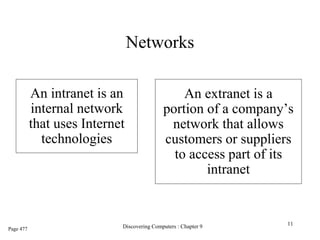
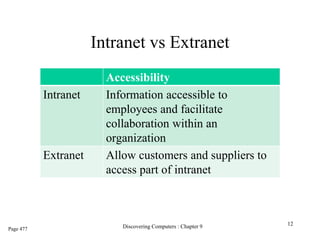
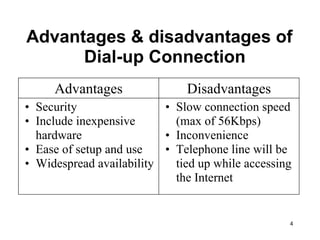
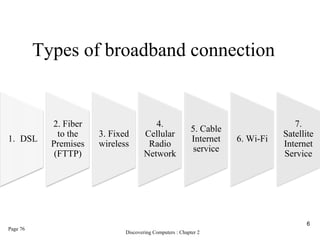
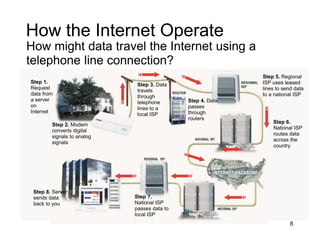
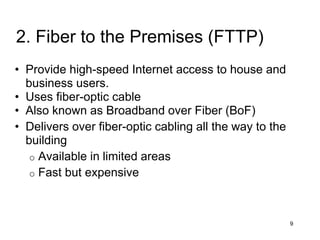
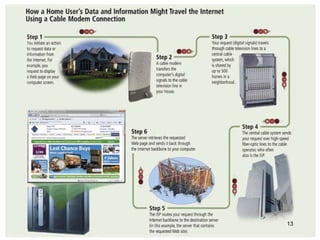
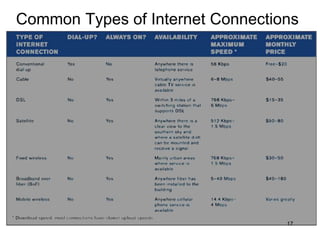
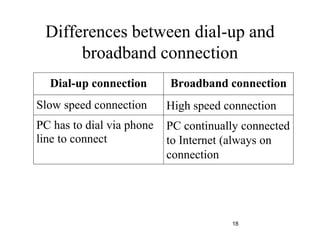
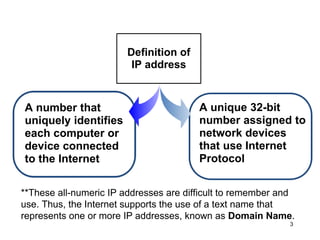
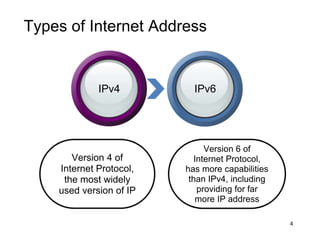
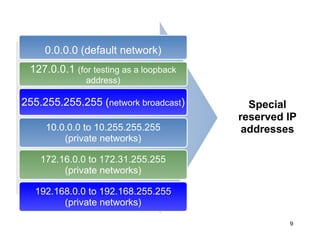
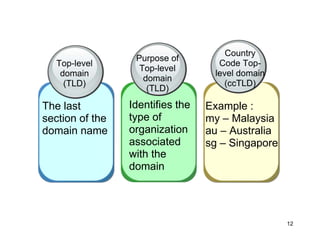
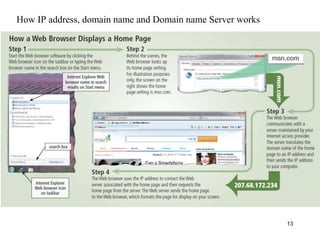
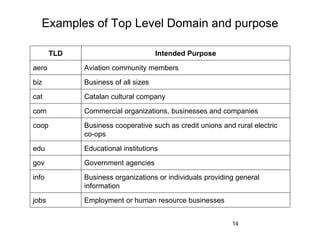
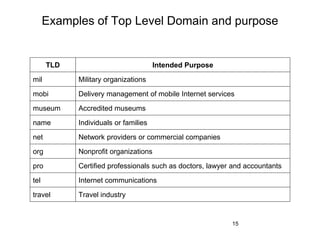
The document provides an overview of the Internet, including its definition, evolution, advantages, and disadvantages. It discusses different types of Internet connections such as dial-up, broadband, DSL, fiber, wireless, cable, Wi-Fi, and satellite. It also describes an Internet service provider's role in providing access to the Internet and lists some examples of ISPs in Malaysia. Finally, it defines Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and their relationship to domain names in allowing users to locate and identify computers on the network.