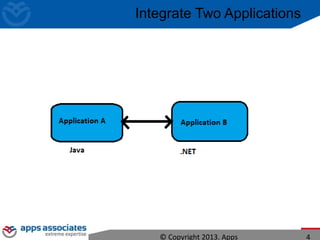
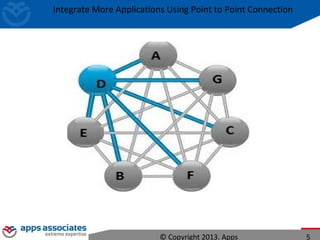
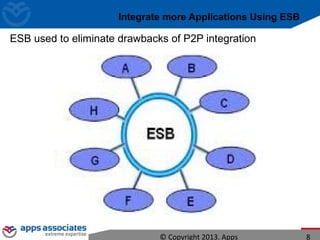
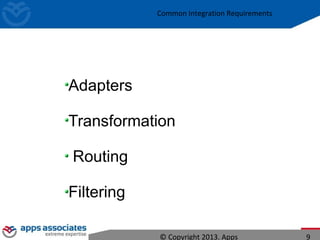
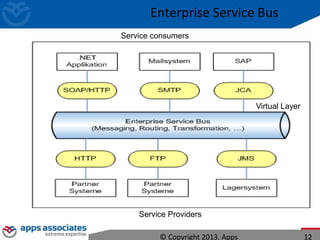
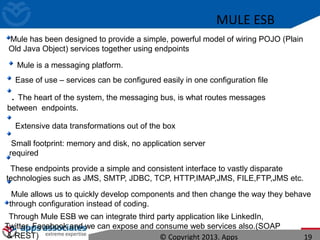
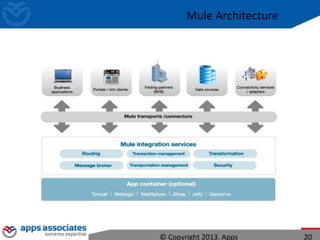
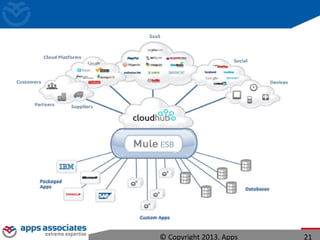
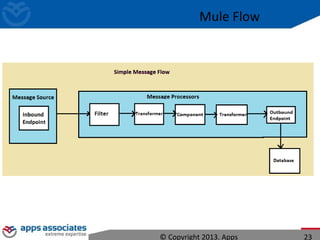
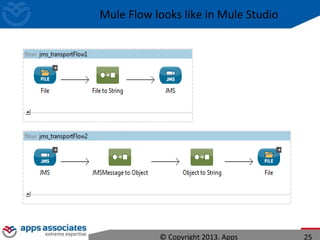
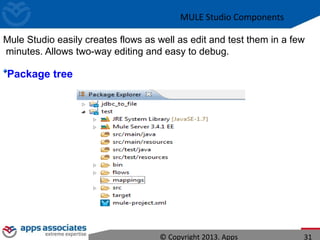
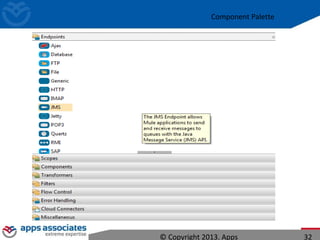
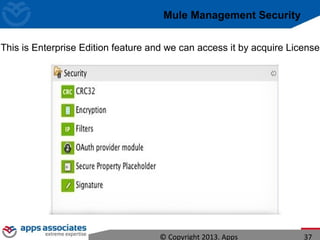
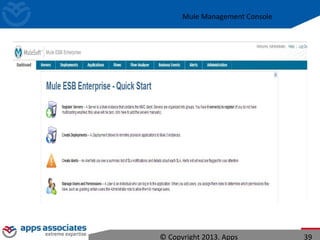
The document discusses Mule ESB, an open source enterprise service bus. It begins with an introduction to integration and ESBs, explaining that an ESB provides fundamental services for connecting different applications and technologies. It then discusses specific features of Mule ESB, including its lightweight and developer-friendly design. The rest of the document demonstrates how to use Mule Studio and Mule ESB, covering topics like Mule flows, messages, components, and the Mule Management Console.