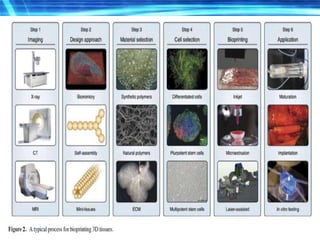
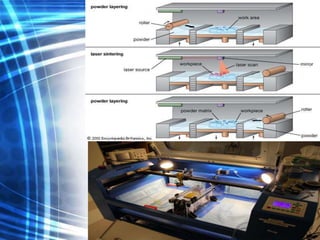
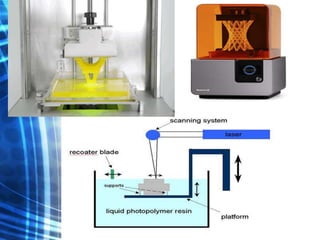
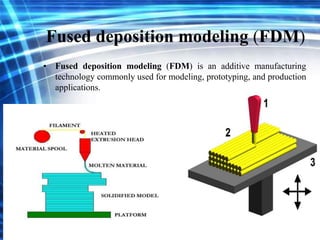
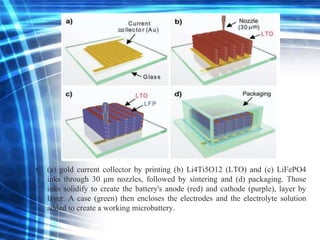
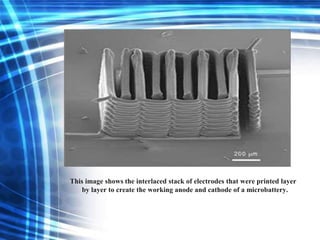
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process where objects are created by laying down successive layers of material, such as plastics, metals, or living cells. There are several common 3D printing methods that differ in how the layers are bonded, such as selective laser sintering (SLS), stereolithography (STL), and fused deposition modeling (FDM). The document discusses the history and development of 3D printing, provides examples of how it can be used to print complex structures like batteries and human tissues, and highlights advantages like rapid prototyping but also challenges like cost and limited strength.