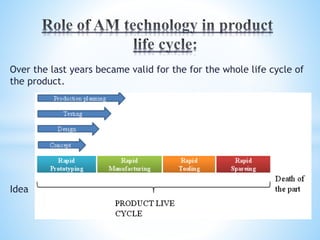
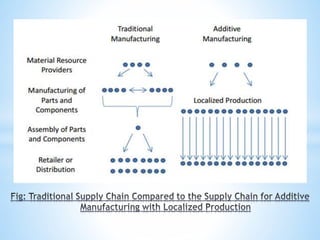
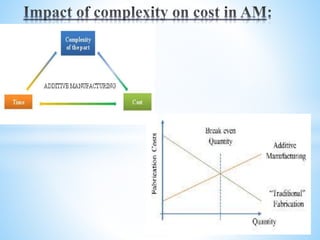
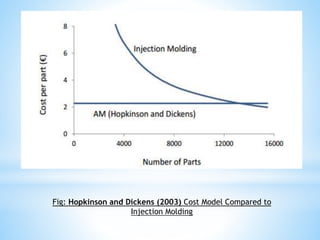
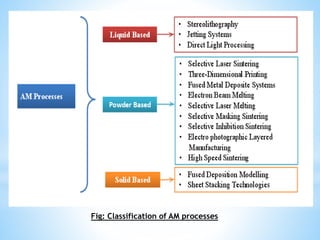
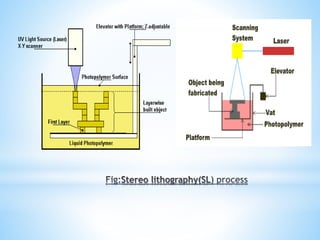
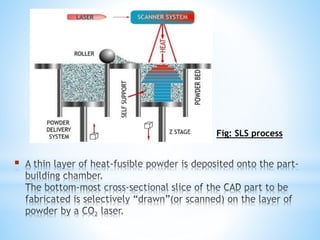
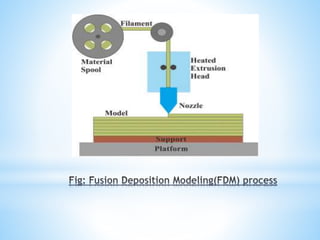
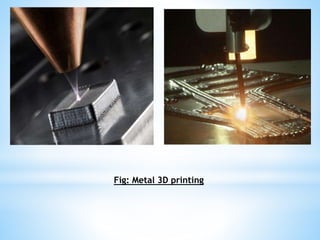
The document discusses additive manufacturing (3D printing) as a transformative technique for creating solid objects from digital models, contrasting it with conventional subtractive manufacturing. It highlights the advantages of additive manufacturing, including rapid prototyping, reduced material waste, and increased customization, while also acknowledging its limitations such as high production costs and slow build rates. Additionally, various processes like stereolithography (SL) and selective laser sintering (SLS) are explored, detailing how they function and their applications across industries like aerospace and medical instruments.