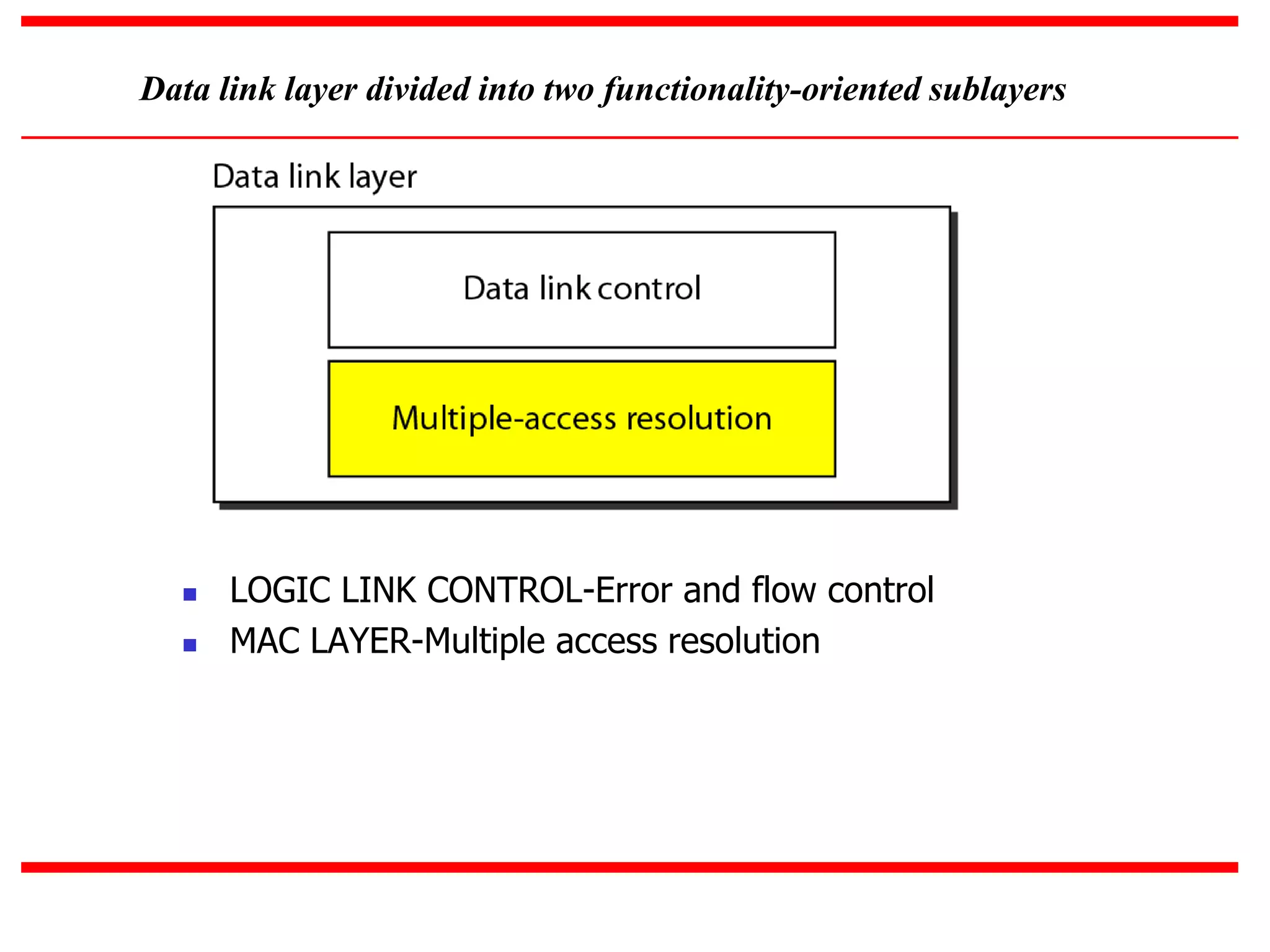
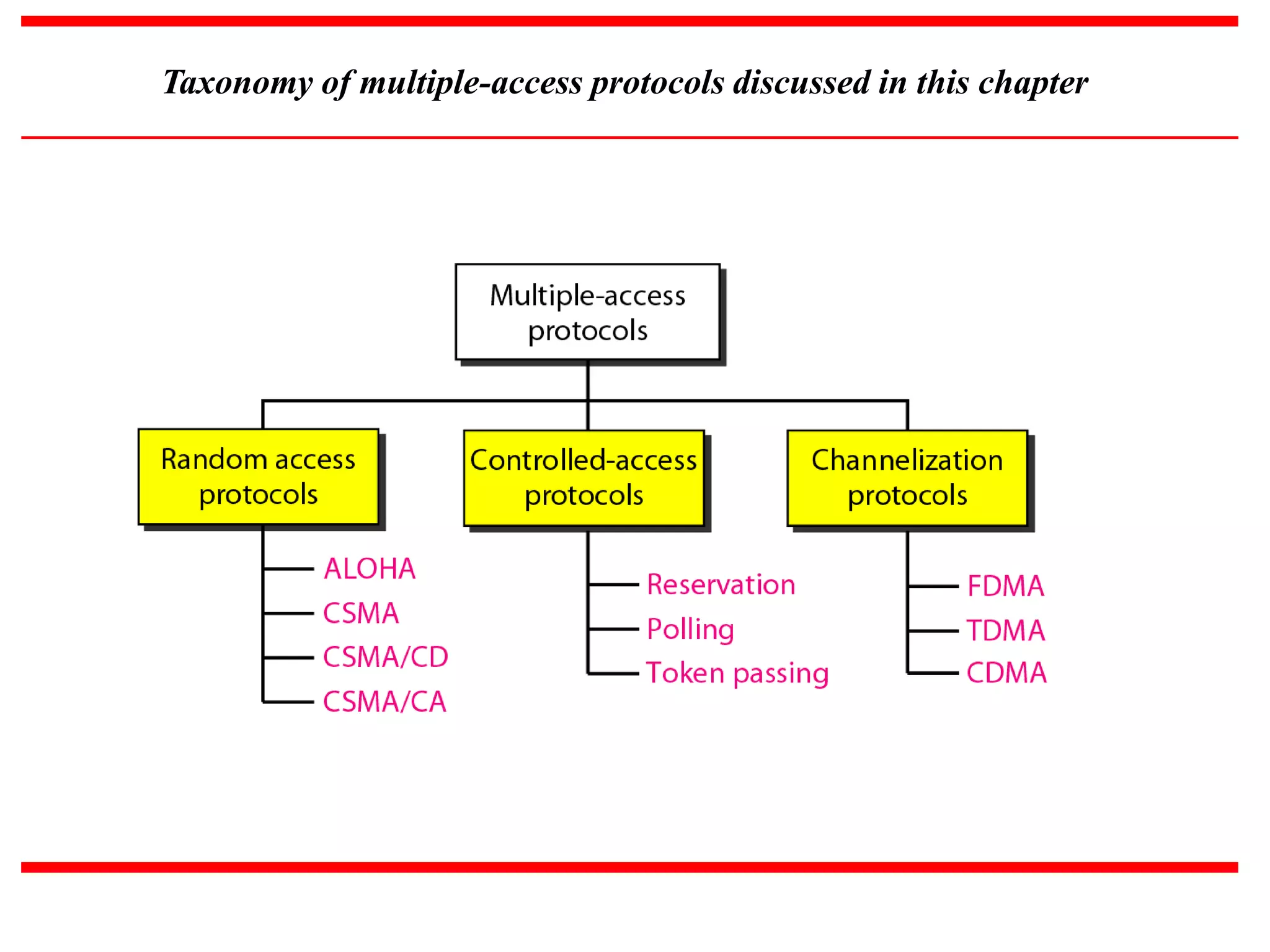
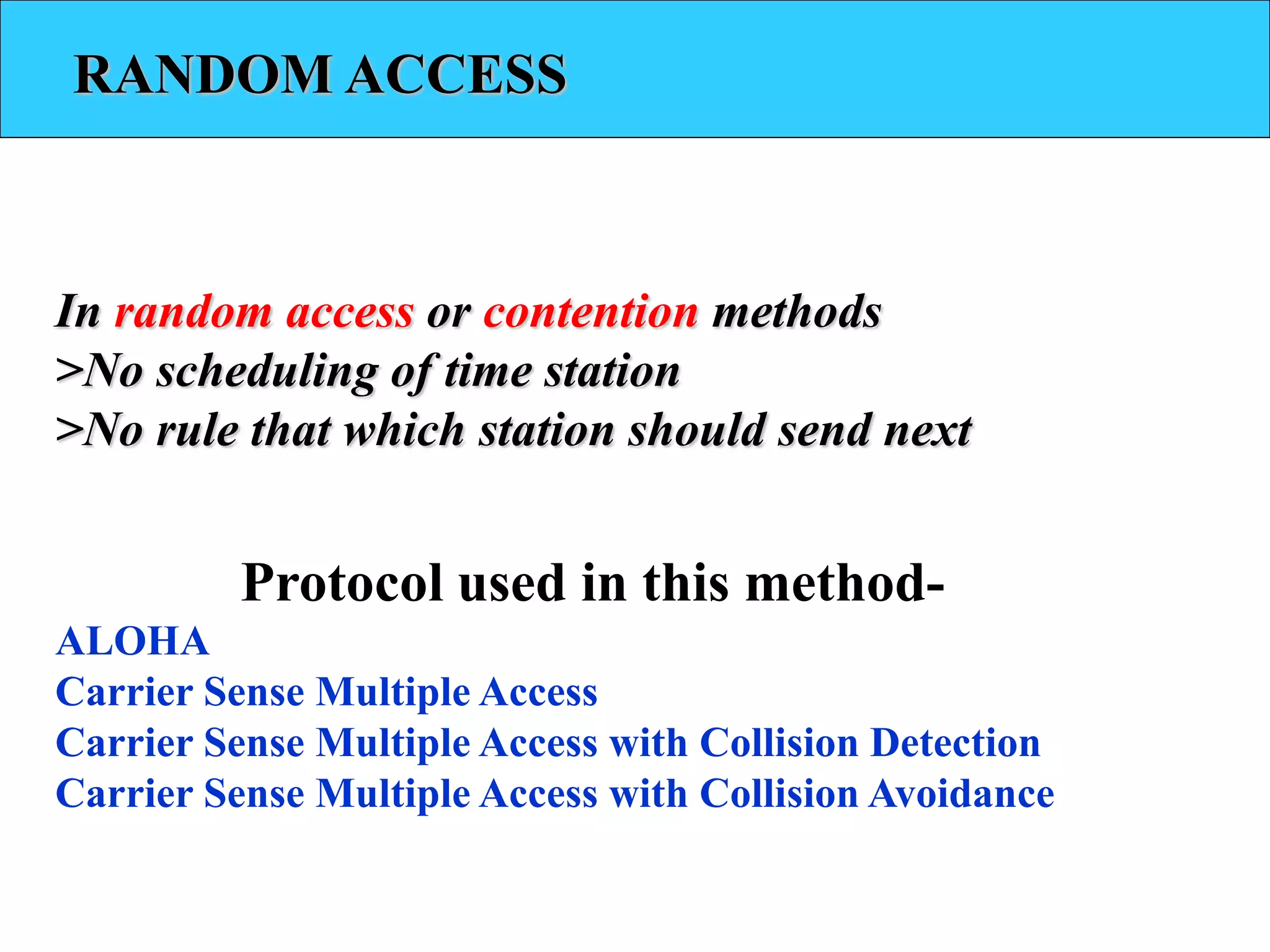
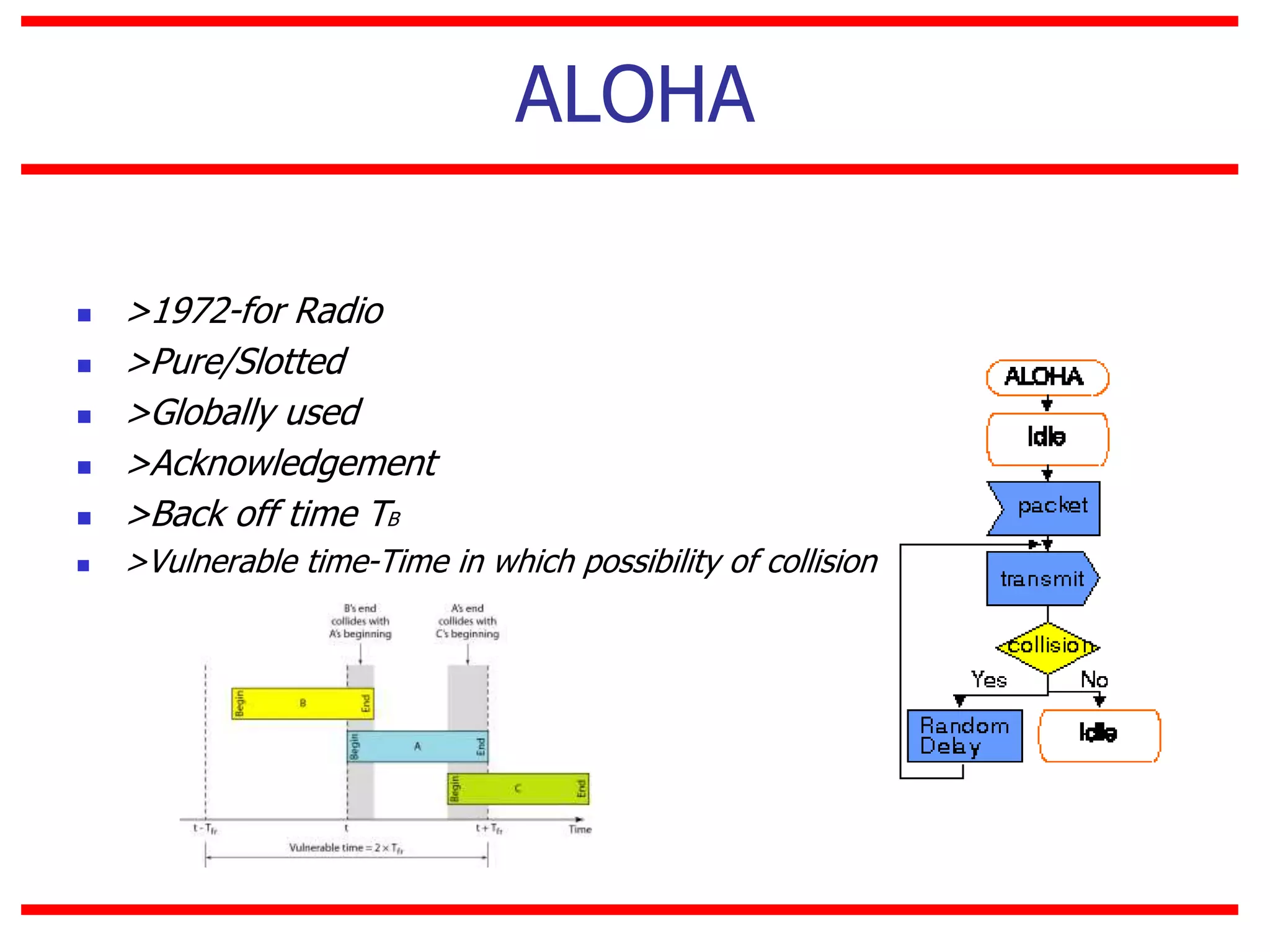
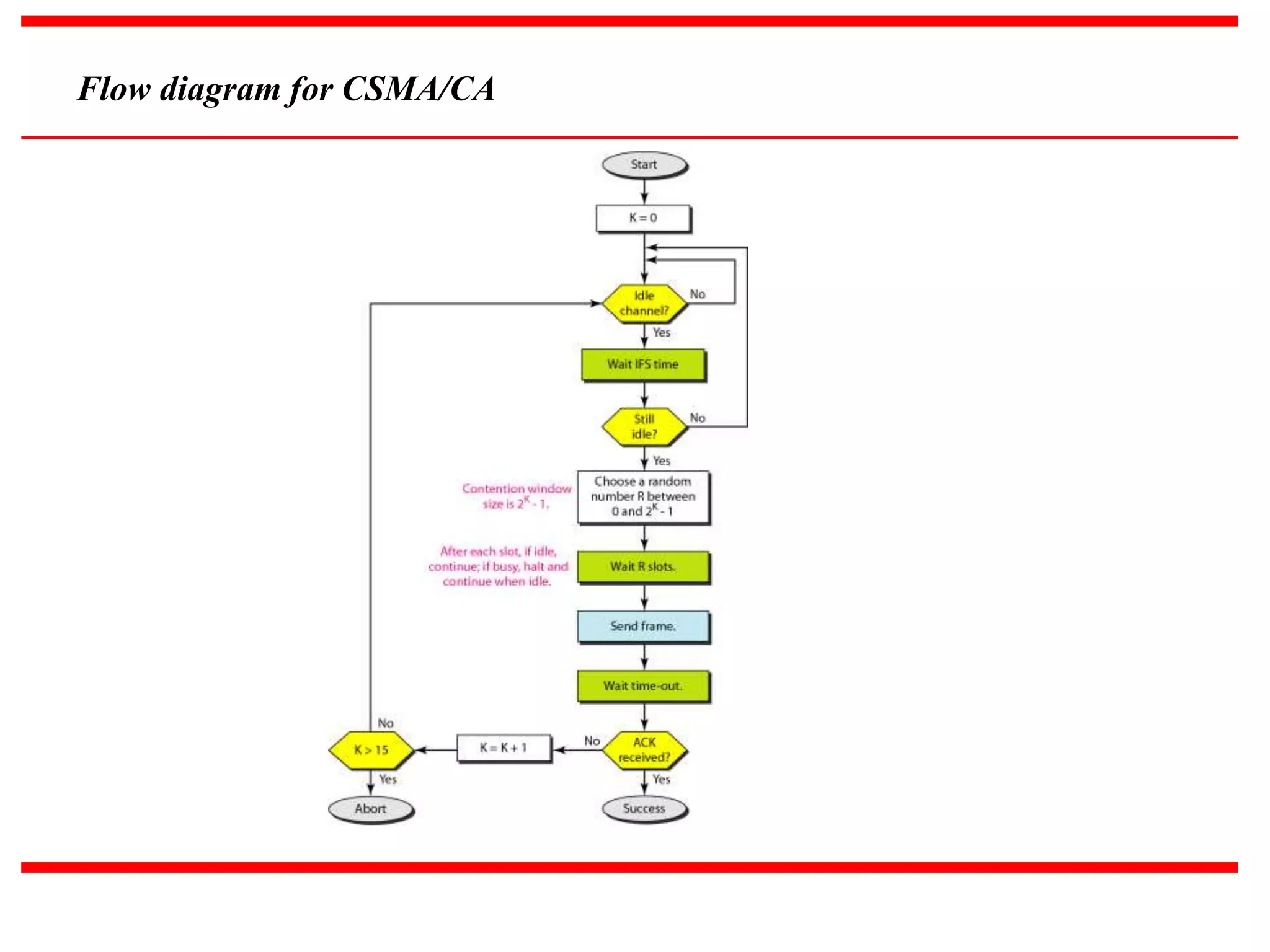
The document discusses different multiple access protocols at the data link layer. It describes random access protocols like ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CD, and CSMA/CA. It also covers controlled access methods using reservation, polling, and token passing. Finally, it mentions channelization techniques for multiple access like FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA that divide the channel bandwidth between stations using frequency, time, or code respectively.