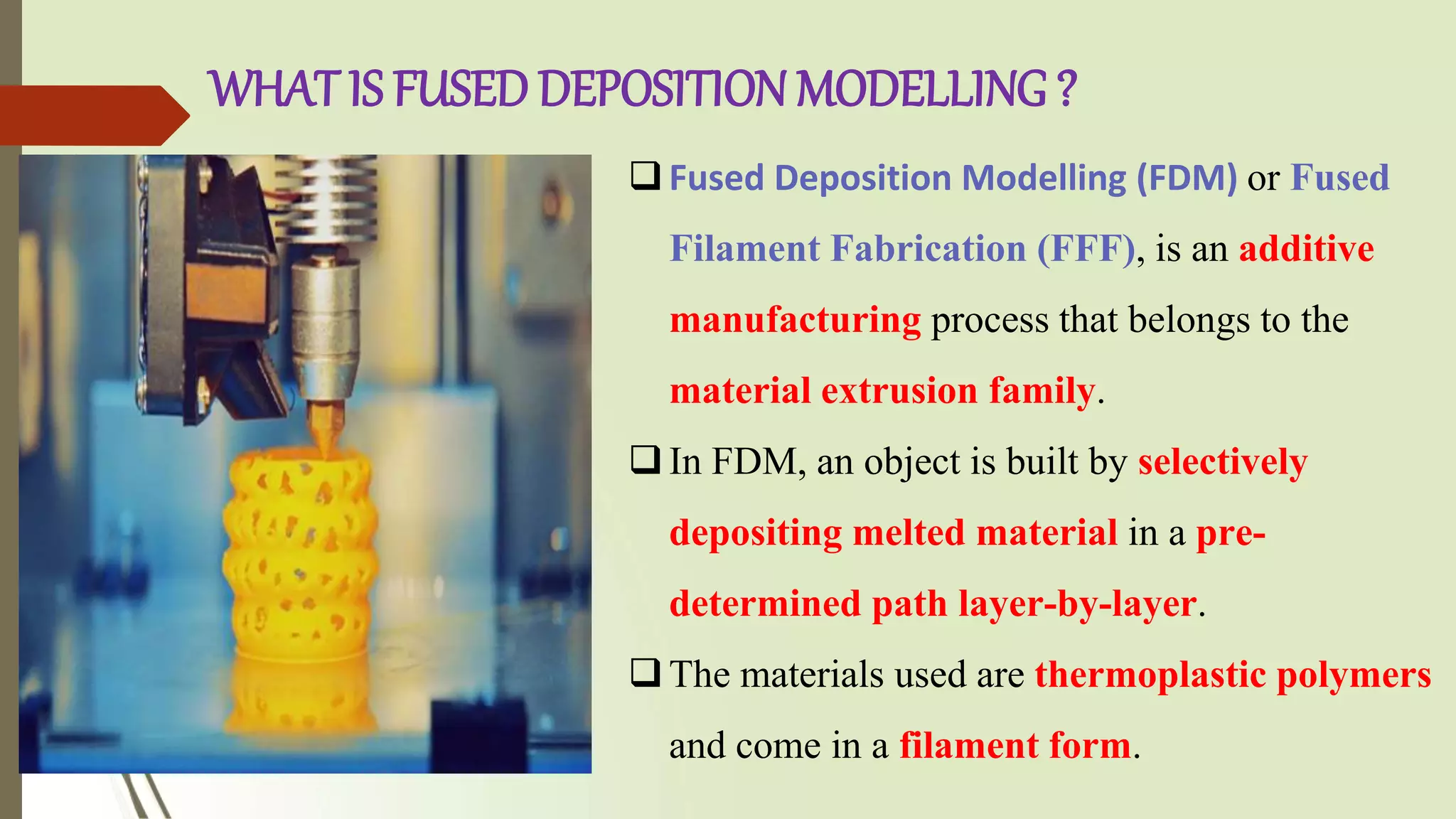
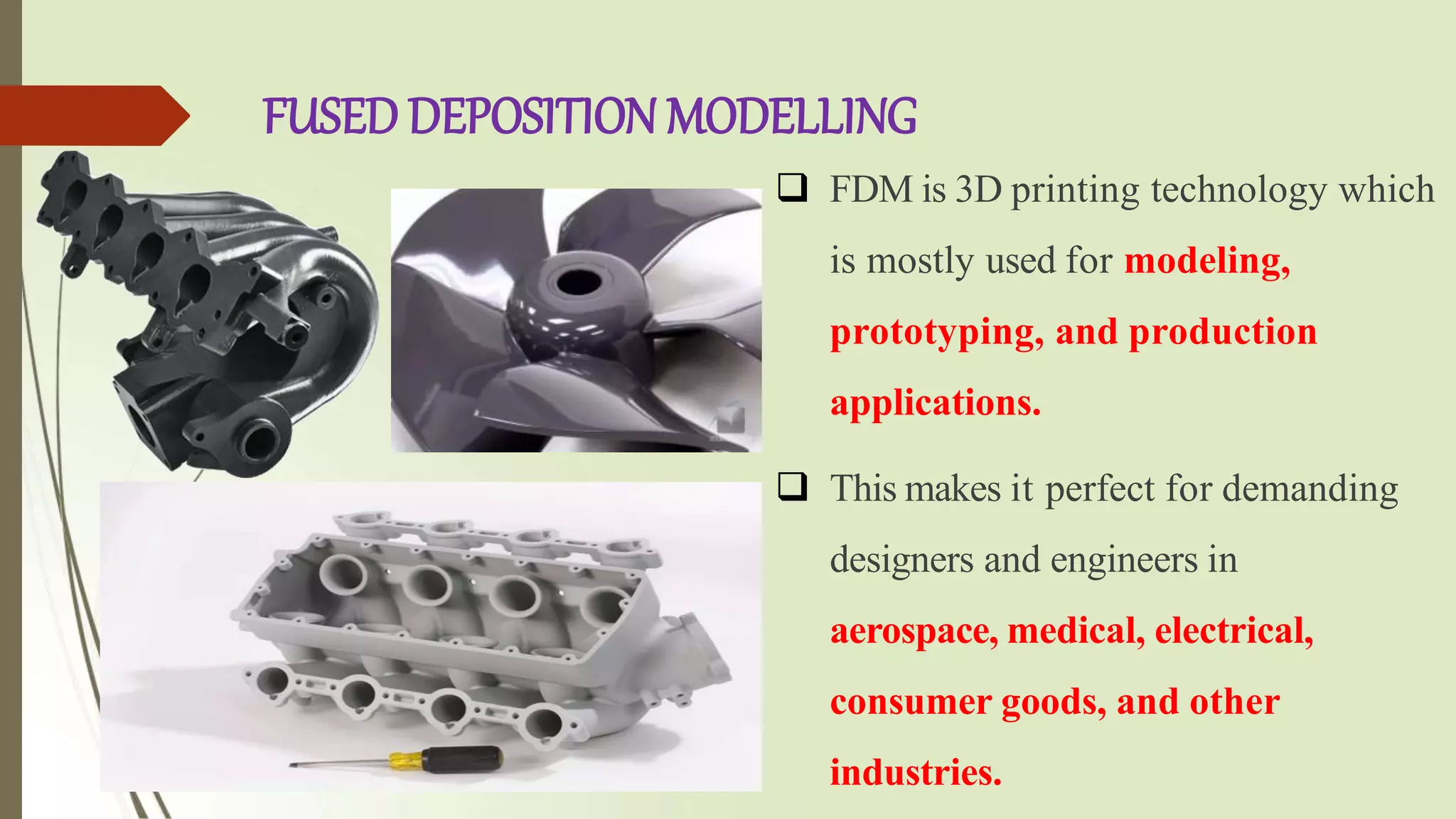
This document provides an overview of fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing technology. It discusses that FDM works by extruding melted thermoplastic through a nozzle to build an object layer by layer. Common materials used are ABS and PLA plastics. FDM printers have advantages of a wide material selection and low cost, but lower accuracy than other technologies. Applications include prototyping, manufacturing tools and end-use parts for industries like automotive, aerospace, medical and more. In conclusion, FDM is well-suited for prototyping and less structurally demanding applications.