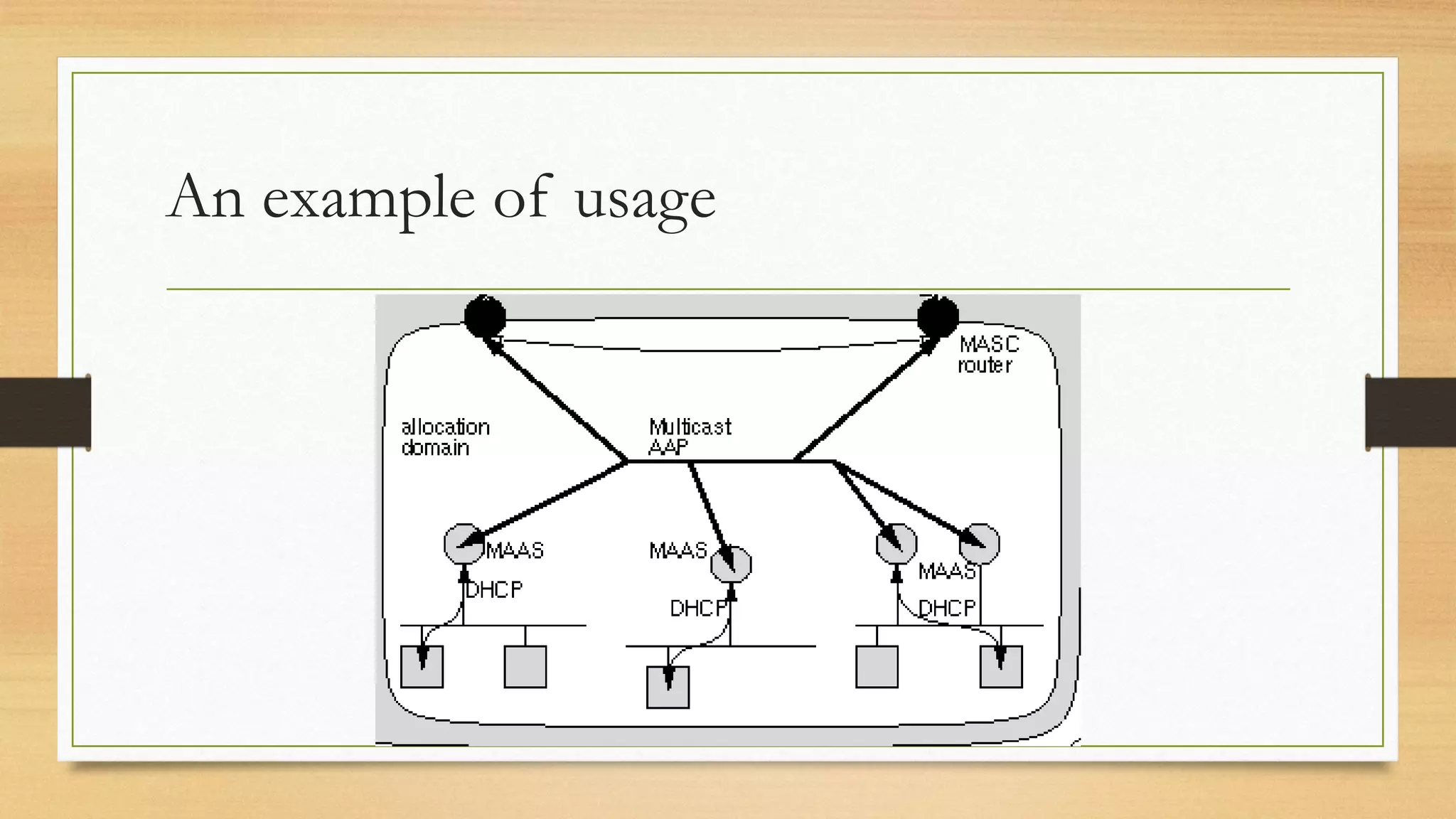
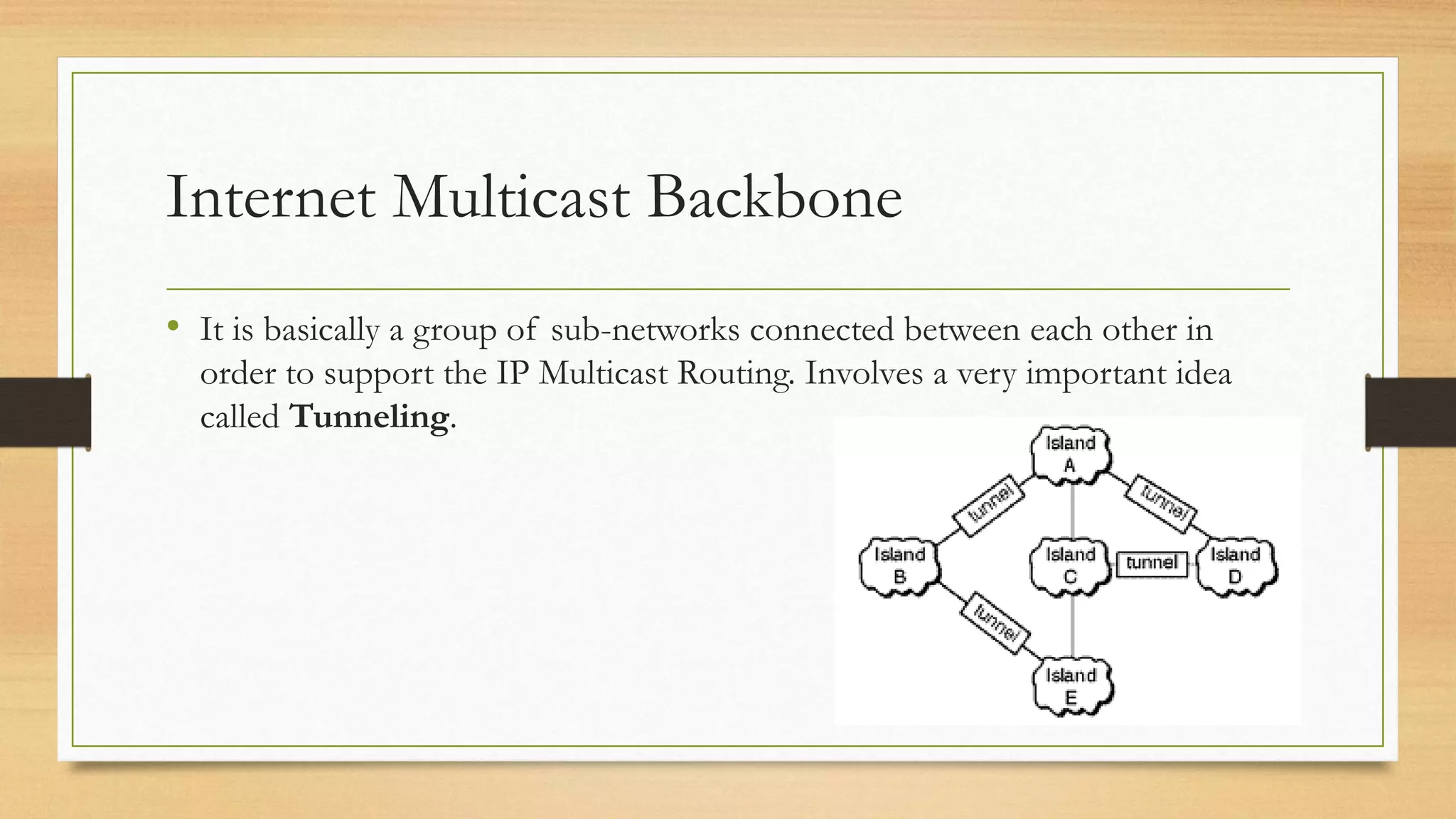
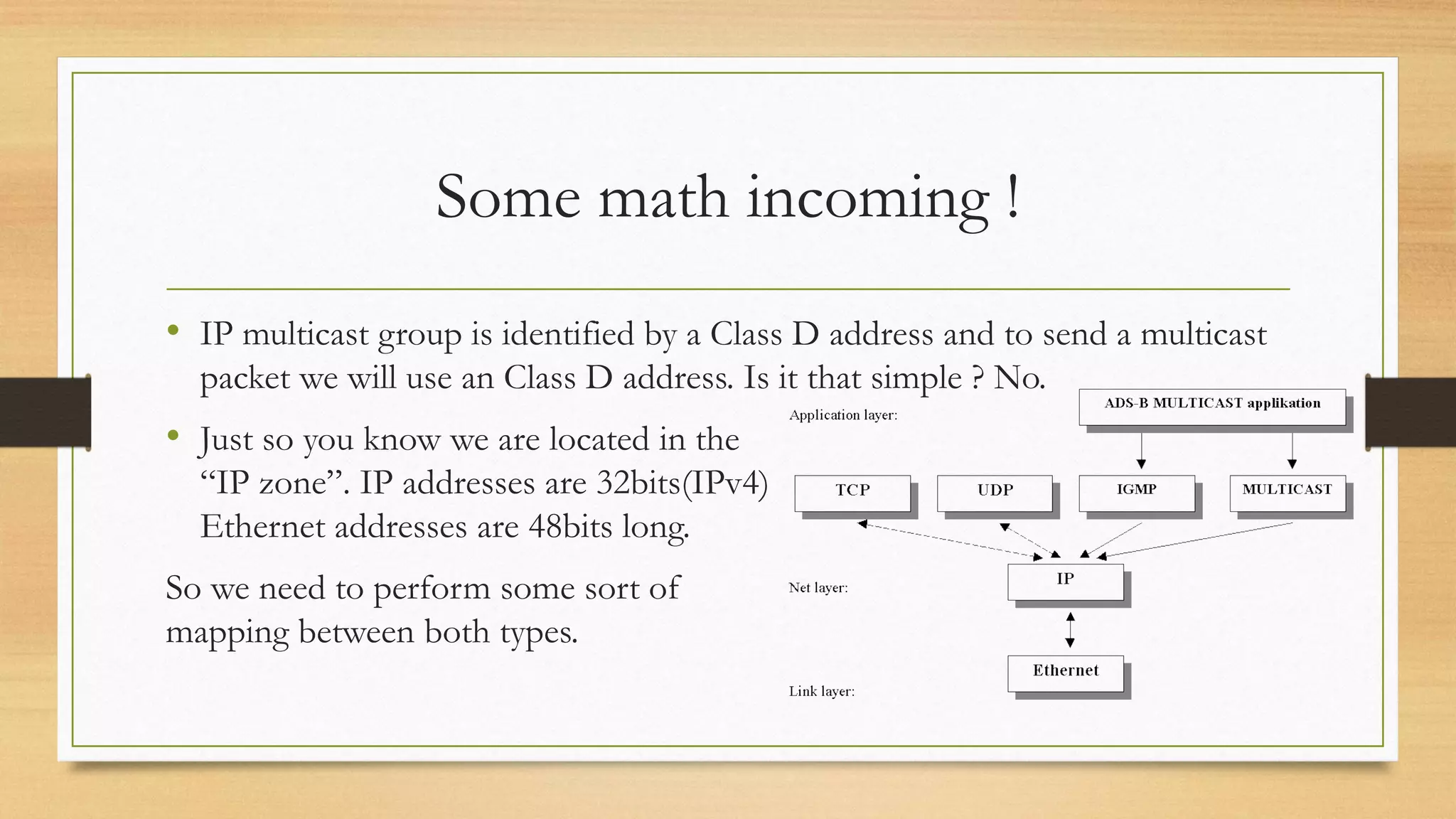
The document provides an overview of IP multicast routing, discussing key concepts such as multicast addressing, protocols (DVMRP, MOSPF, PIM), and algorithms used in multicast. It highlights the efficiency of multicast over unicast and broadcast, explaining how multicast reduces network overload by allowing messages to be sent only to interested hosts. The document also elaborates on group membership protocols, such as IGMP, and their importance in managing group communication in multicast routing.