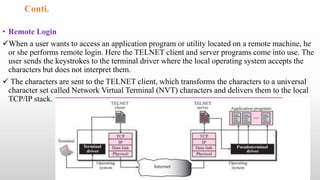
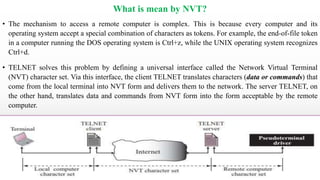
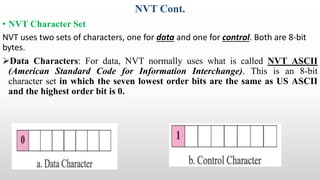
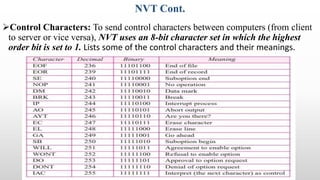
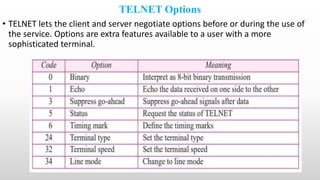
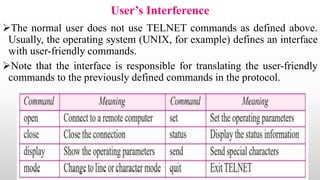
Telnet is a networking protocol used for remote computer access, functioning primarily over TCP/IP networks on port 23, and it sends all messages in clear text, leading to its replacement by more secure protocols like SSH. The document outlines various aspects of Telnet, including its working mechanism, the use of Network Virtual Terminal (NVT) character sets, options negotiation, modes of operation, and security concerns associated with its usage. Despite its historical significance, Telnet's lack of security features raises issues for modern applications.