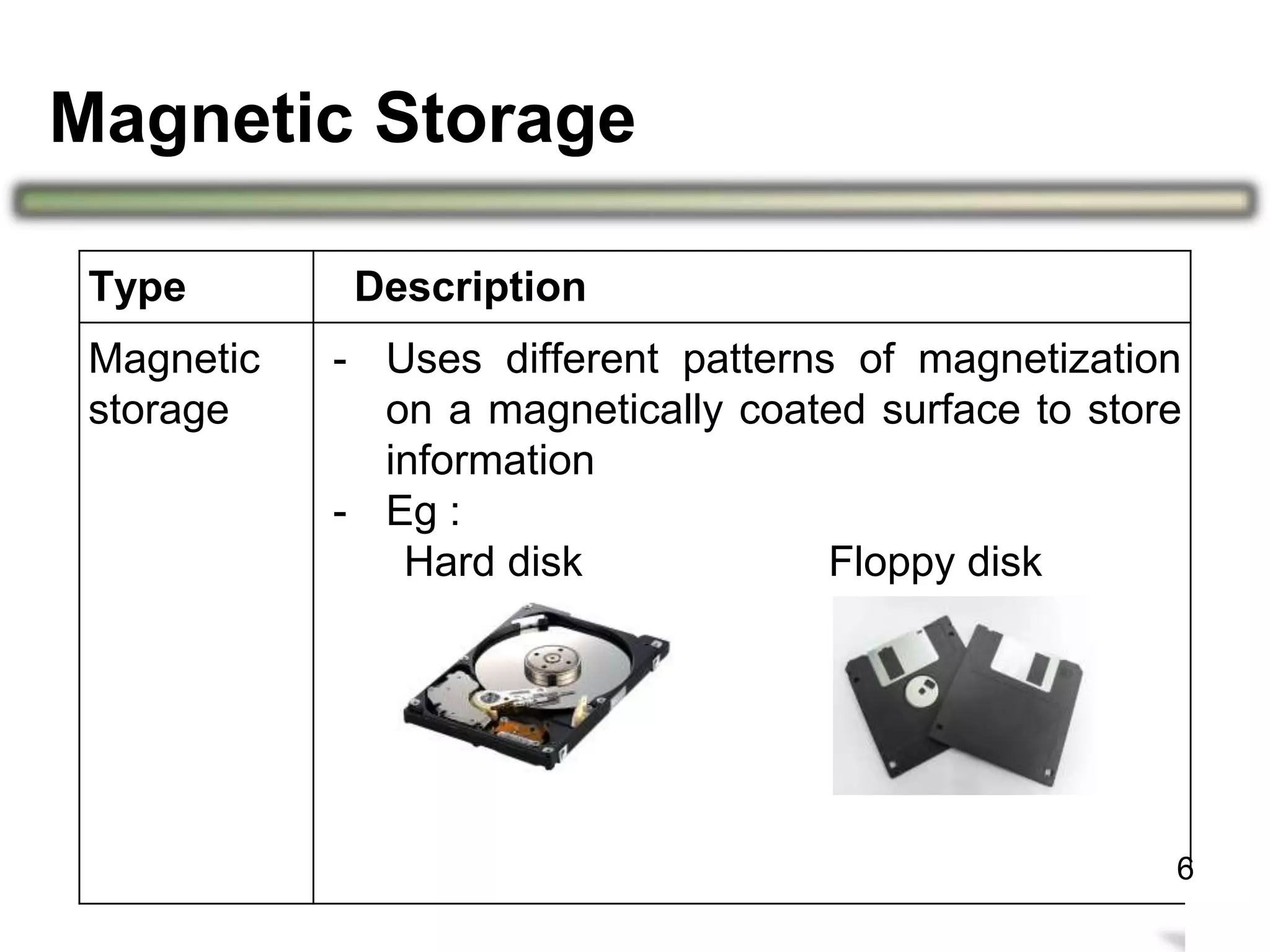
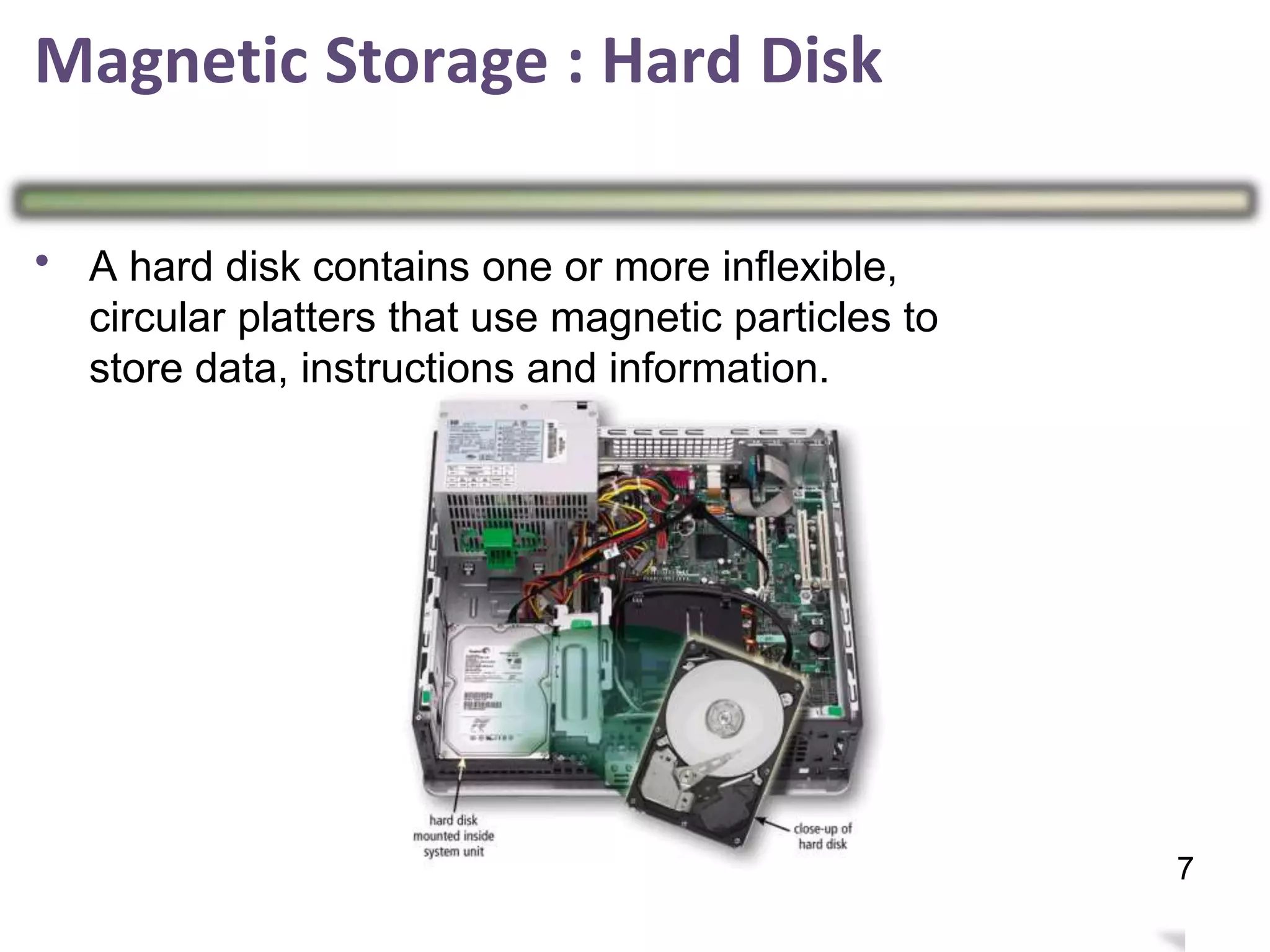
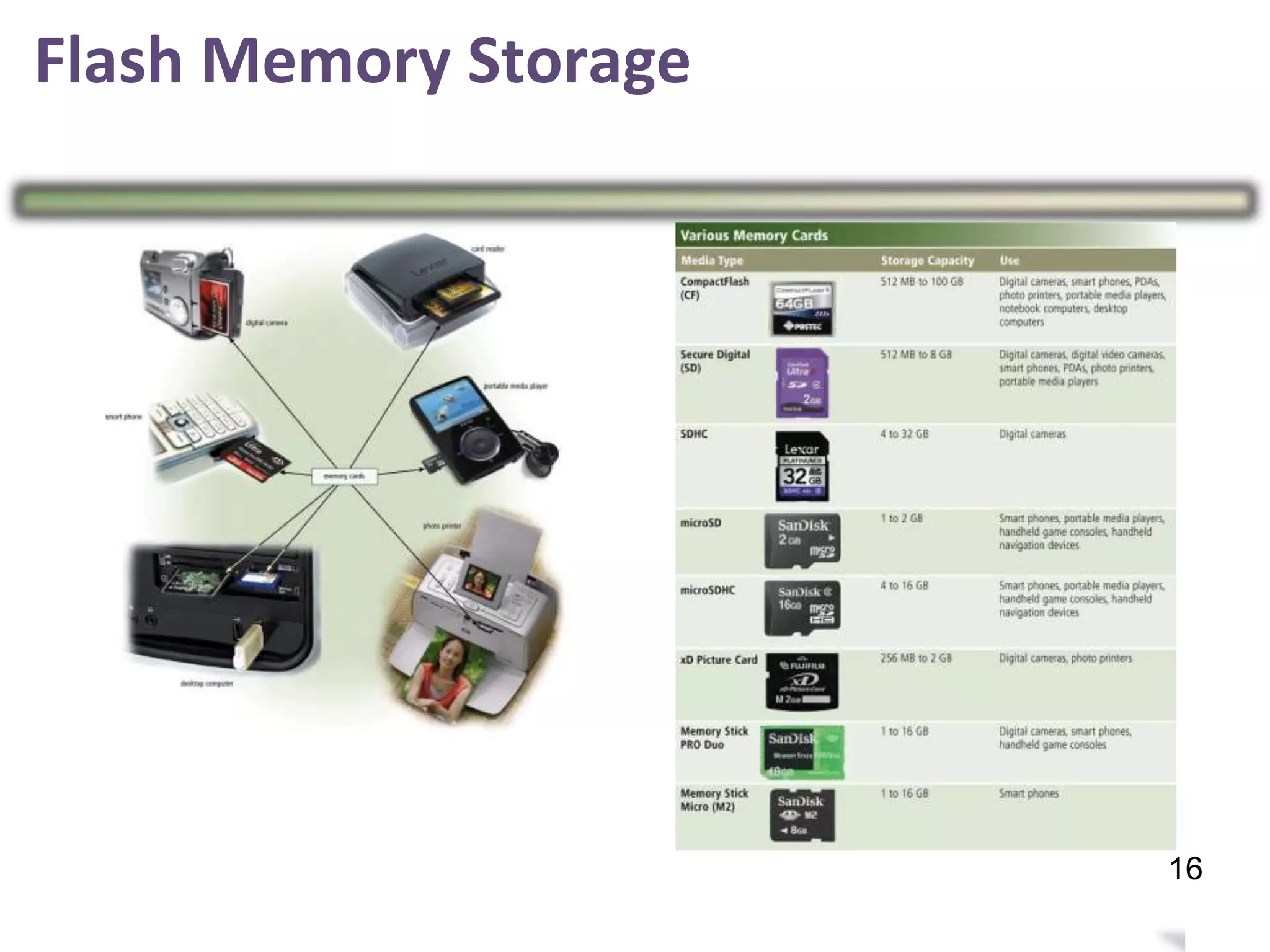
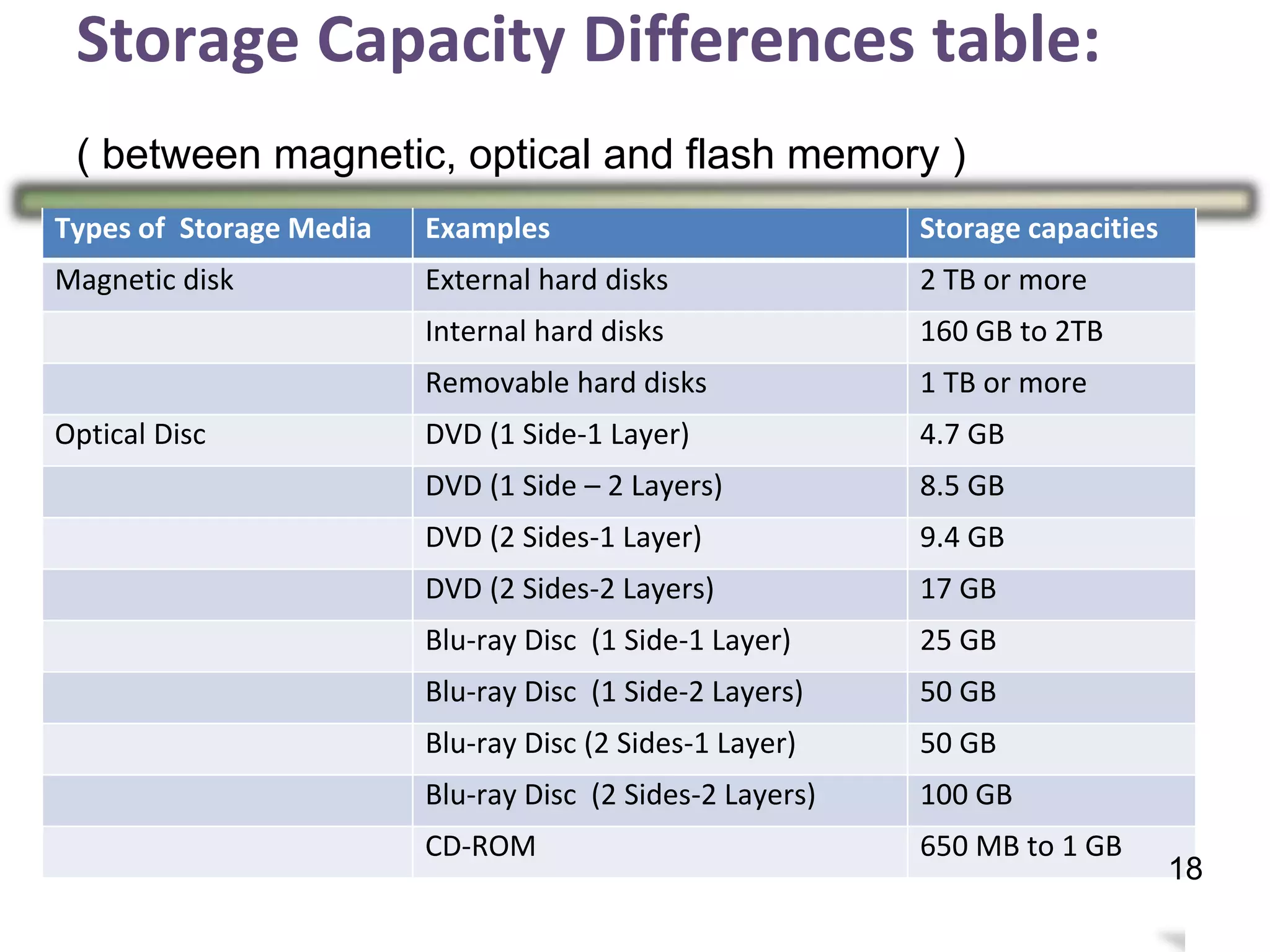
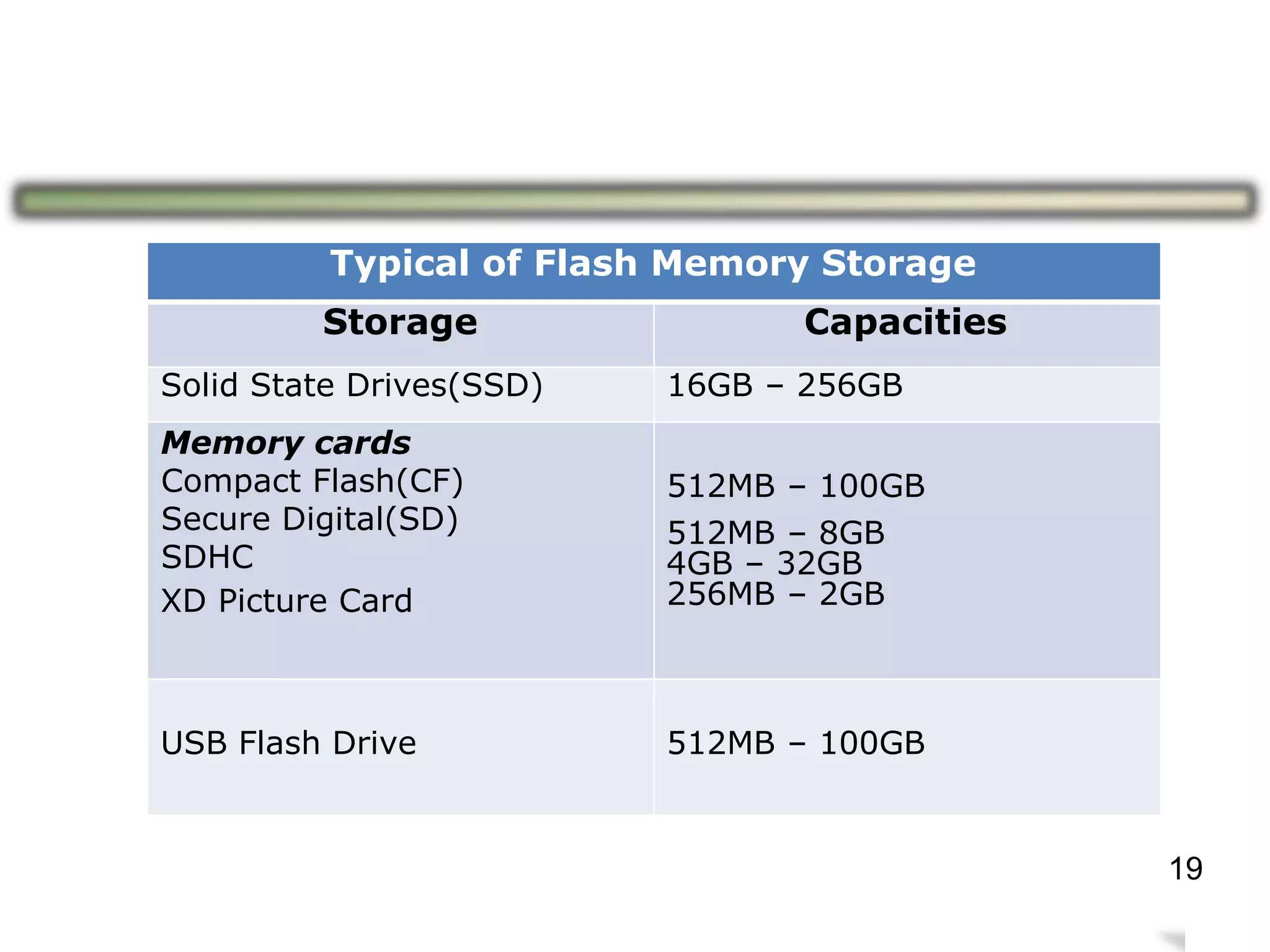
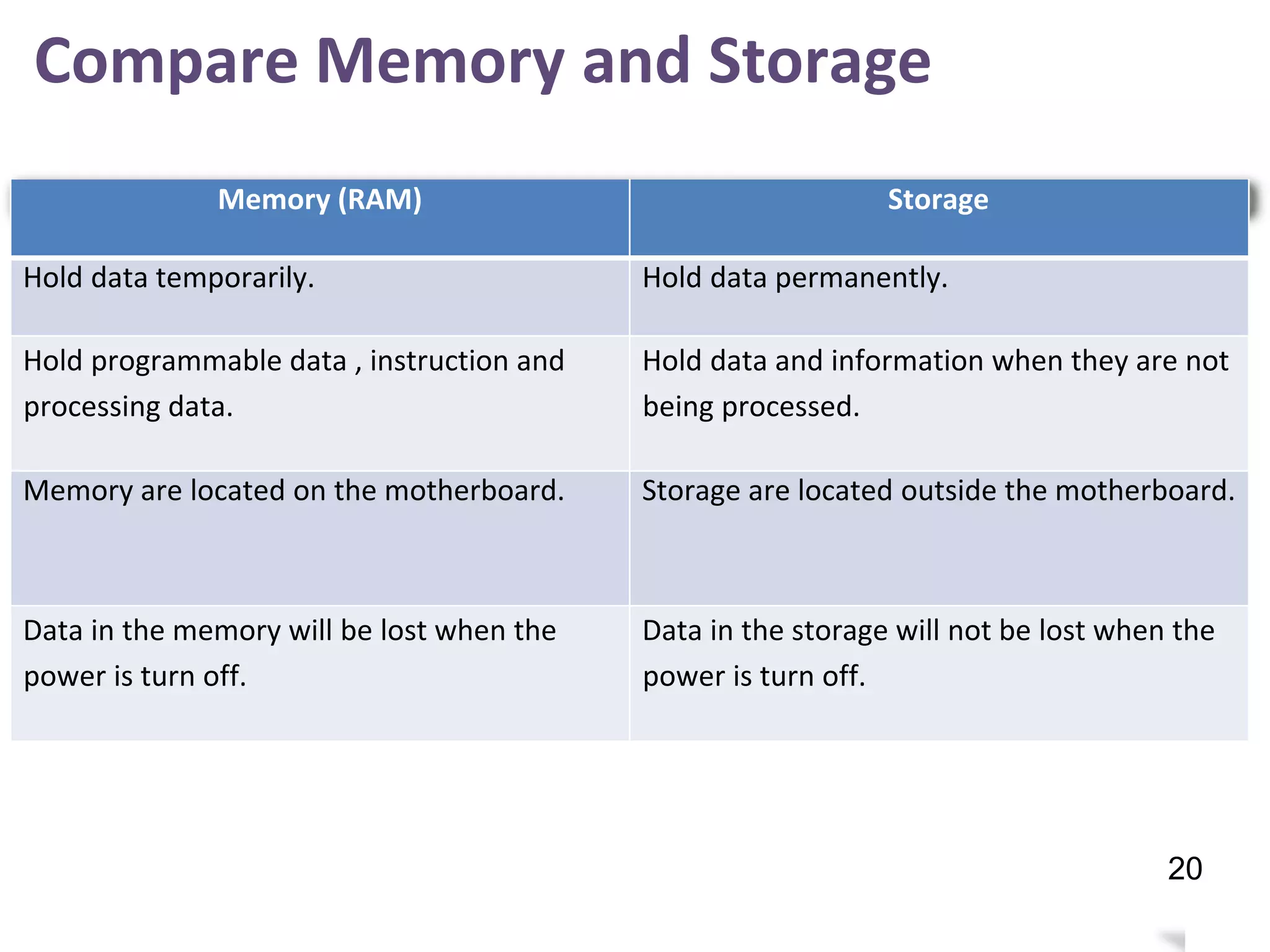
Storage holds data, instructions, and information for future use on physical storage media like hard disks, optical discs, flash memory. There are three main types of storage media: magnetic storage including hard disks and floppy disks, optical storage like CDs and DVDs, and flash memory storage like solid state drives, memory cards, and USB flash drives. Storage capacity differs between media, with hard disks holding terabytes, optical discs holding gigabytes, and flash memory ranging from megabytes to gigabytes depending on the device. Memory and storage differ in that memory holds data temporarily during processing while storage holds data permanently when not in use.