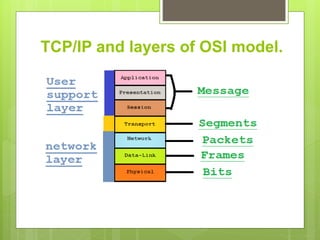
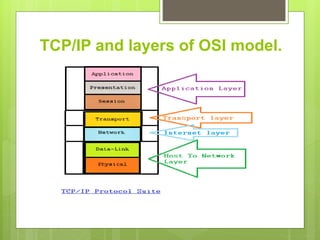
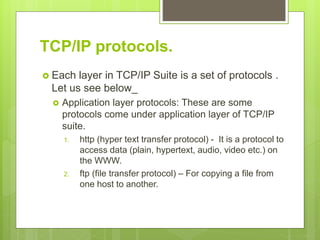
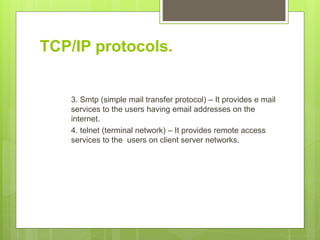
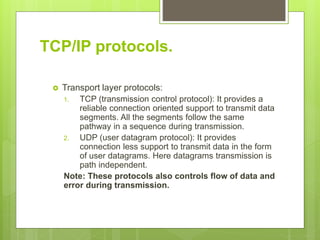
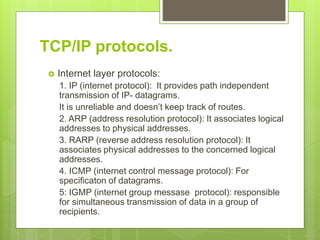
This document discusses the TCP/IP protocol suite and its layers. It begins by explaining that the OSI model was developed in 1970 as a networking standard, while TCP/IP was developed prior as a stack of protocols. It then notes that TCP/IP layers correspond to the OSI model layers. The document proceeds to describe some of the key protocols in each TCP/IP layer: application layer protocols include HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and Telnet; transport layer protocols are TCP and UDP; and internet layer protocols comprise IP, ARP, RARP, ICMP, and IGMP. Finally, it states that the host to network layers do not specify any special protocols.