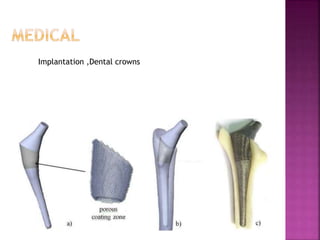
Additive manufacturing (AM) involves creating objects layer by layer from 3D model data, contrasting with traditional subtractive manufacturing. Common materials used in 3D printing include various plastics like ABS and PLA, as well as metals such as steel and titanium, with applications in diverse fields like medical, automotive, and education. The process typically begins with a design in CAD software, followed by printing, showcasing the versatility and innovation of modern manufacturing technologies.