Embed presentation
Download to read offline



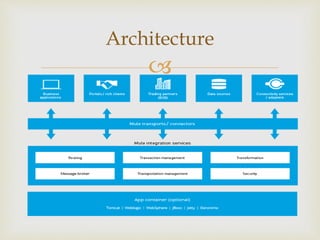


Mule is a lightweight Java-based enterprise service bus (ESB) and integration platform that allows developers to quickly and easily connect applications to exchange data. It enables integration of existing systems regardless of technology by supporting standards like JMS, Web Services, JDBC, and HTTP. Mule provides capabilities for service creation and hosting, service mediation to shield services from different message formats and protocols, and message routing, filtering, aggregation and resequencing based on content and rules. It also allows for data transformation across varying data formats and transport protocols.




