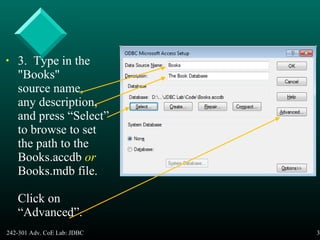
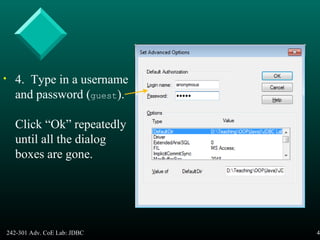
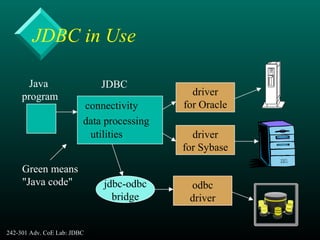
This document provides an introduction and overview of Java Database Connectivity (JDBC). It discusses what JDBC is, the different types of JDBC drivers, how to connect to databases using JDBC, and how to execute SQL statements and process result sets. It also covers how to access database metadata and provides examples of using JDBC to connect to and query a Microsoft Access database.












![242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC 19
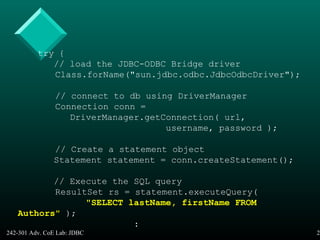
5. SimpleJDBC.java
// SimpleJDBC.java
// Displays the firstnames and lastnames
// of the Authors table in the Books db.
import java.sql.*;
public class SimpleJDBC {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// The URL for the Books database.
// ’Protected' by a login and password.
String url = "jdbc:odbc:Books";
String username = "anonymous";
String password = "guest";
:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdbc-150827044419-lva1-app6891/85/Jdbc-drivers-19-320.jpg)