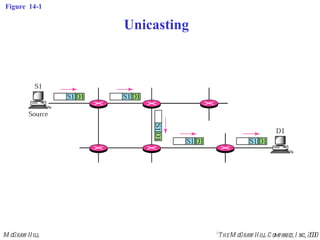
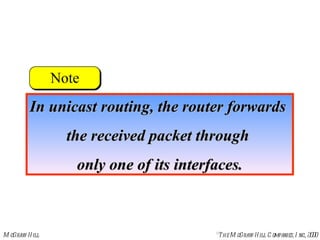
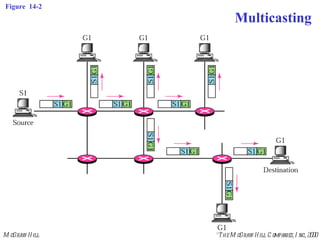
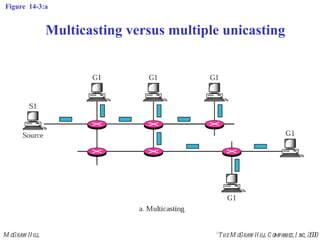
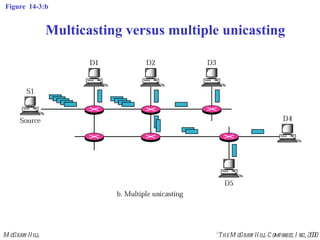
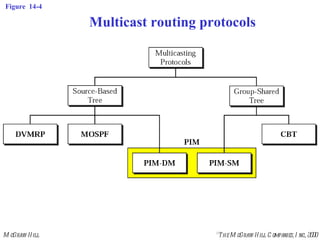
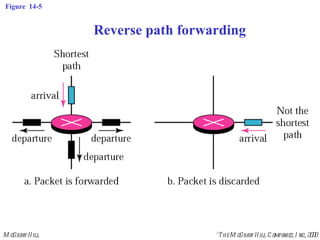
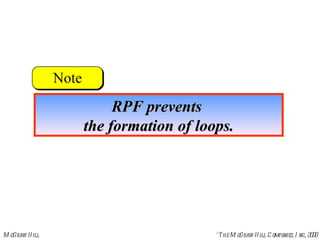
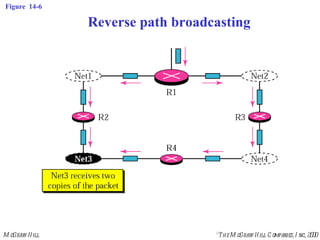
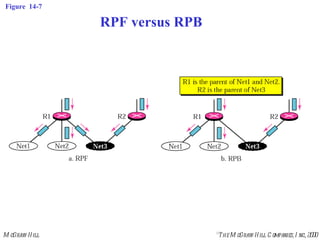
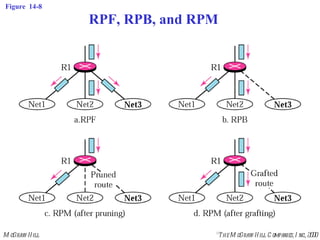
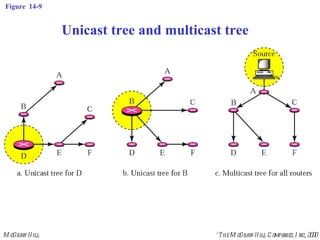
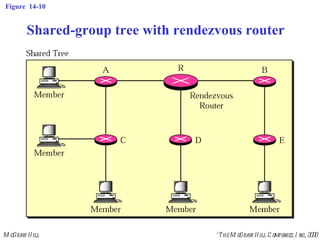
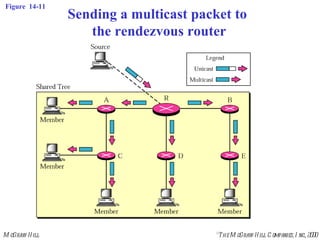
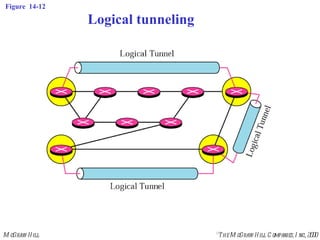
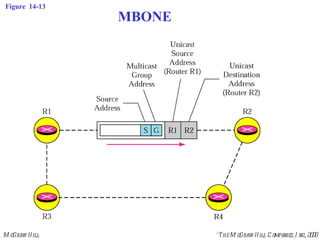
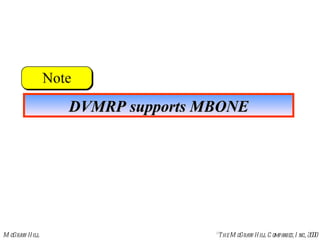
This document discusses multicast routing protocols. It introduces concepts like multicast trees, reverse path forwarding, and describes several multicast routing protocols including DVMRP, MOSPF, CBT, PIM, and MBONE. DVMRP uses reverse path forwarding and pruning/grafting to efficiently route multicast traffic to multiple receivers. PIM comes in two variants - PIM-DM for dense networks and PIM-SM for sparser wide area networks. MBONE enables multicast routing over the Internet using logical tunneling between multicast routers.