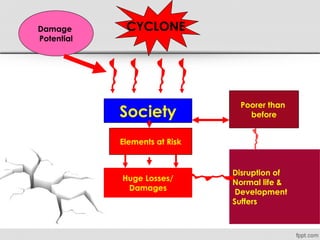
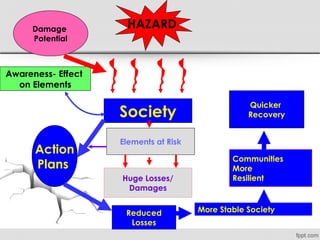
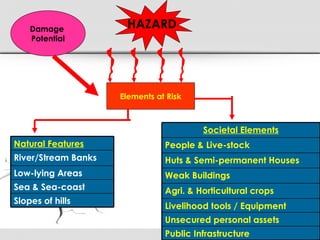
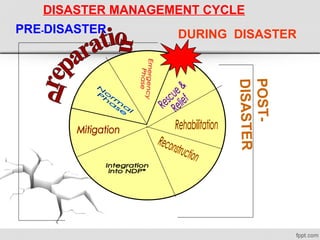
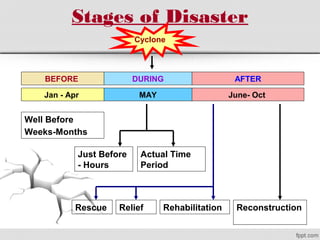
The document discusses various natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and droughts, highlighting their causes, impacts, and human vulnerabilities. It provides specific examples of disasters with associated casualties and damages, emphasizing the need for effective disaster management strategies and community preparedness. Furthermore, it outlines the role of individuals and organizations in mitigating risks and promoting environmental awareness.