Embed presentation
Download to read offline




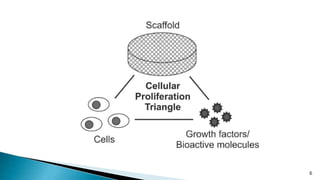


Tissue engineering involves using cells, biomaterials as scaffolds, and signaling molecules to create living tissues and organs. It can be used to repair or replace damaged tissues like bone, cartilage, blood vessels, skin, and bladder. The goal is also to produce better organs for transplantation. Biomaterials serve as scaffolds that encourage cell growth and tissue regeneration by providing a structure similar to the body's native extracellular matrix. Cells, scaffolds, and signaling molecules are the key components in tissue engineering.







