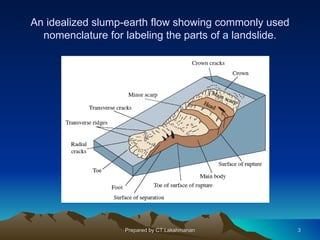
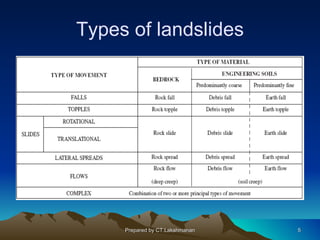
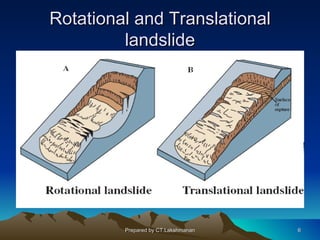
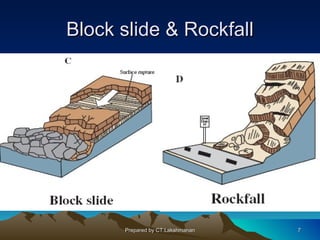
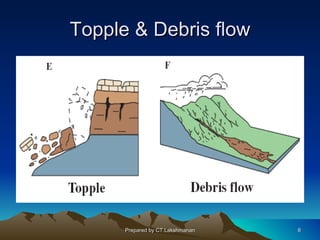
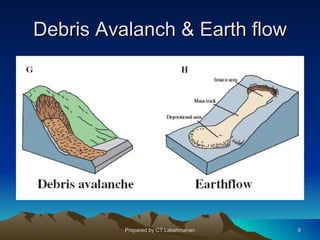
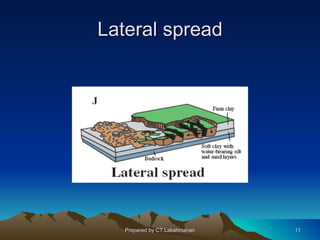
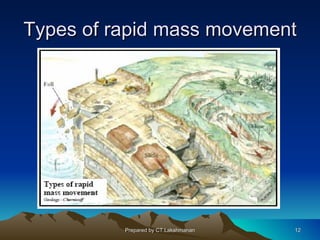
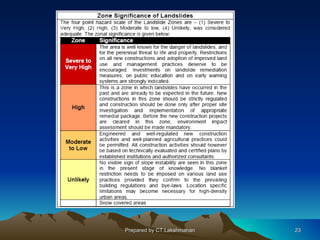
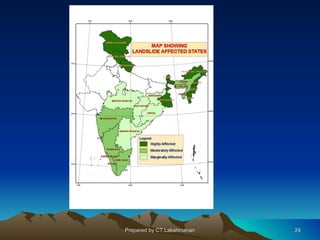
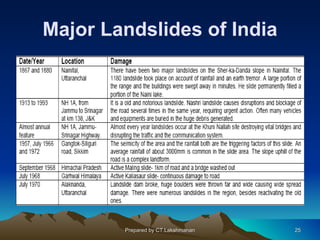
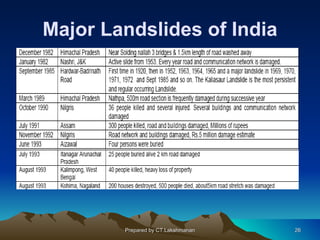
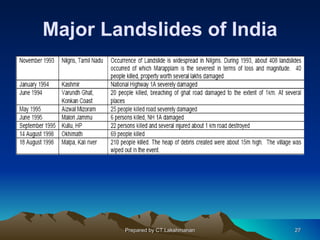
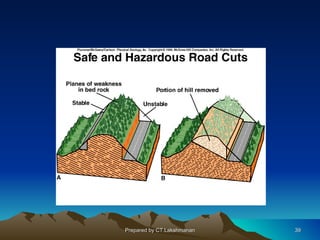
This document discusses landslides, including their classification, causes, and mitigation strategies. It defines a landslide as the downward and outward movement of slope-forming materials along surfaces of separation. Landslides are classified based on depth, type of movement, and speed. Key causes of landslides include geological weaknesses, erosion, rainfall, excavation, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions. Main mitigation strategies involve hazard mapping, land use planning, retaining walls, drainage control, engineered structures, vegetation, and insurance. Increasing slope stability also requires preventing rising groundwater levels in landslide areas.