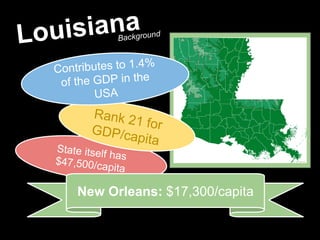
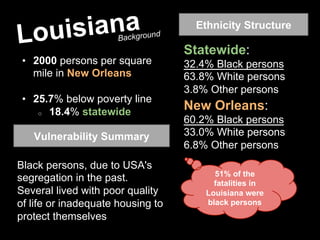
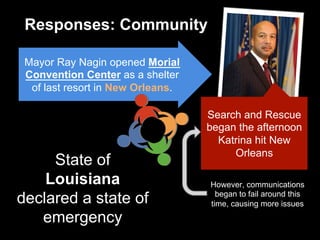
Hurricane Katrina caused over $108 billion in damage when it hit Louisiana, Florida, and Mississippi as a Category 5 hurricane in 2005. It destroyed over 200,000 homes and displaced 800,000 people. New Orleans was especially hard hit due to being below sea level, with levees and floodwalls failing in over 50 locations. The impacts and response were greatly influenced by the high poverty levels and segregation that left many vulnerable black communities exposed. International aid was provided to assist with recovery.