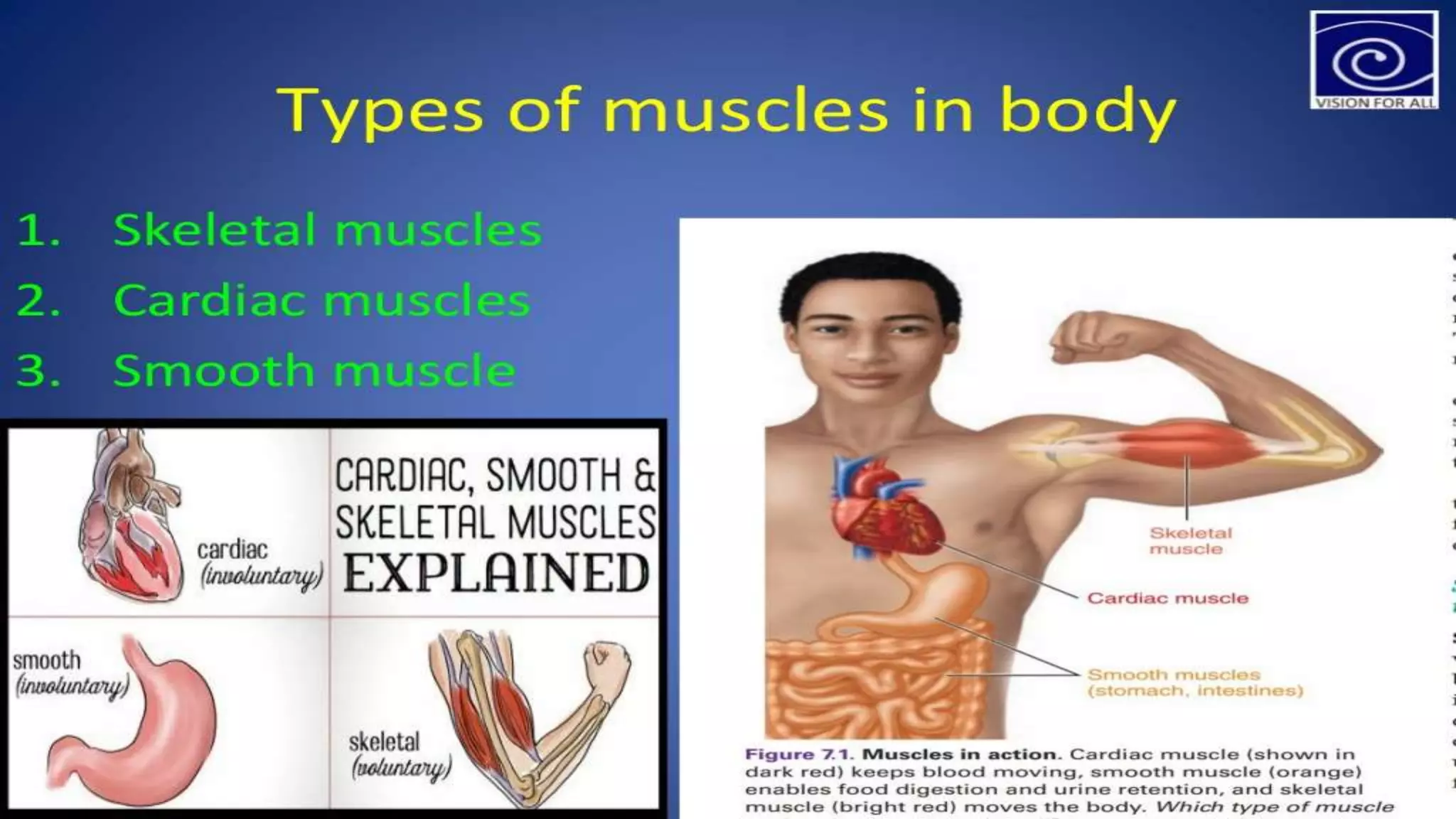
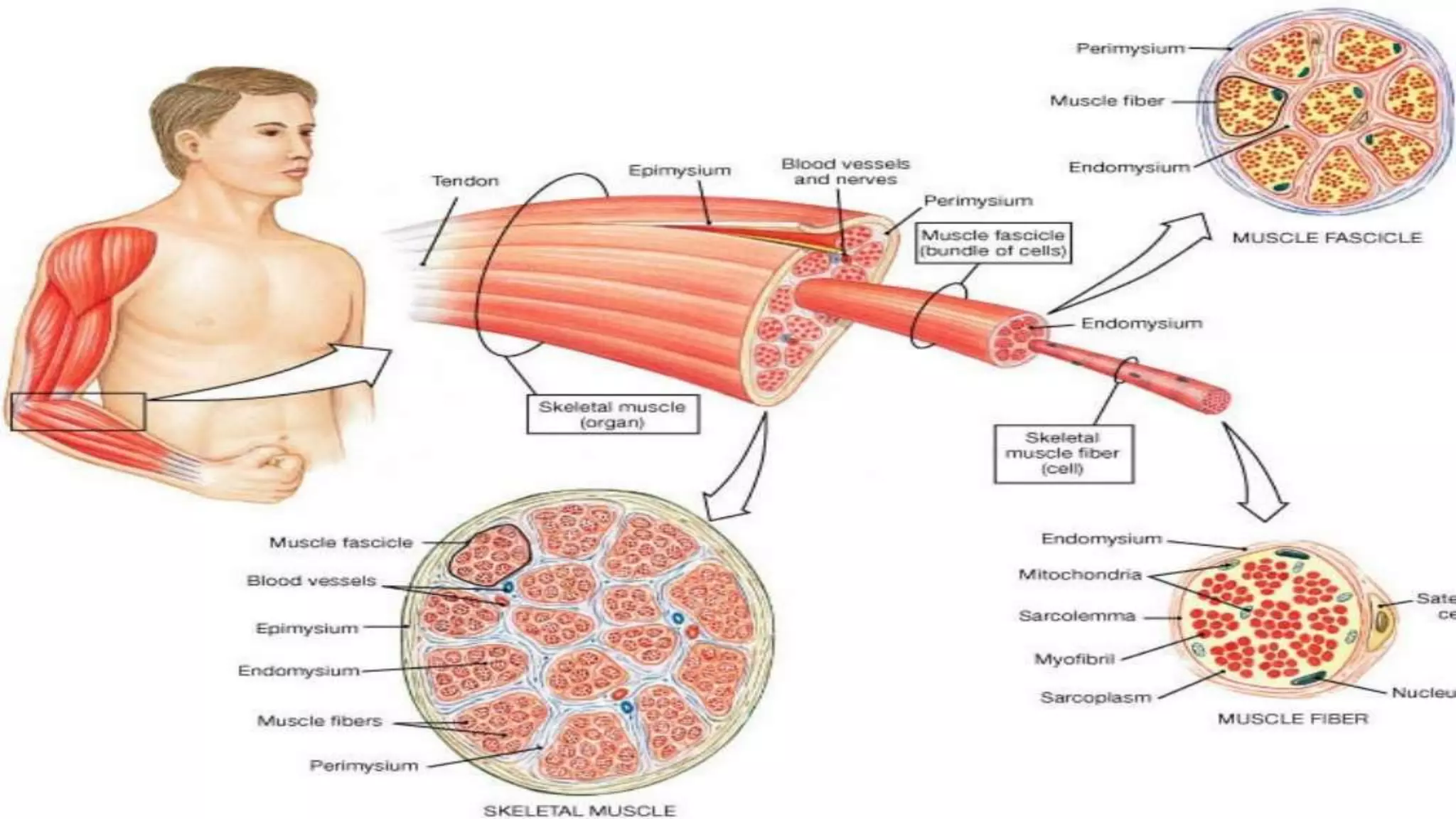
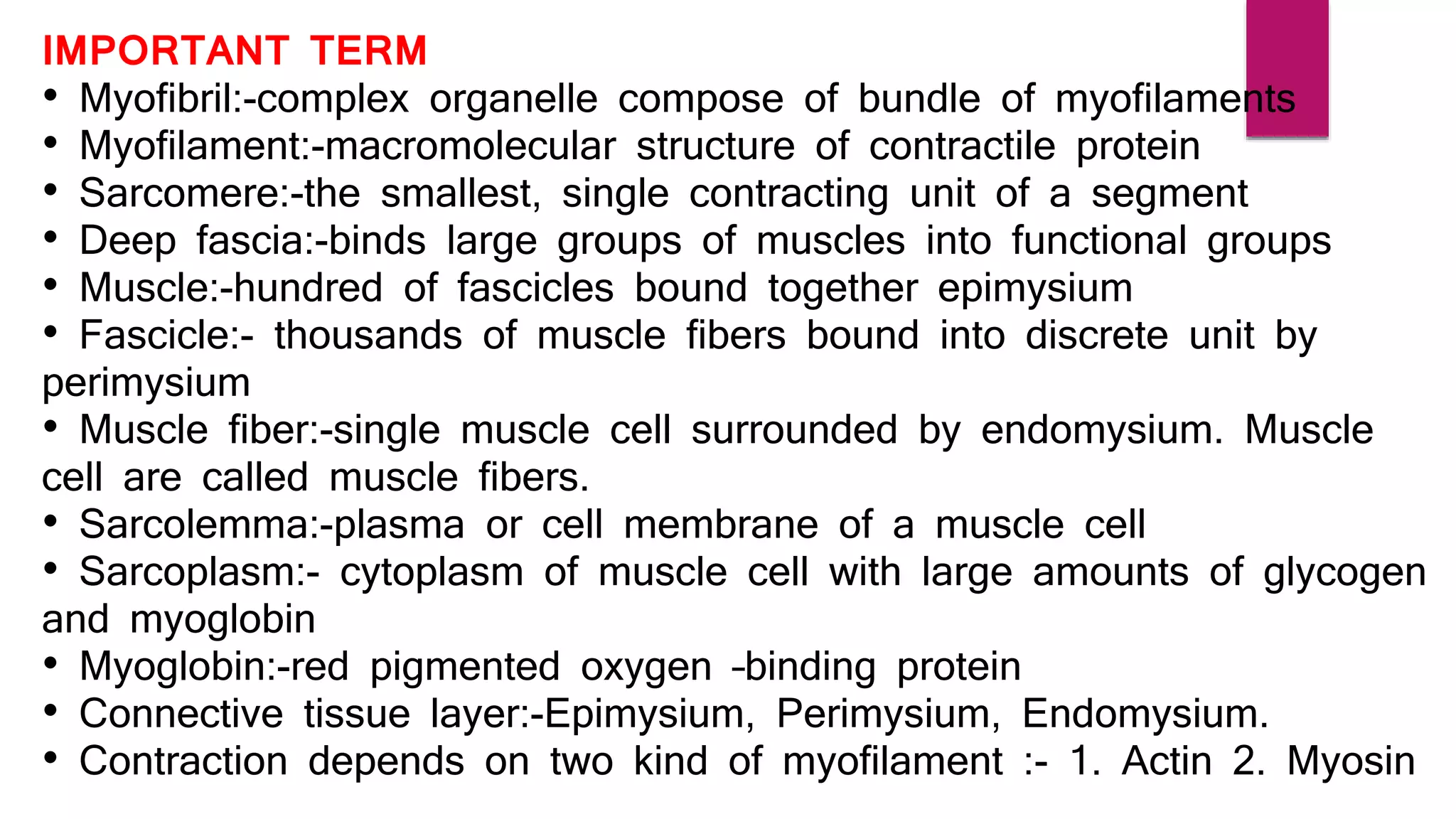
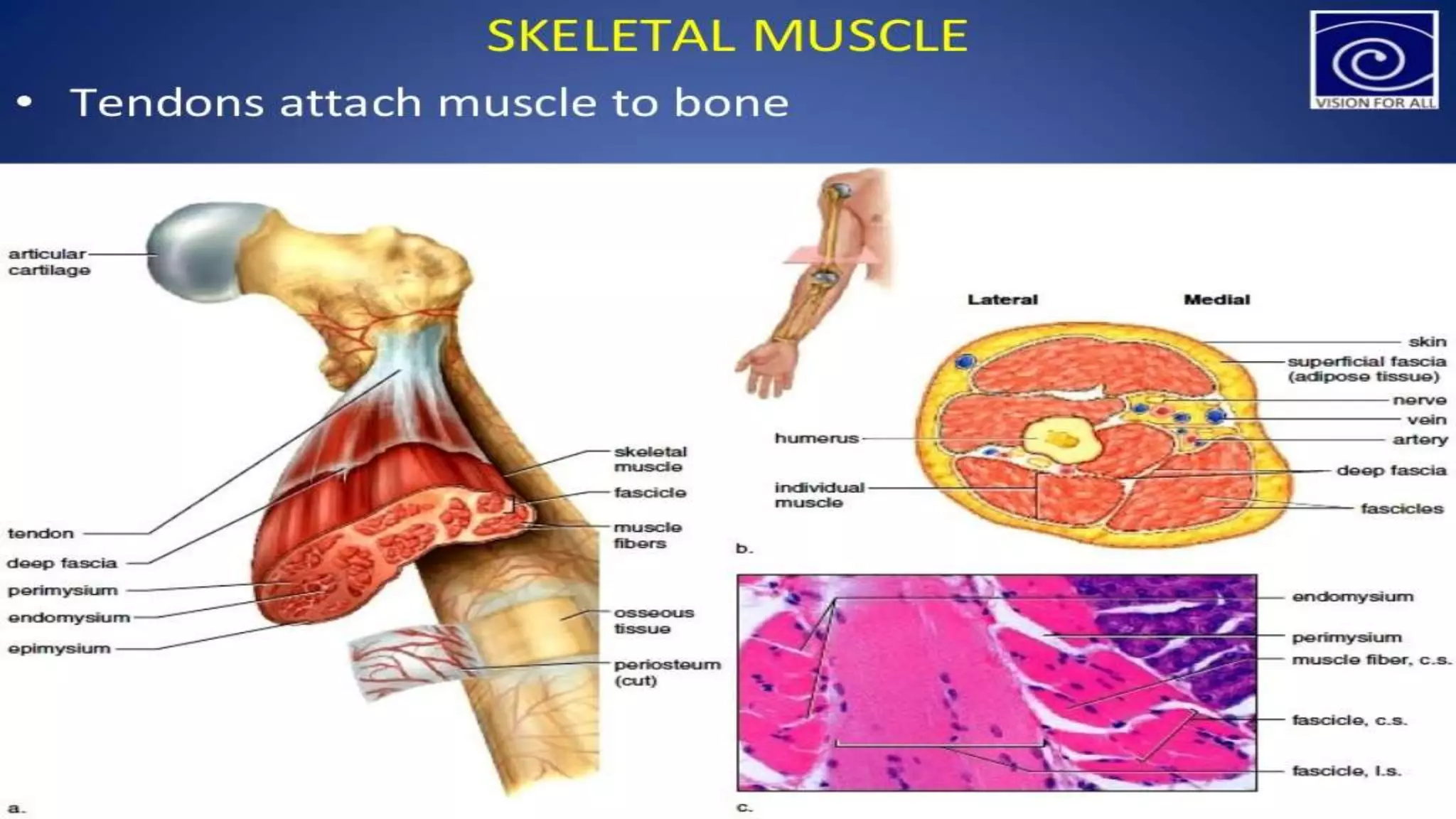
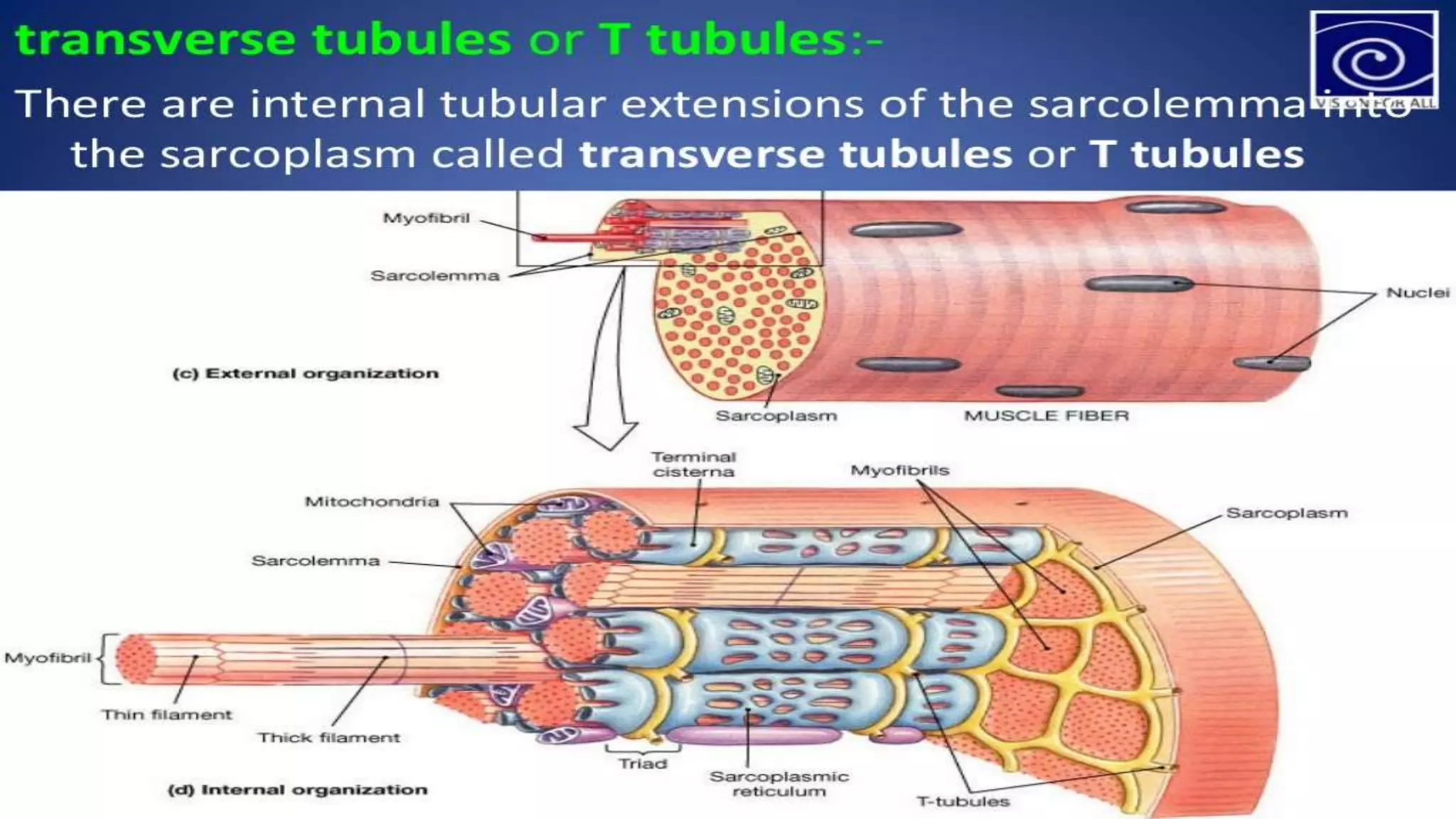
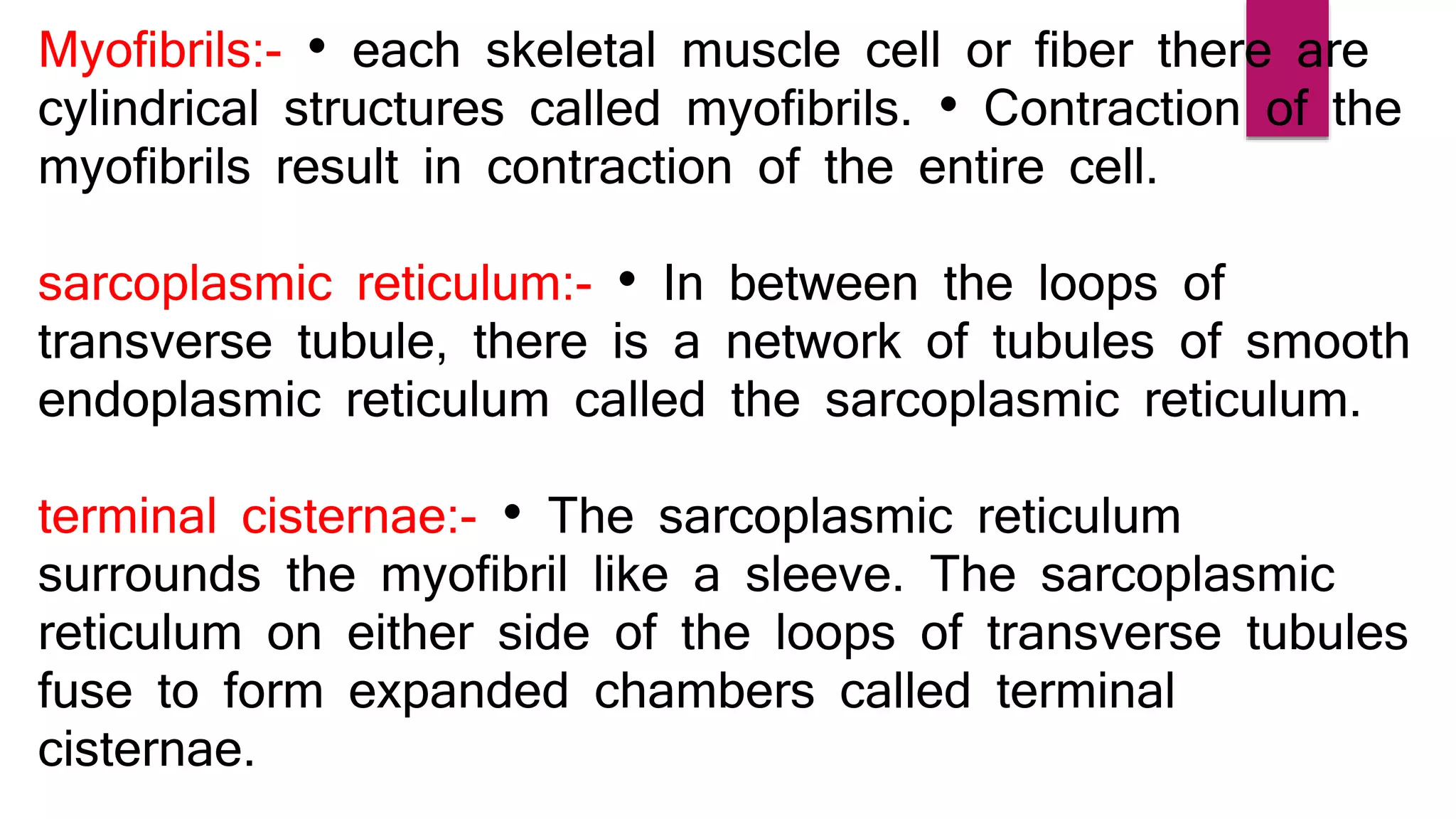
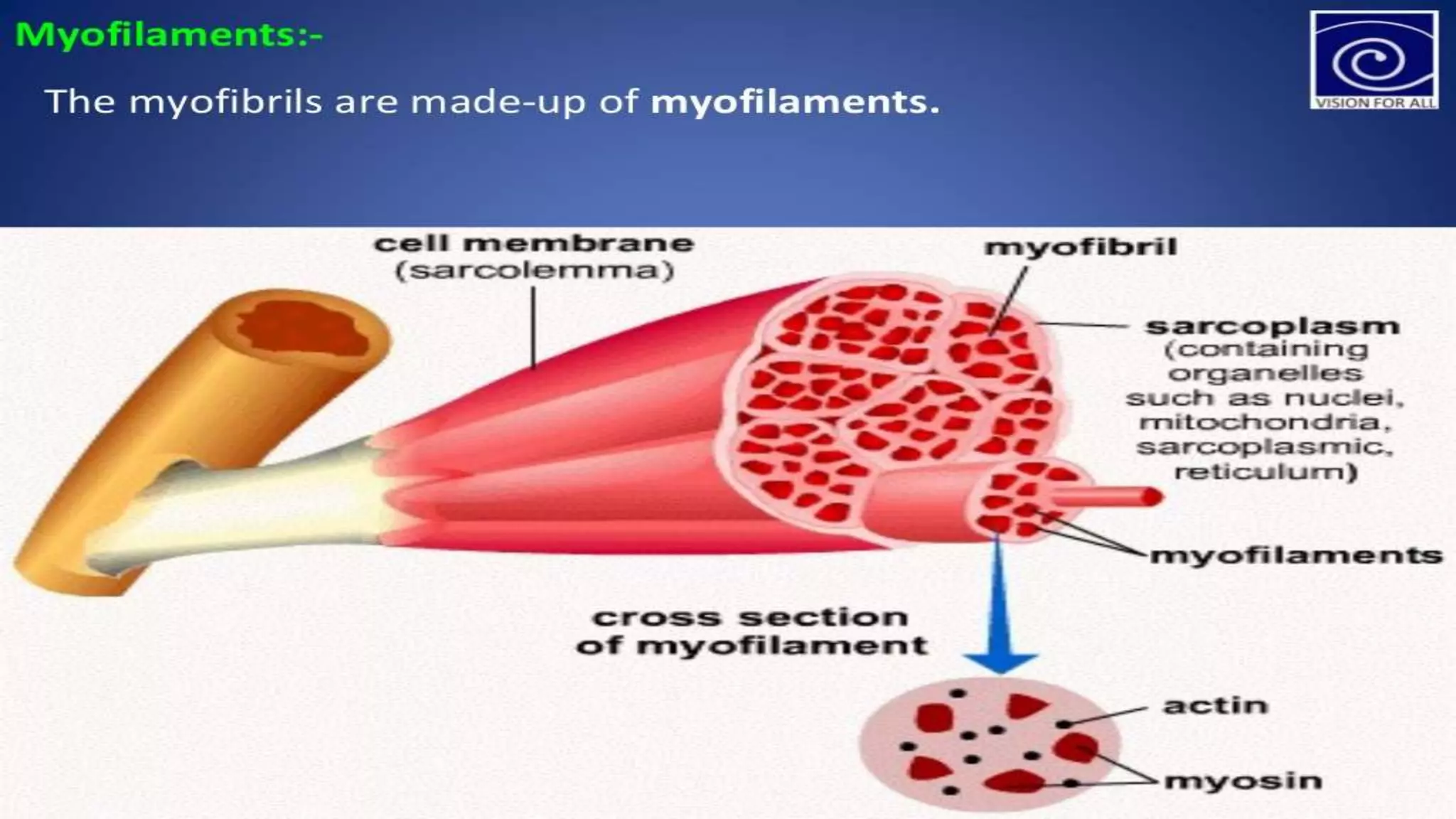
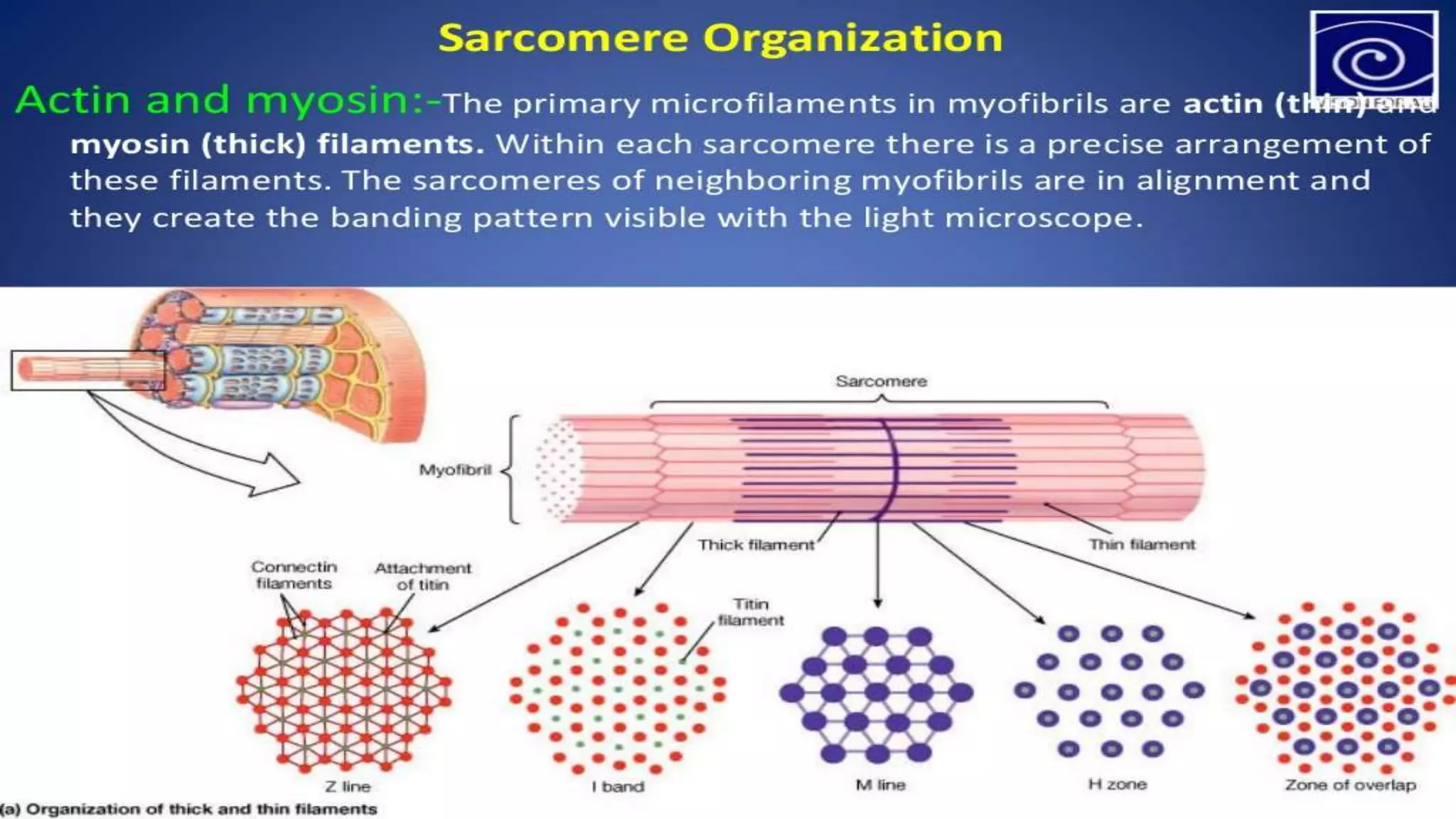
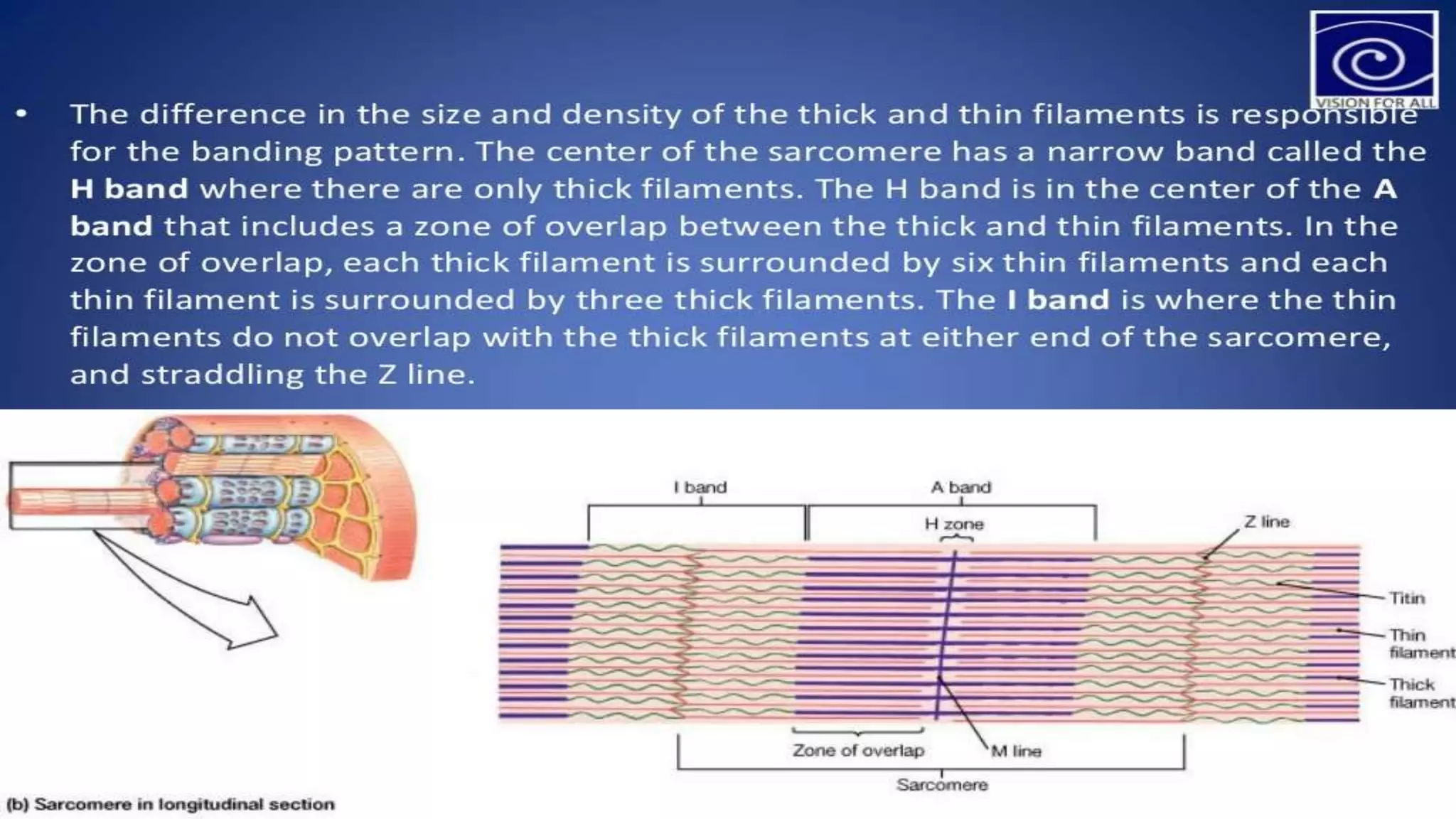
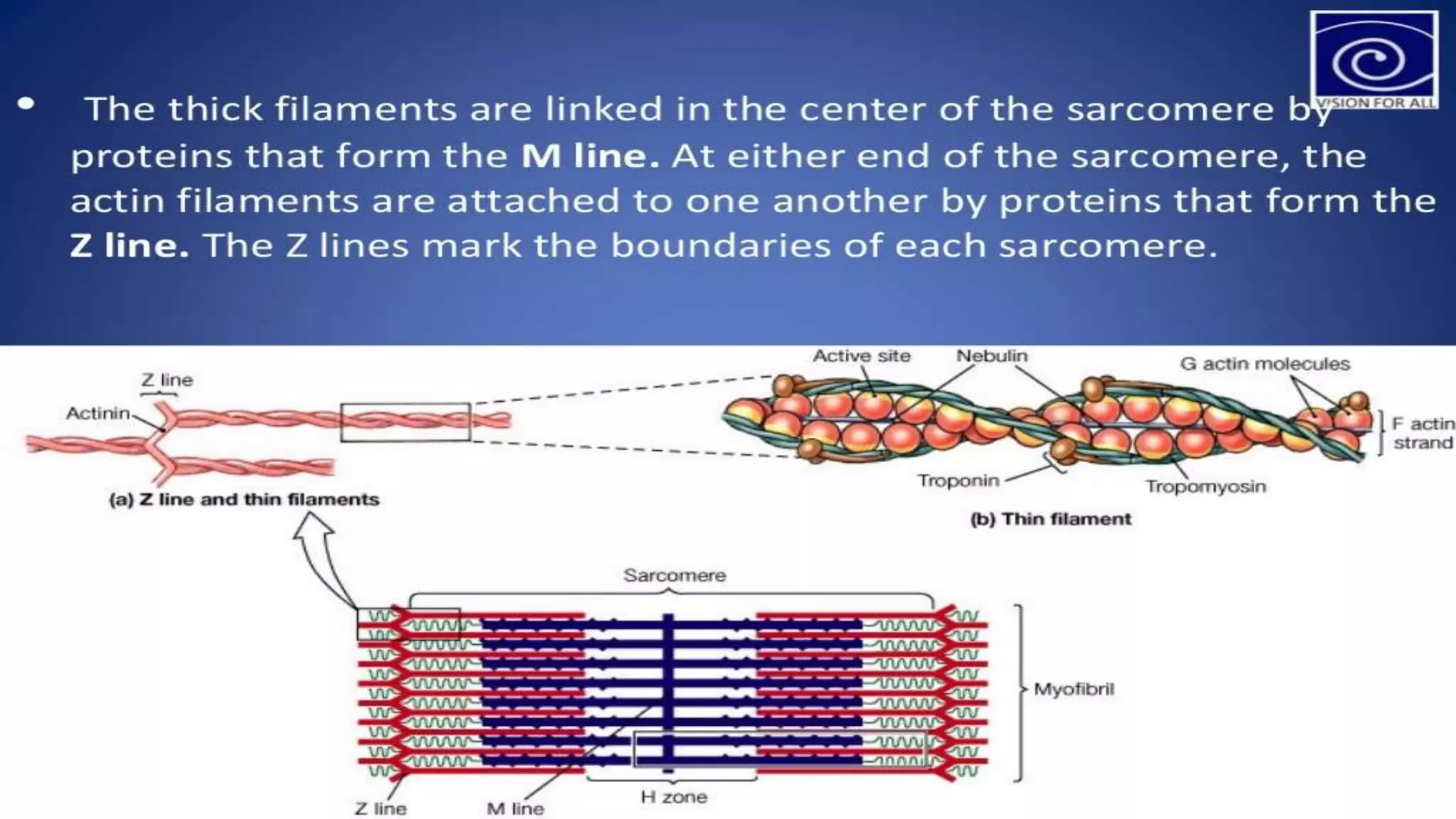
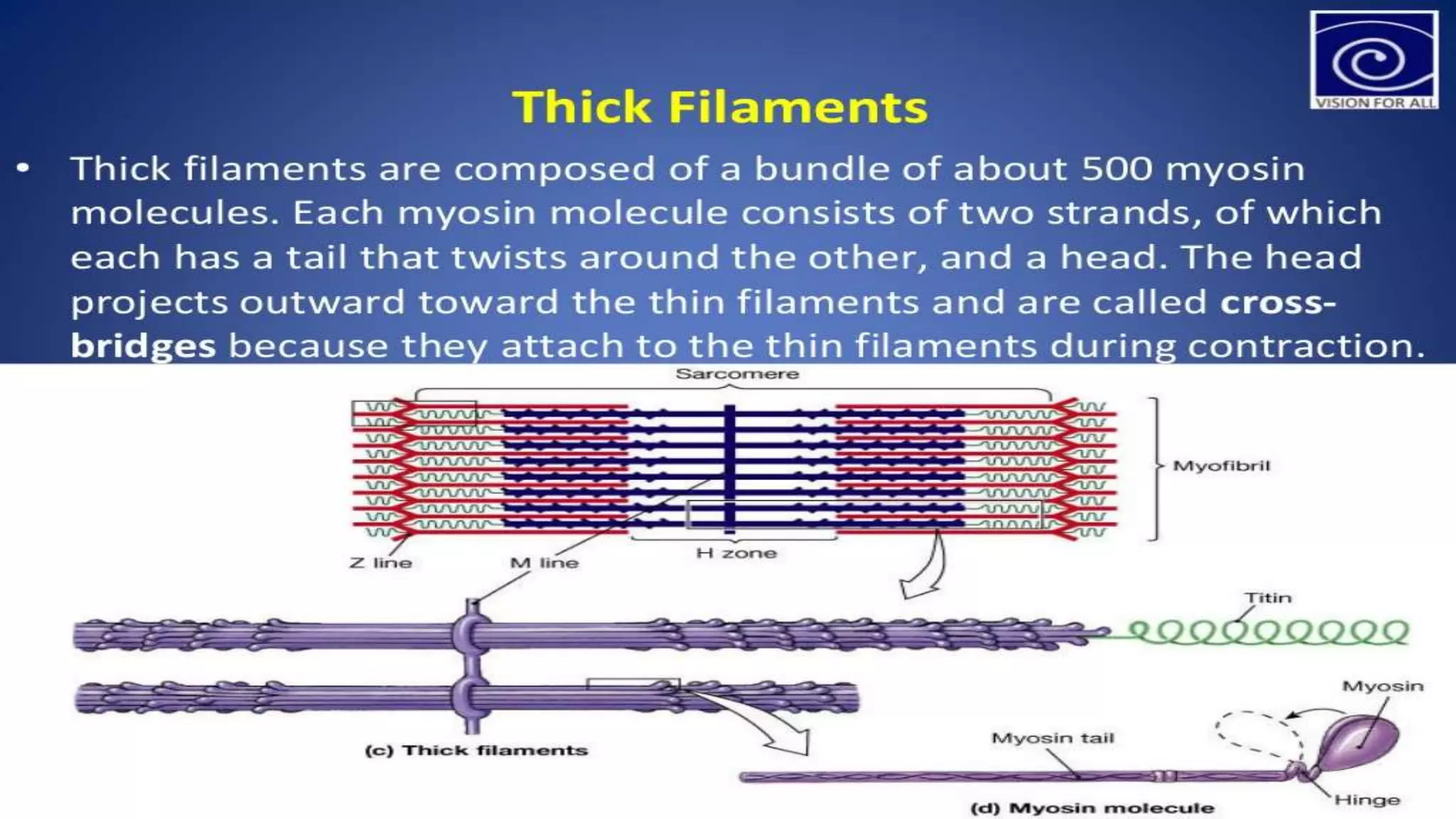
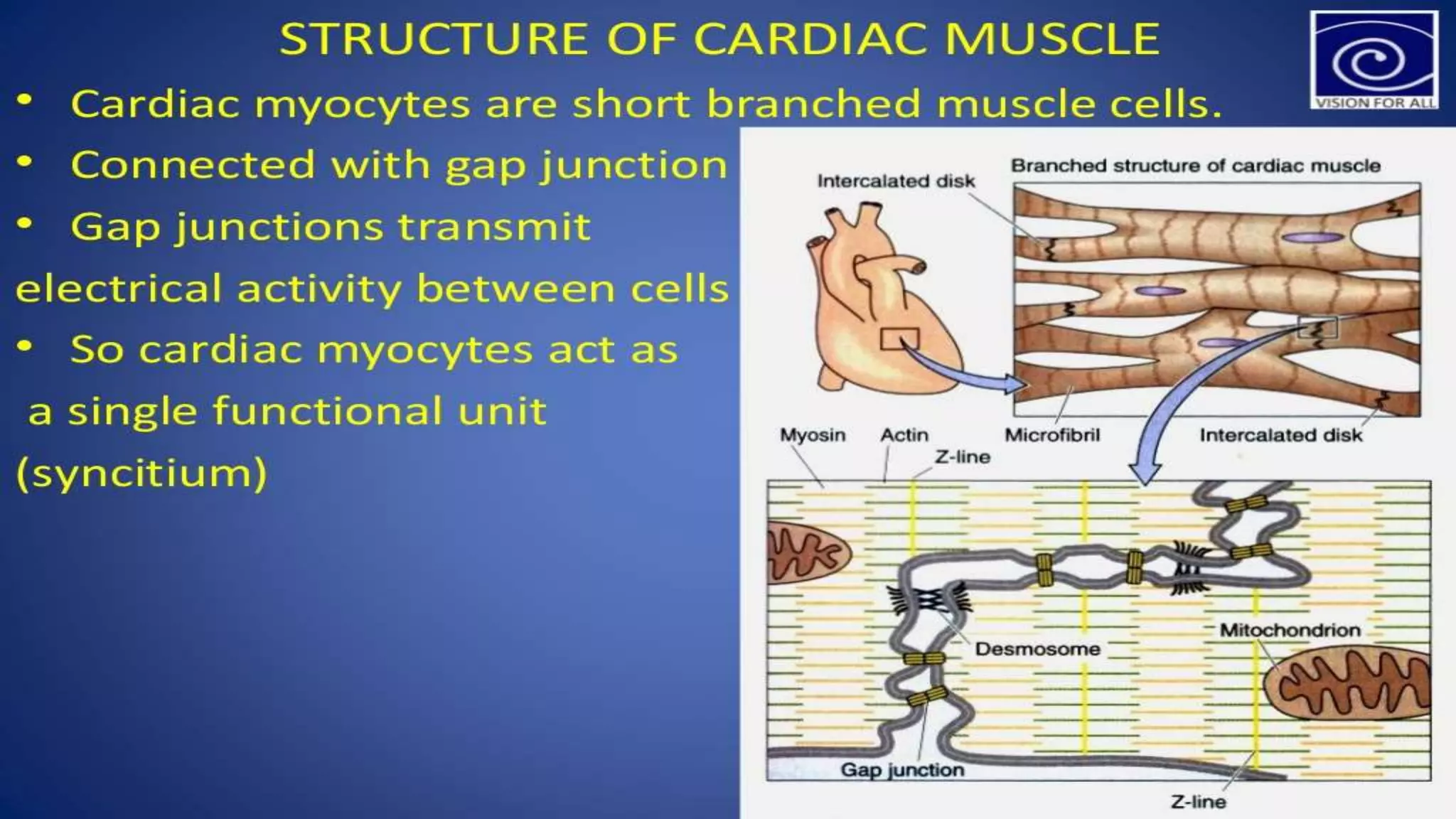
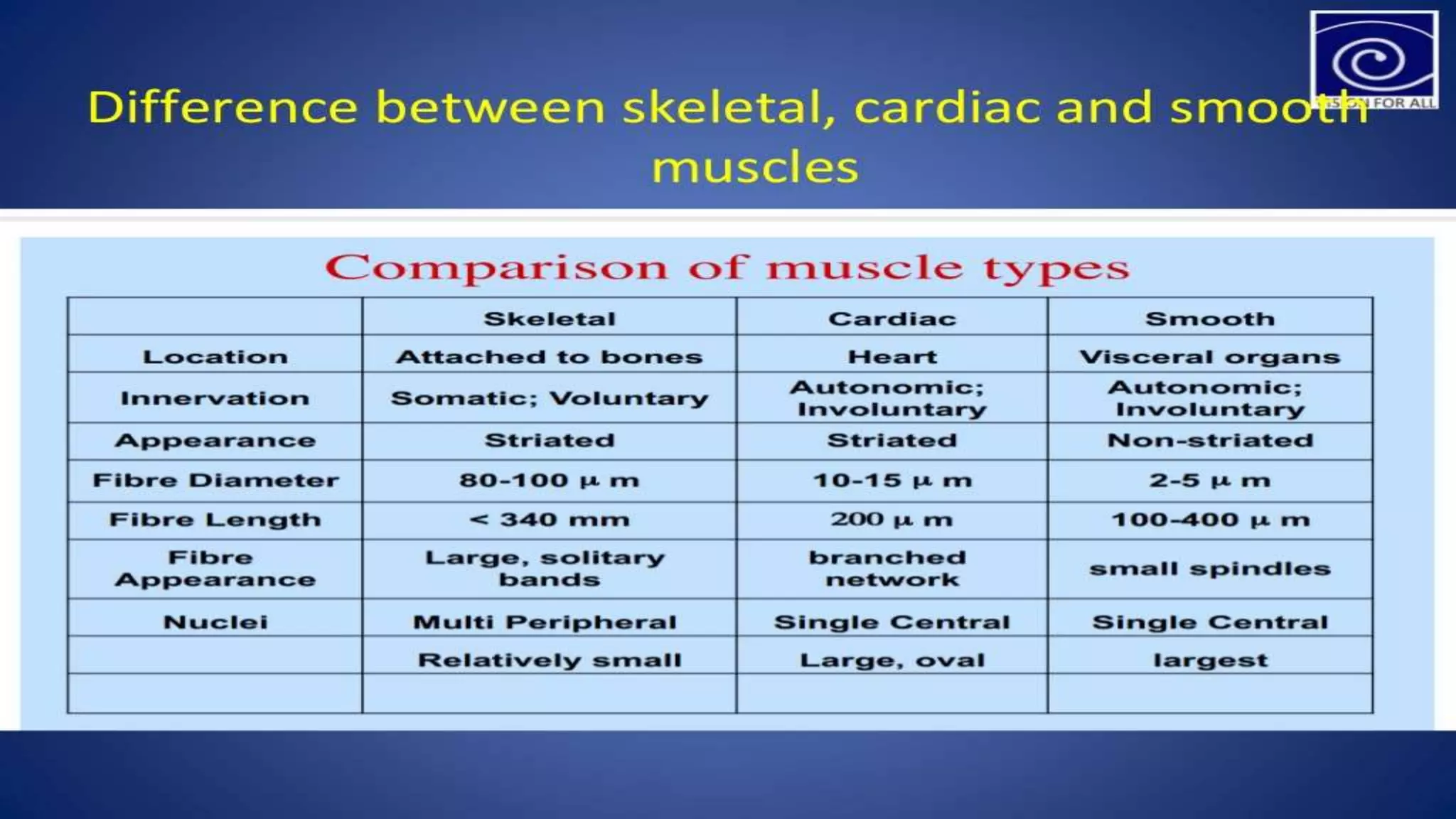
There are three main types of muscle in the human body - skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle.
Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, attaching to bones to enable movement. Cardiac muscle is also striated and found only in the heart, contracting involuntarily to pump blood. Smooth muscle is non-striated and involuntary, surrounding internal organs to aid processes like digestion and blood flow. All three muscle types contract through the sliding filament mechanism of actin and myosin but differ in structure, control, and function.