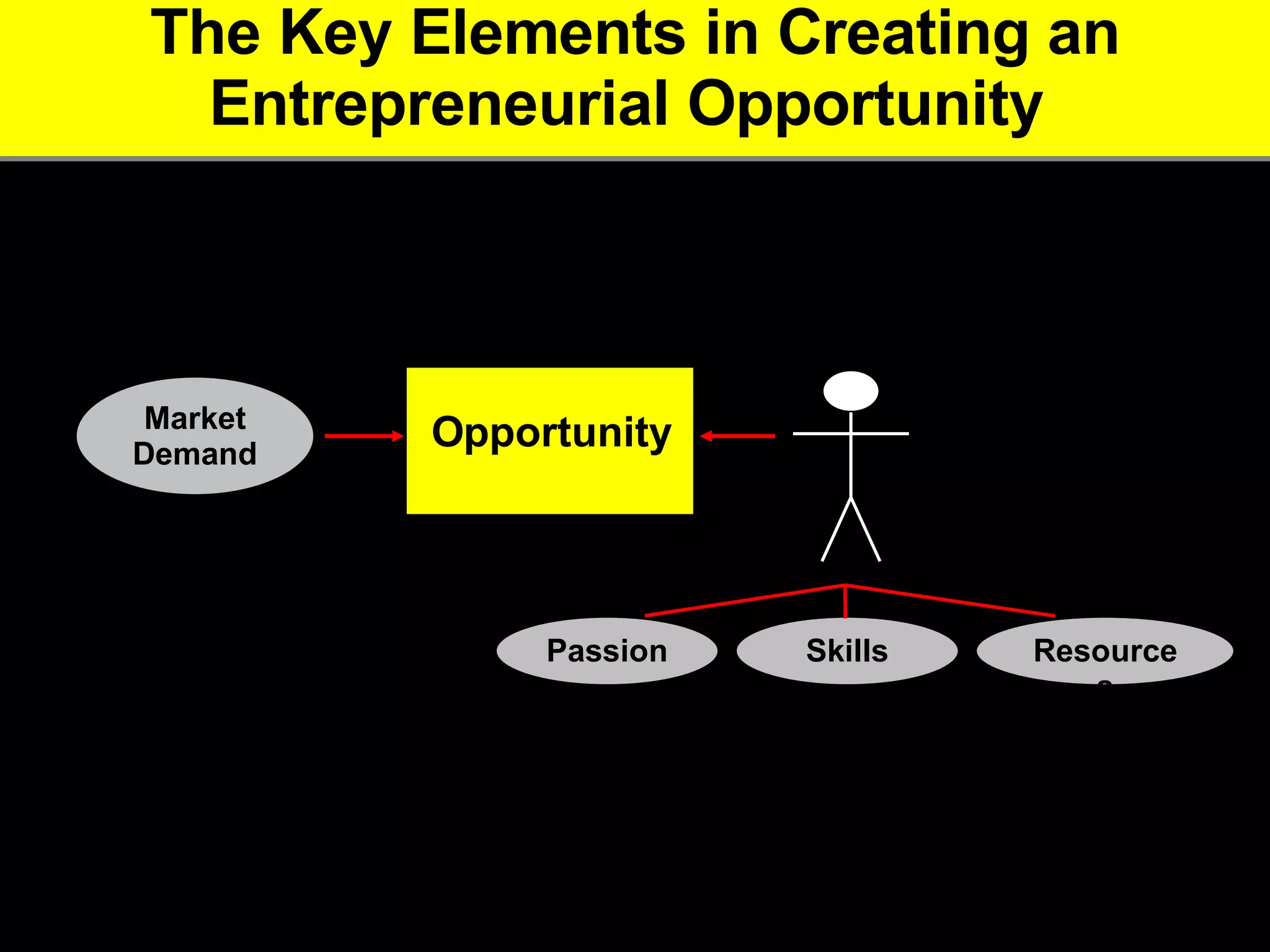
3. The key advice is that entrepreneurs must have a deep understanding of customer needs, competitors, and how to financially sustain the business in order to successfully start a new venture.









![Assessing an Opportunity [VENTURE] Concept Attractiveness Competitive Advantage [ENTREPRENERIAL TEAM] Low Low High High Market Size Market Growth Differentiation Customer Need Skills Resources Passion / Energy Network 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bad-to-worse-1206282988946001-2/75/Bad-To-Worse-11-2048.jpg)
![Response [VENTURE] Concept Attractiveness Competitive Advantage [ENTREPRENERIAL TEAM] Low Low High High Avoid / Wait & Reassess in Future Build / hire / develop the required capabilities Identify / exploit a specific under served niche Revise product or business model Invest and pursue the opportunity 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bad-to-worse-1206282988946001-2/75/Bad-To-Worse-12-2048.jpg)


























![Go out and do it… Business In A Box www.biz-box.net Email – Slides [email_address] Blog – Slides [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bad-to-worse-1206282988946001-2/75/Bad-To-Worse-50-2048.jpg)