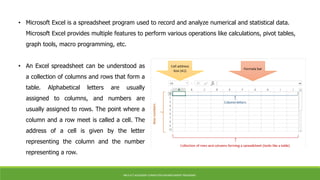
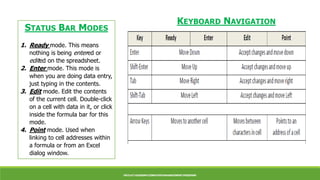
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet program used to record and analyze numerical data. An Excel spreadsheet is organized into columns and rows that form a table, with cells located at each intersection point addressed using column letters and row numbers. Excel provides functions like SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, MIN, and MAX to perform calculations on data ranges. Basic Excel skills include opening and navigating worksheets, entering formulas, formatting cells, printing, and using keyboard shortcuts.