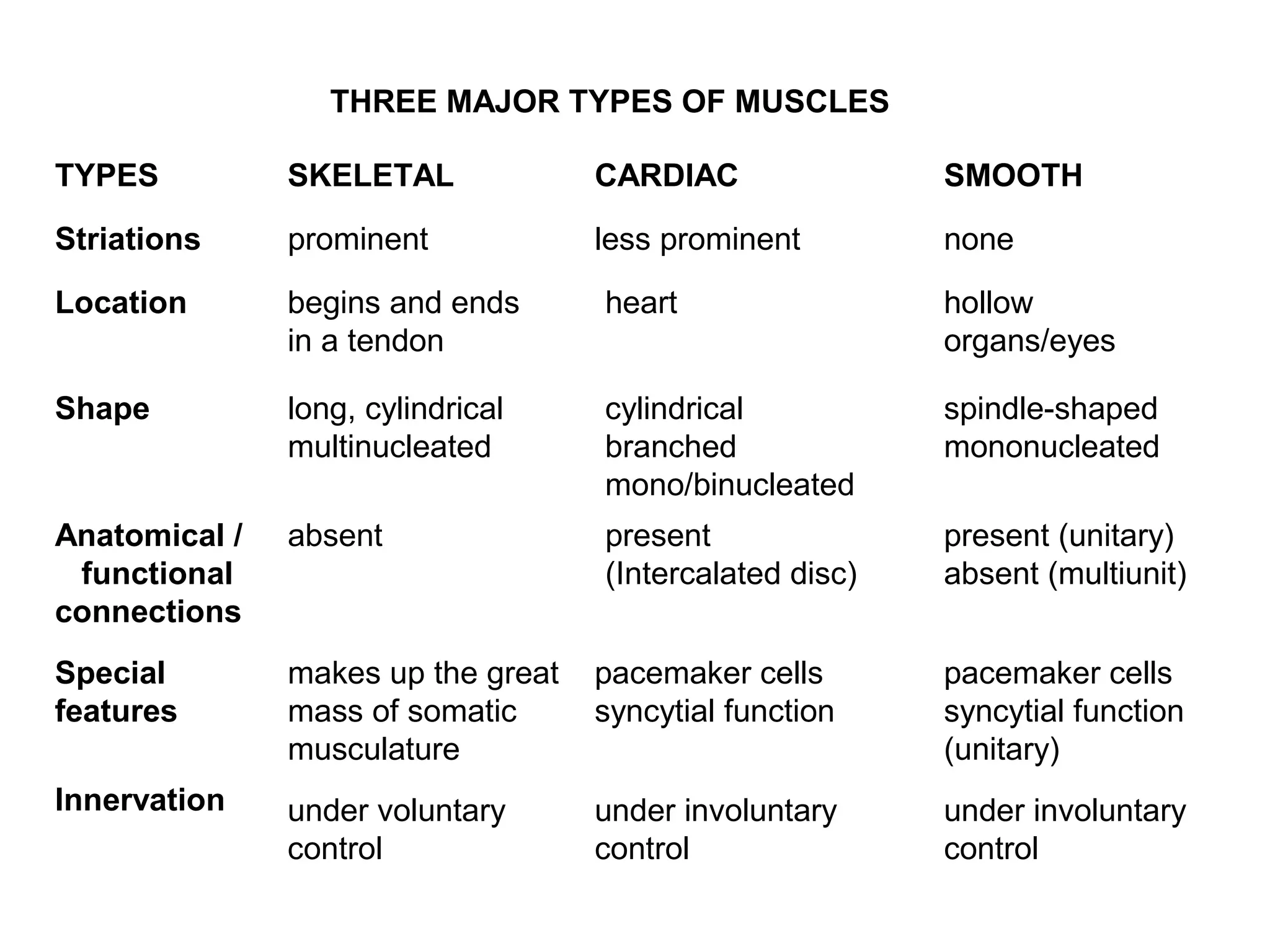
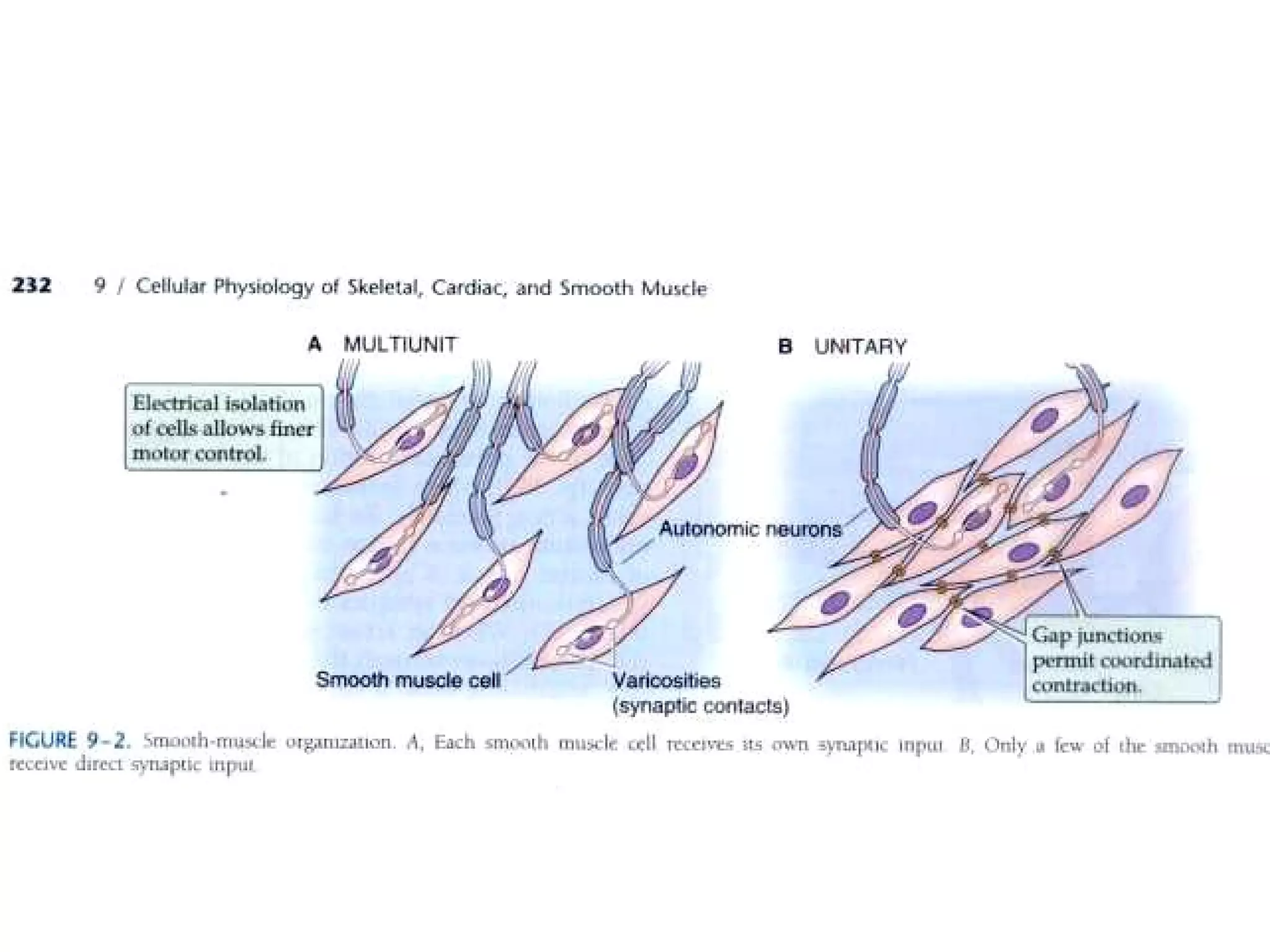
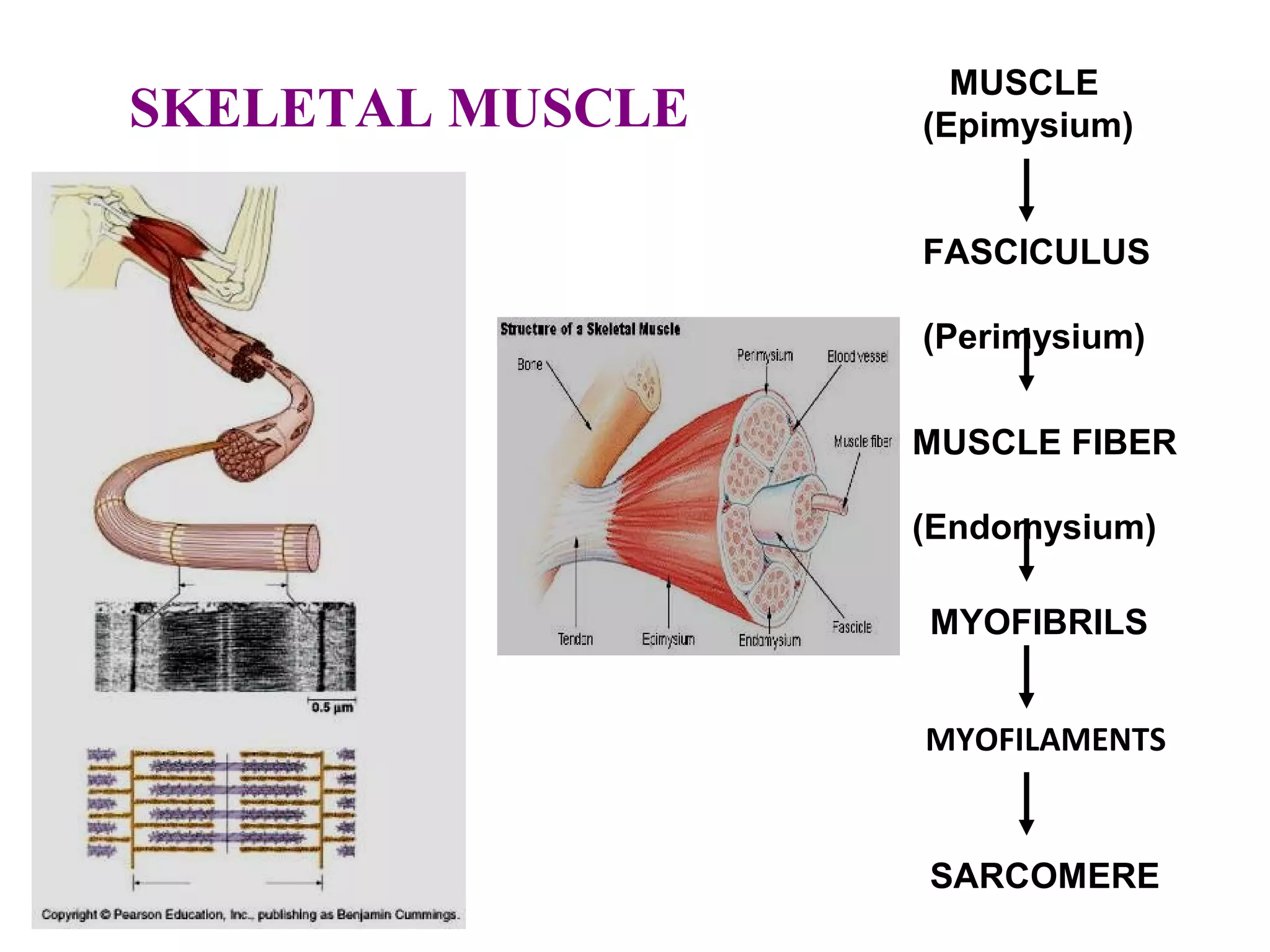
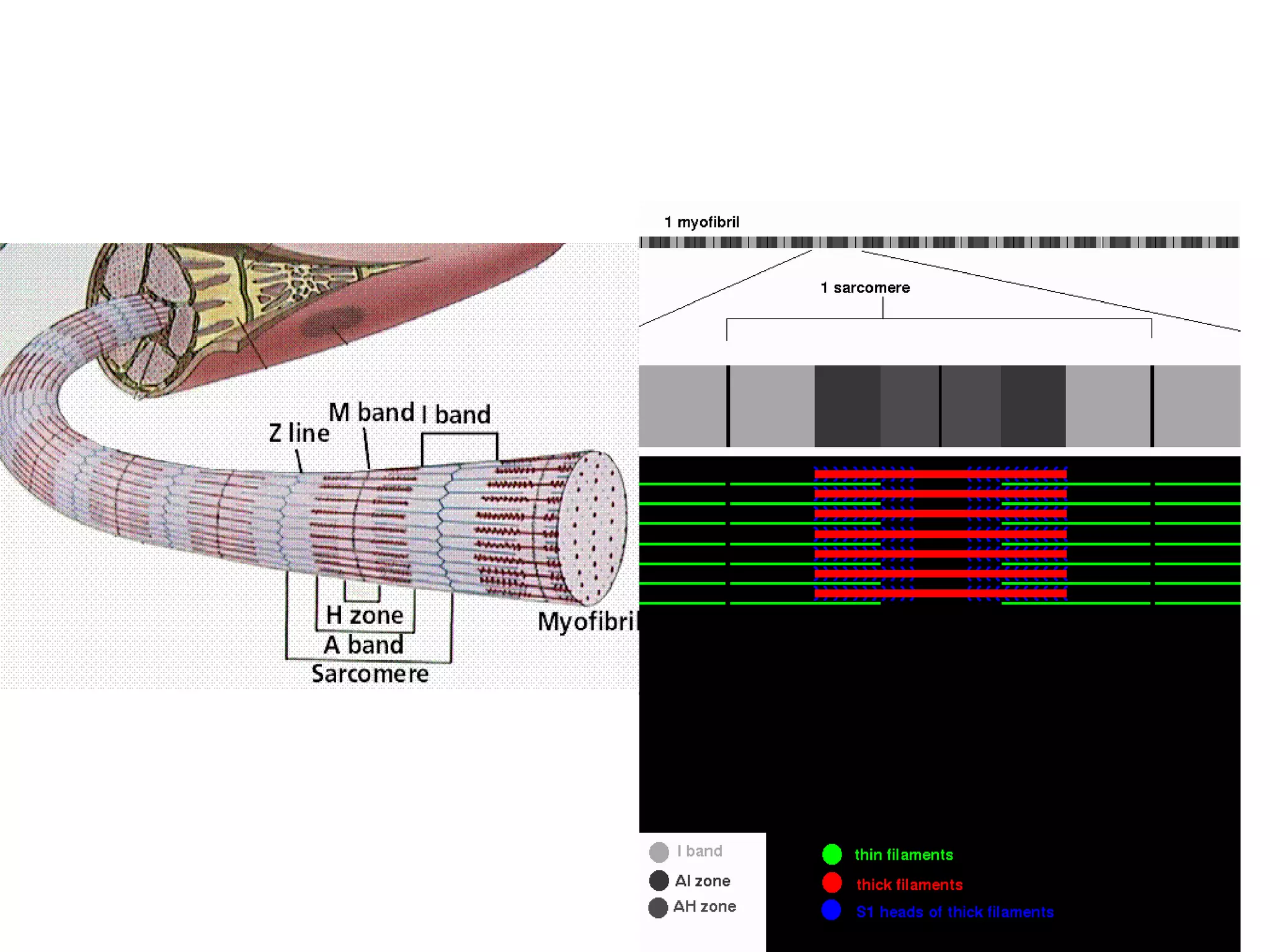
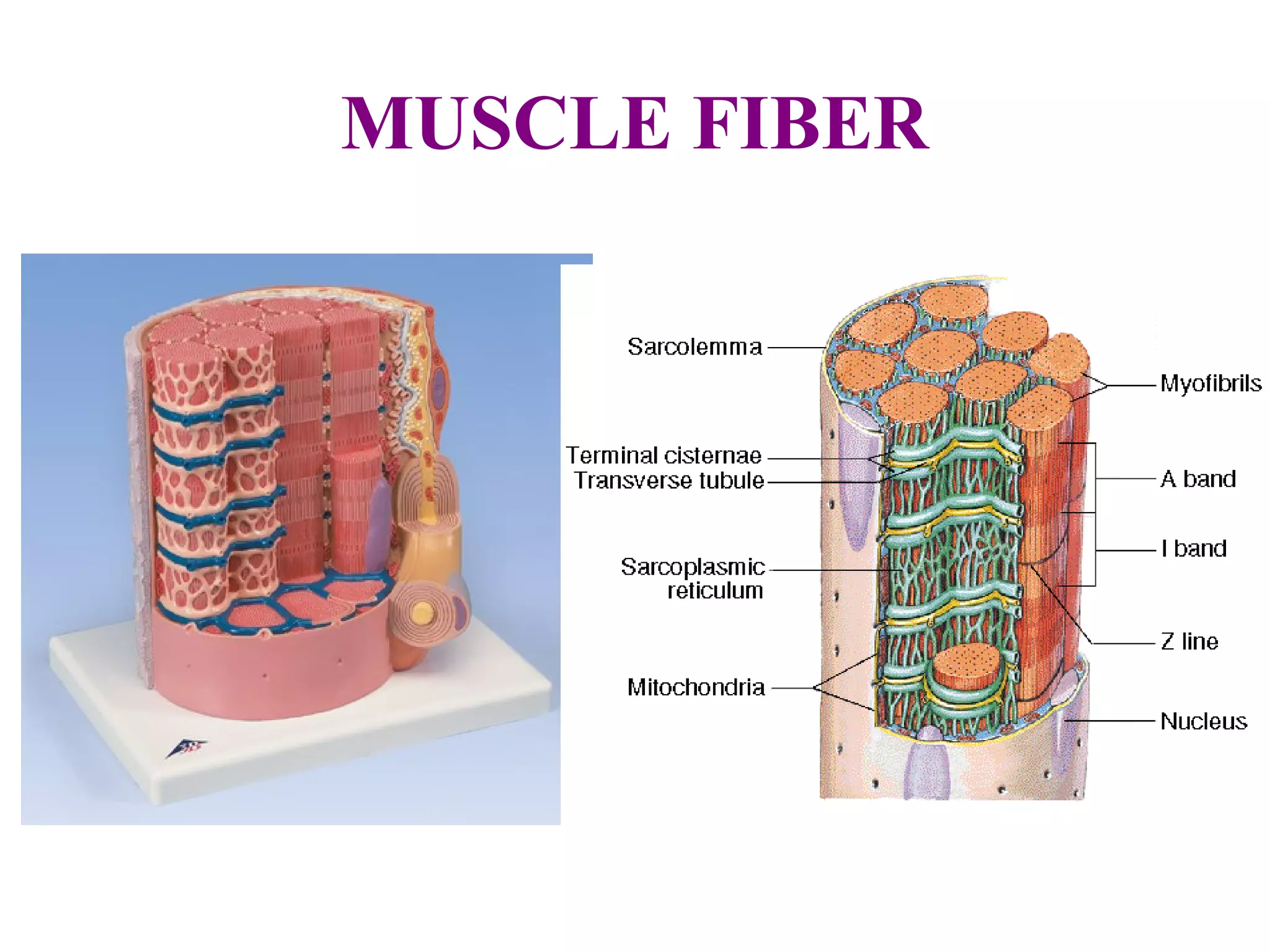
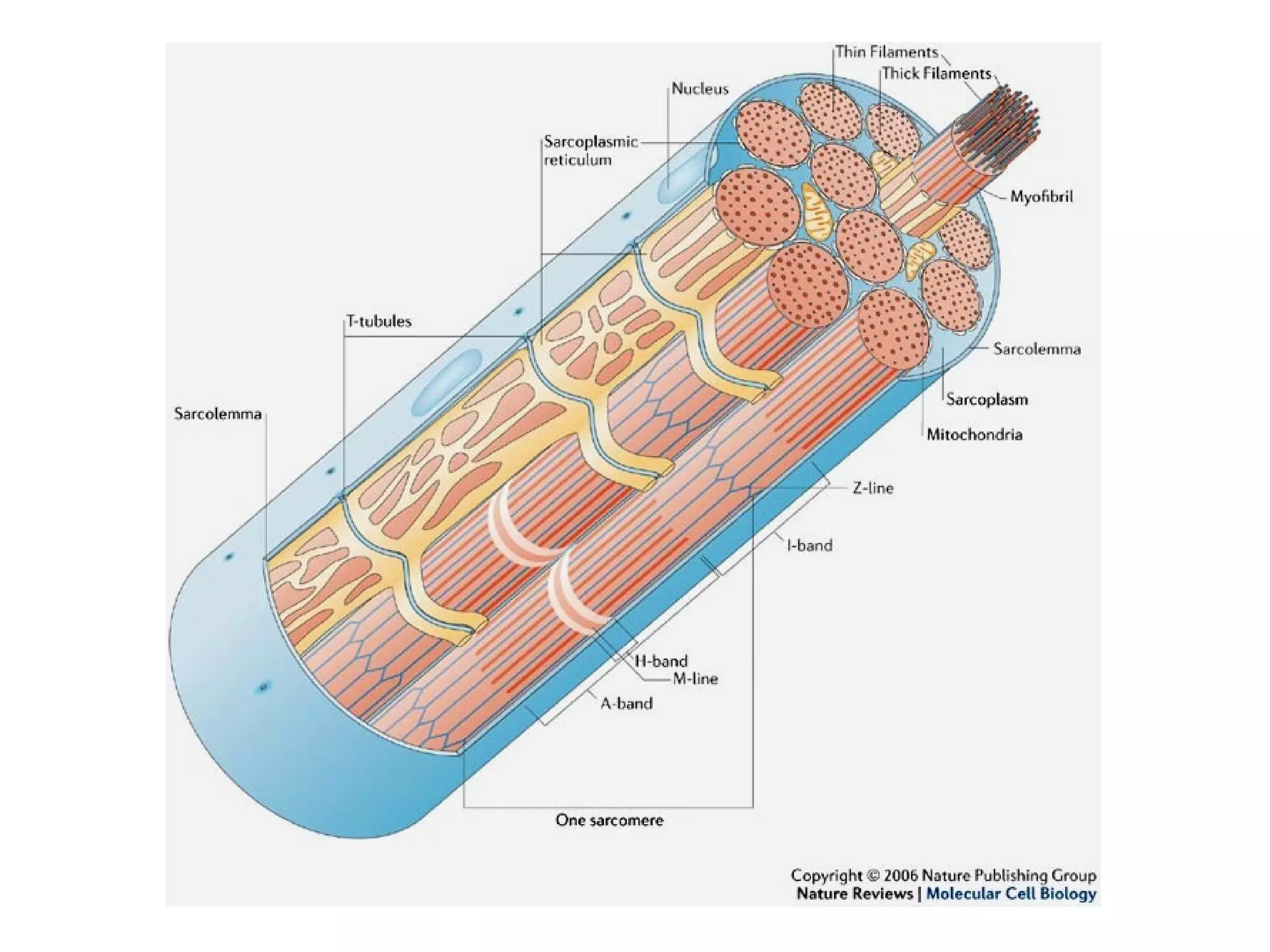
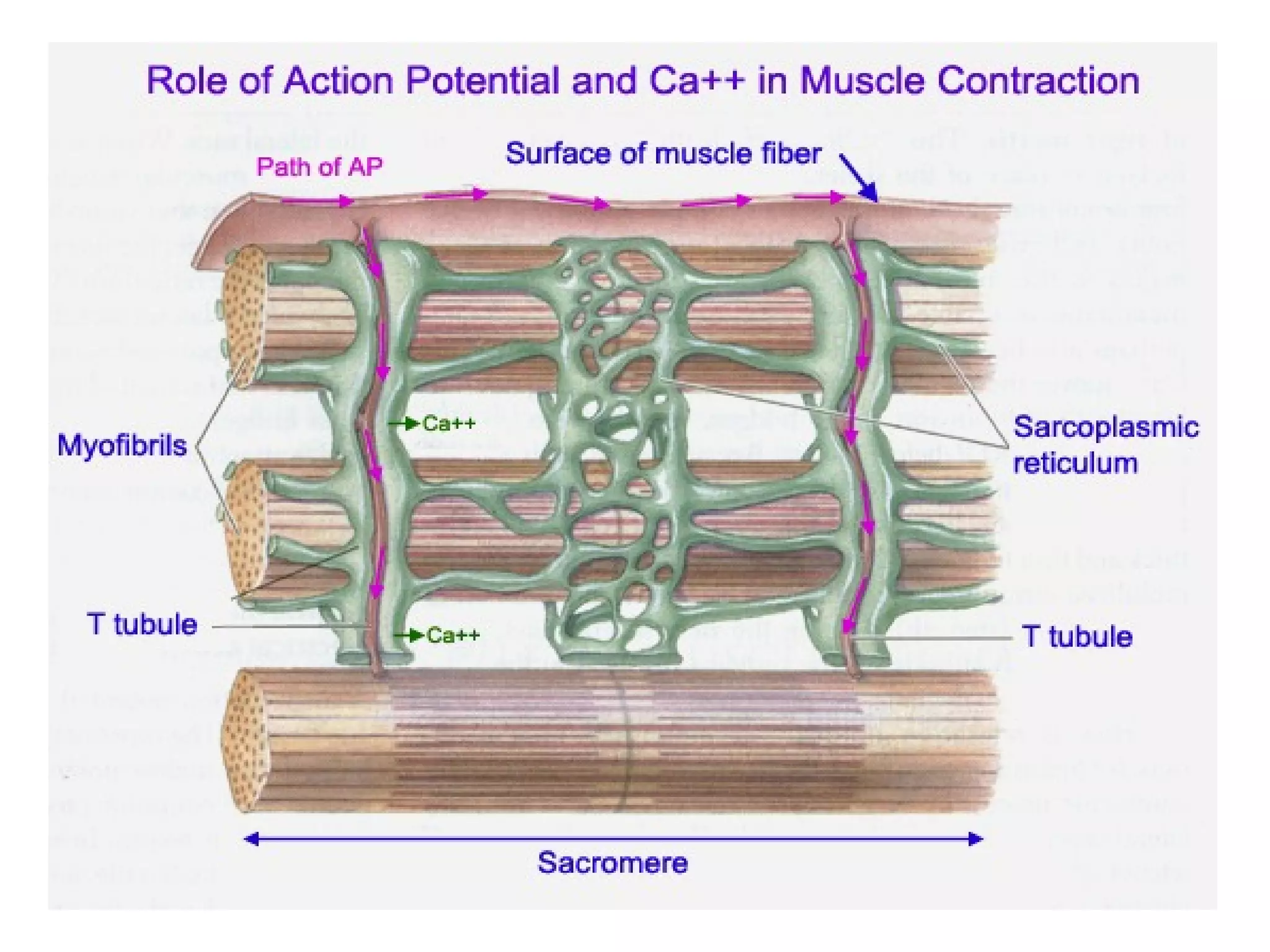
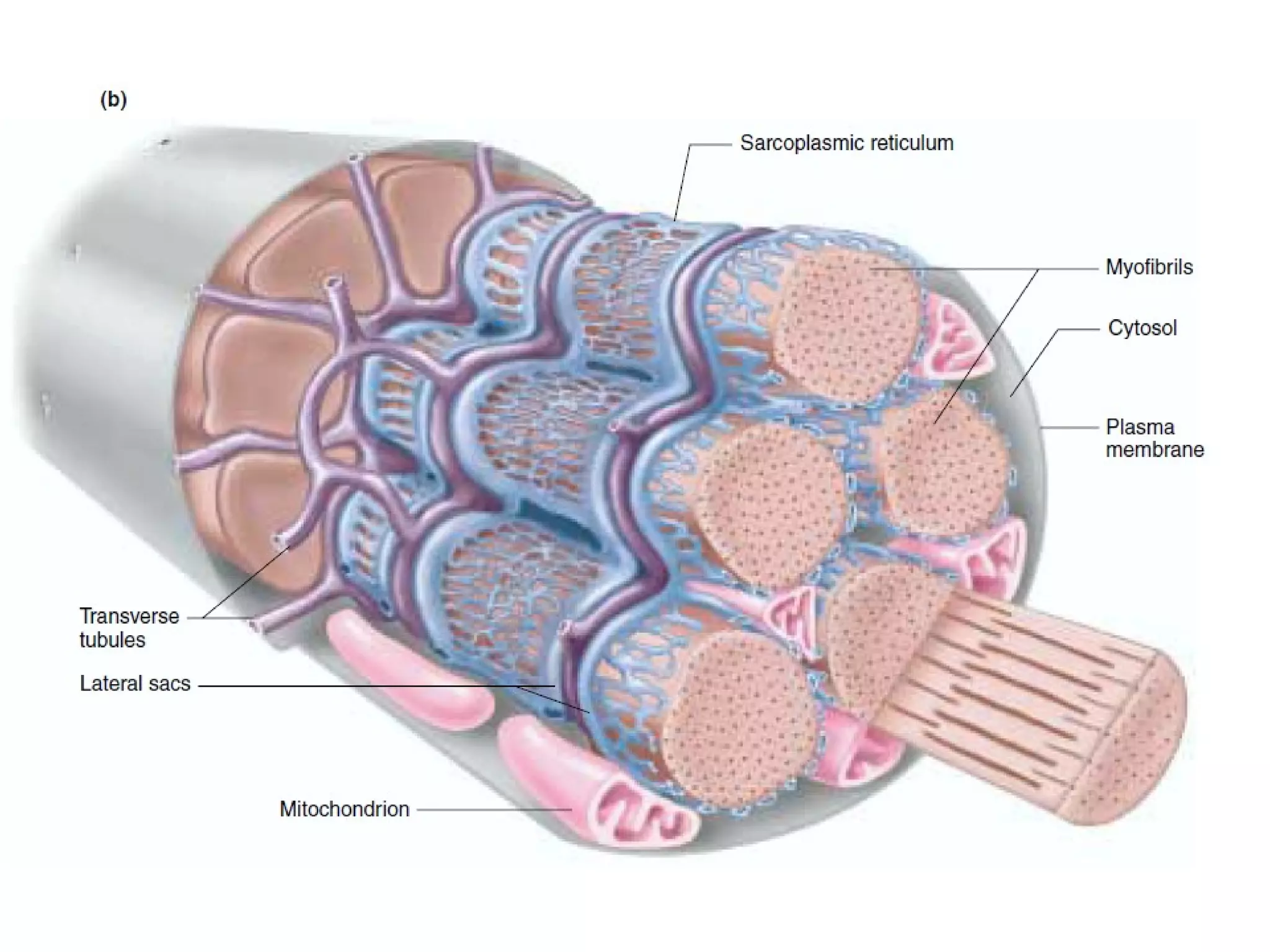
Muscle cells are excitable cells that can transmit action potentials and convert chemical energy into mechanical movement. There are three main types of muscle: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscle is striated, voluntary, and connects to bones. Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and has intercalated discs. Smooth muscle is non-striated and involuntary. Muscle contraction occurs via the sliding filament model, where myosin heads attach to actin and generate a power stroke, pulling the thin filaments toward the center. Contraction requires ATP hydrolysis to allow myosin to detach from actin and reattach further along. The length-tension relationship shows that muscle develops maximum tension at its optimal length.



























































































![Slow- and Fast-Twitch Fibers (continued)
• Slow-twitch (type I fibers):
– Red fibers.
– High oxidative capacity for aerobic respiration.
– Resistant to fatigue.
– Have rich capillary supply.
– Numerous mitochondria and aerobic enzymes.
– High [myoglobin].
• Soleus muscle in the leg.
www.freelivedoctor.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/skeletalmuscleraghu-170622122810/75/Skeletal-muscle-Physiology-101-2048.jpg)




























