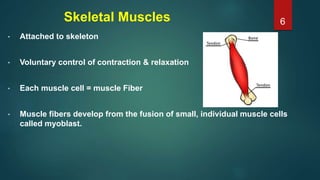
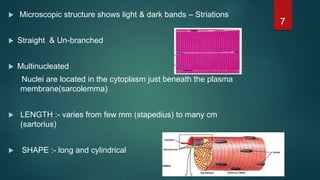
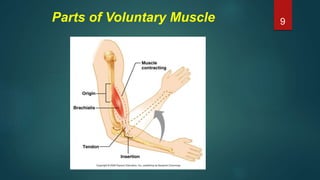
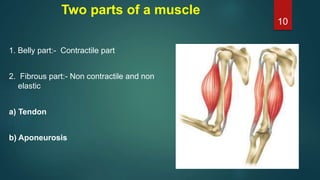
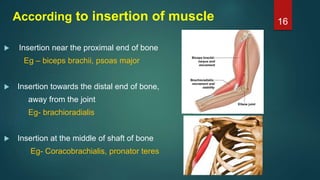
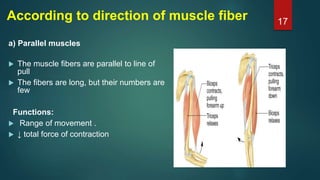
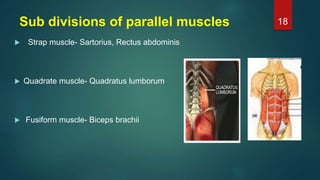
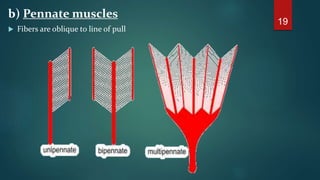
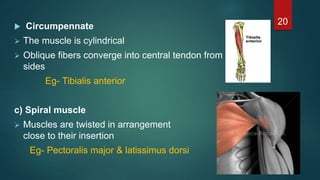
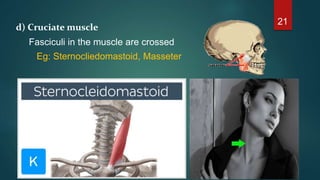
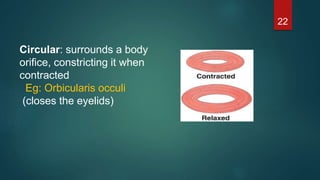
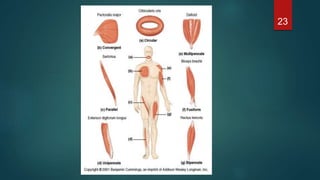
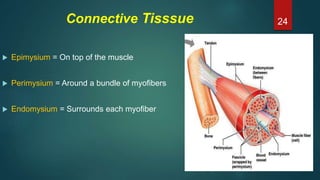
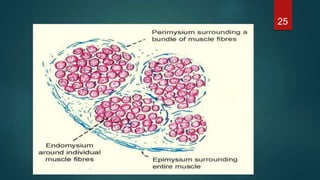
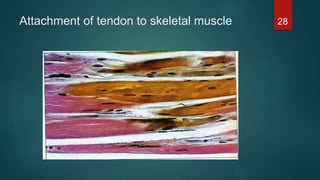
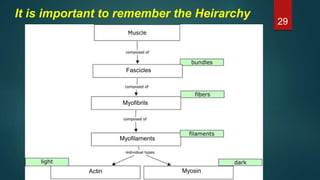
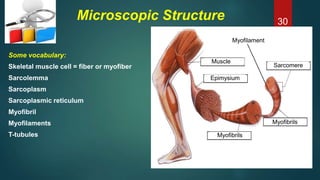
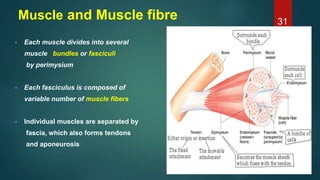
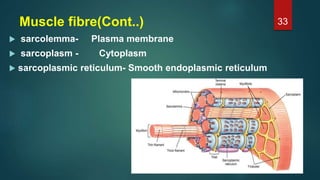
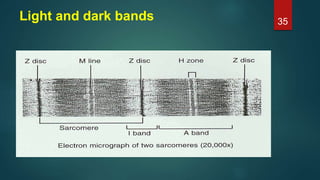
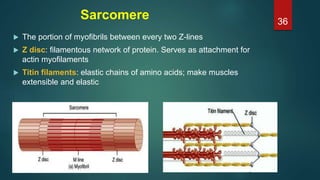
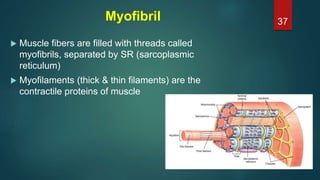
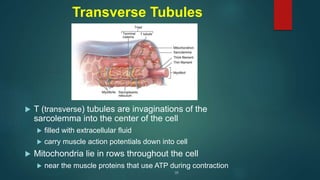
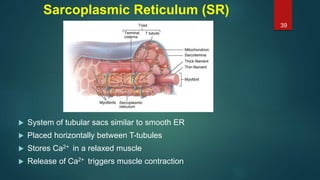
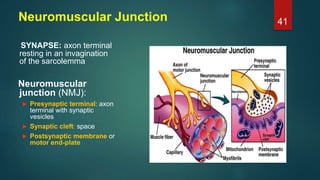
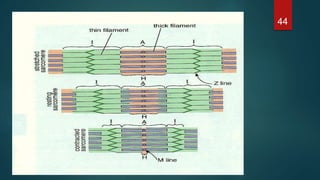
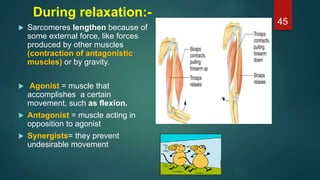
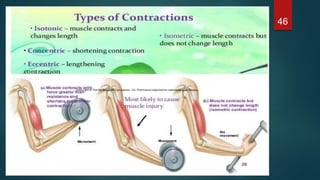
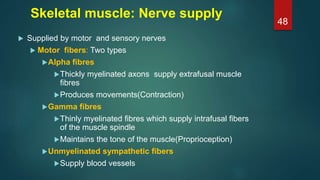
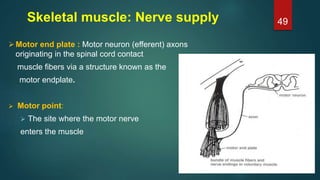
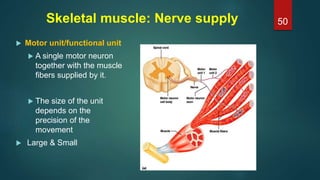
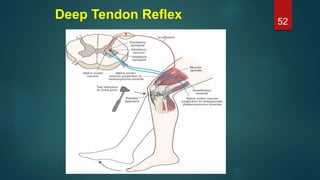
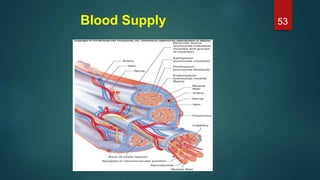
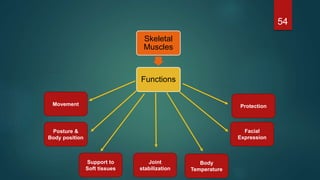
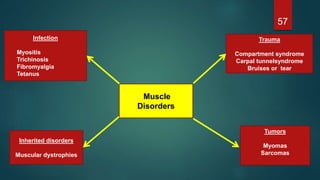
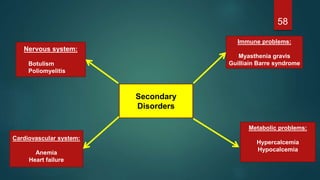
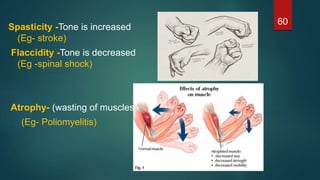
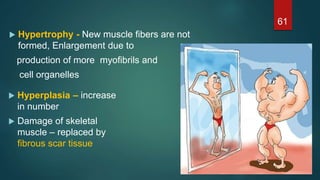
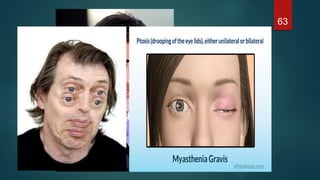
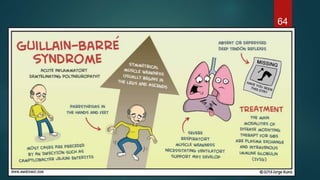
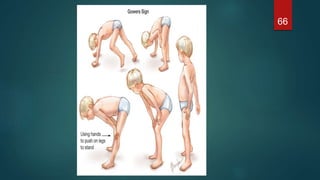
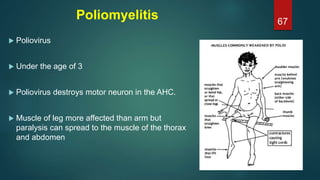
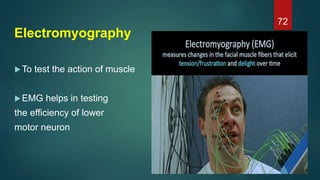
This document provides an overview of skeletal muscle. It begins with an introduction to muscle tissue and its role in movement. It then discusses the classification, microscopic structure, physiology, and applied anatomy of skeletal muscle. Key points include that skeletal muscle is striated, voluntary, and attached to bones. Microscopically, it contains sarcomeres made up of actin and myosin filaments. Contraction occurs via the sliding filament model. Skeletal muscle has multiple functions and can be impacted by injuries, diseases, fatigue, and other disorders.