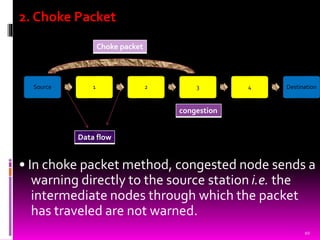
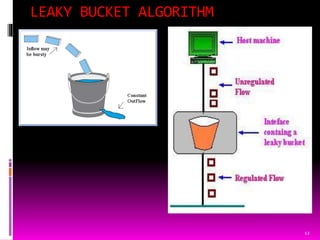
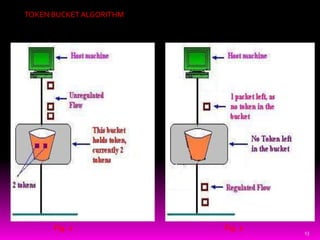
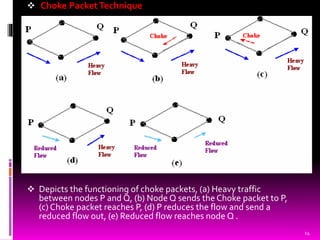
This document presents an overview of computer network congestion and congestion control techniques. It defines congestion as occurring when too many packets are present in a network link, causing queues to overflow and packets to drop. It then discusses factors that can cause congestion as well as the costs. It outlines open-loop and closed-loop congestion control approaches. Specific algorithms covered include leaky bucket, token bucket, choke packets, hop-by-hop choke packets, and load shedding. The document concludes by noting the importance of efficient congestion control techniques with room for improvement.








![Reference
Computer control overview written by S. Chen
“What is Congestion Control Describe the
Congestion Control Algorithm commonly used.”
written by DineshThakur.
Computer Network:A system aproach,5E by Larry
L. Peterson & Bruce S. Davie
[Ramakrishnan 1990] K. K. Ramakrishnan and Raj
Jain, "A Binary Feedback Scheme for Congestion
Avoidance in Computer Networks", ACM
Transactions on Computer Systems,Vol.8, No.2, pp.
158-181, May 1990.
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/congestion-140527034130-phpapp02/85/Congestion-on-computer-network-18-320.jpg)