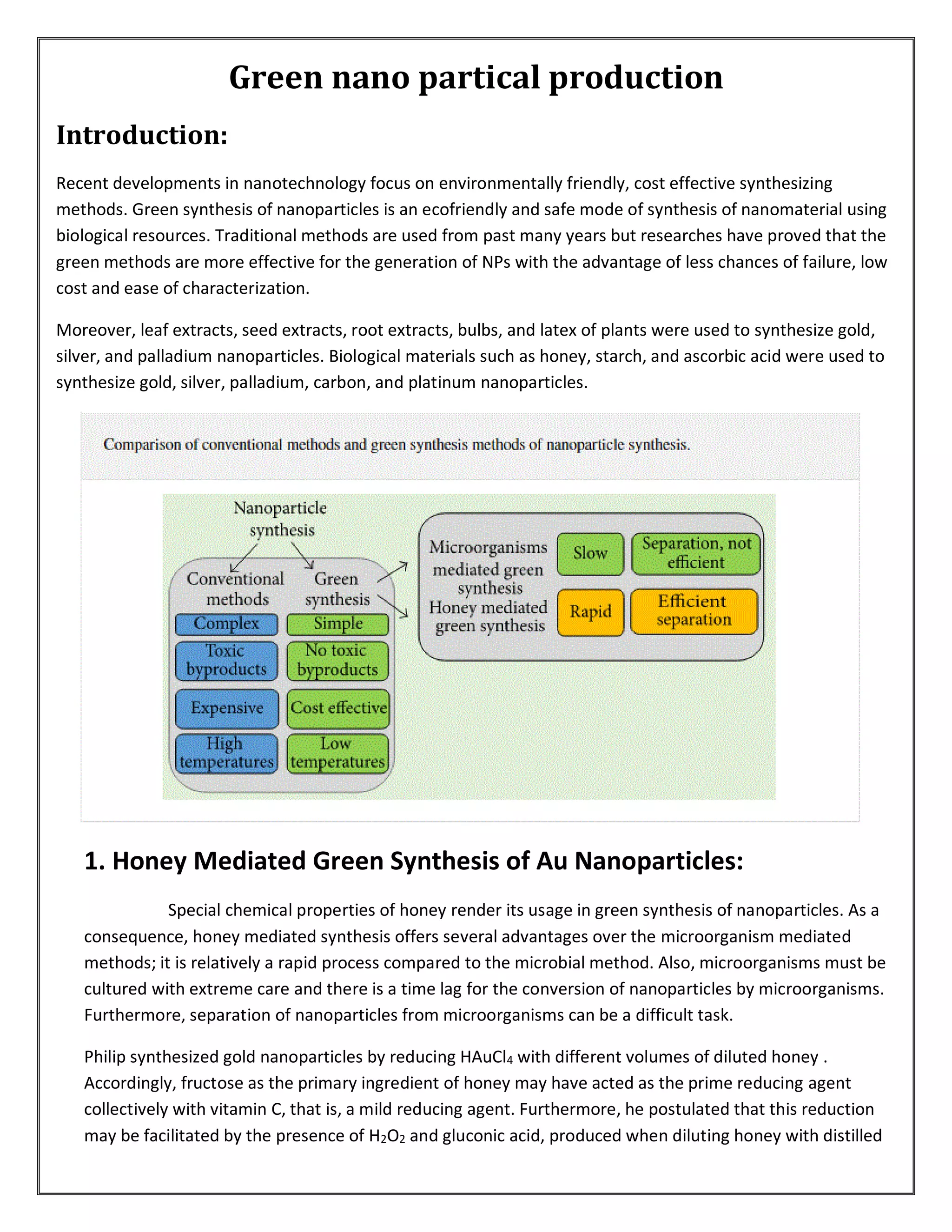
This document discusses green synthesis methods for producing different types of nanoparticles. It describes using plant extracts, honey, and microorganisms to synthesize silver, gold, zinc oxide, and cadmium sulfide nanoparticles. The green synthesis methods are environmentally friendly and cost effective alternatives to traditional chemical production techniques. Some key advantages of green synthesis include using natural reducing and capping agents, operating at ambient temperatures and pressures, and producing nanoparticles with applications in areas like dentistry, water purification, and environmental remediation.




![the concentration of solid extracts. Afterward, zinc precursors and plant extracts are reacted under
various pH and temperature conditions ]. If the extract is used as an aqueous solution, the zinc
precursors are added into the solution after the react ion Zinc NPs are filtered.
4. Synthesis of CdS NPs:
Nanoparticle production using microbial forms has a significant prospective to support nanoparticles
synthesis that does not require any of the toxic and hazardous, chemicals that are routinely used.
Cadmium sulphide nanoparticles (CdS) was chosen as a compound of interest due to its high stability,
excellent physical, chemical and structural properties, ease of preparation and handling. CdS nanoparticles
are being used widely used for the cancer diagnosis and antimicrobial treatment.
Bacillus licheniformis strain is used in this method. The bacterial strain was inoculated on nutrient broth.
The isolate was maintained in nutrient agar for further study.
The initiated culture was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 15 minutes. The pellet was washed repeatedly to
remove remnant media. The biomass was carefully weighed and deionized water was added. This set up
(in an Erlenmeyer flask) was maintained in a shaker for 30 minutes at 200 rpm. 0.1 mM of cadmium
chloride and 0.01 mM of sodium sulphide was added to the mixture. Post incubation, the contaminants
were excluded using acetone and water to obtain pure nanoparticles.
Applications of green nanotechnology:
From recent years, dramatic changes in the interest of researchers developed for the green
nanotechnology and number of science publications are expanding ceaselessly. Green NPs have differing
impact on the utilization of metallic NPs. They assume an imperative part to expanding the utility of NPs in
pharmaceutical field particularly.
Dentistry :
Ag-NPs have been utilized in dental instruments and swathes. Joining of Ag-NPs into orthodontic glue can
increase or keep up the shear bond nature of orthodontic cement while expanding its confirmation from
microorganisms.
Purification of drinking water:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/greennanoparticalsynthesis-200711095714/75/Green-nanopartical-synthesis-6-2048.jpg)
