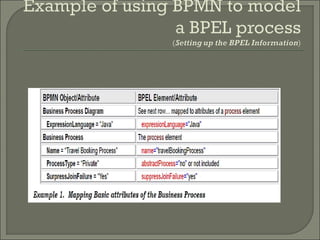
Business process management (BPM) aims to align organizations with client needs through efficient and flexible processes. BPM activities include design, modeling, execution, monitoring, and optimization of processes. Design defines new processes, modeling simulates process variations, execution automates processes, monitoring tracks process performance, and optimization improves processes based on monitoring data. BPM uses tools like process engines for modeling and execution, analytics for issue identification, and collaboration tools to remove barriers.