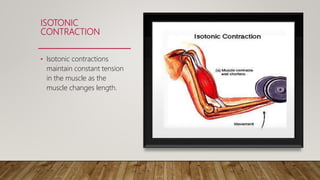
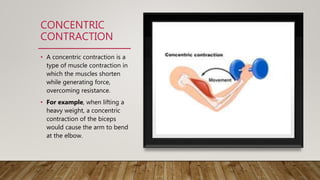
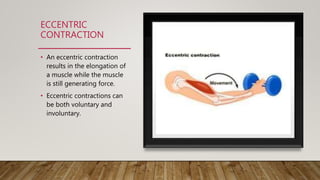
There are two types of muscle contractions: isotonic and isometric. Isotonic contractions maintain constant tension as the muscle changes length, and include concentric contractions where muscles shorten against resistance, and eccentric contractions where muscles elongate while generating force. Isometric contractions generate force without changing muscle length. Muscle contraction occurs via the sliding filament theory, where the actin filament slides into the myosin filament in the A band region, causing sarcomeres to shorten and Z lines to move closer together. This occurs through a cross-bridge cycling process using ATP energy.