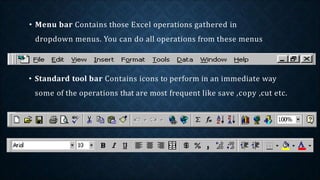
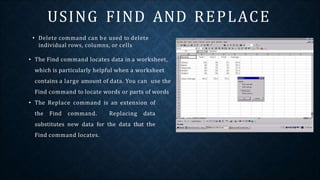
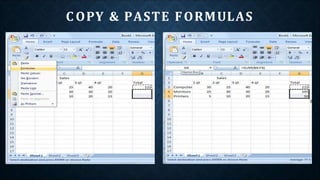
This document provides an overview of topics that will be covered in a Microsoft Excel training course, including basic and advanced features. The main goals of the course are to help professionals enhance their Excel skills through hands-on exercises and practice with techniques ranging from basic functions to more powerful tools like pivot tables, macros, and statistical/graphing functions. Mastering these Excel skills will allow delegates to more efficiently manage and analyze worksheet data.


















![VLOOKUP Function
The VLOOKUP function is a premade function in Excel, which
allows searches across columns.
It is typed =VLOOKUP and has the following parts:
=VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_n
um, [range_lookup])
Lookup_value: Select the cell where search values will be
entered.
Table_array: The table range, including all cells in the table.
Col_index_num: The data which is being looked up. The input
is the number of the column, counted from the left:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/excelbreifoverview-230312212702-8daf51e9/85/Excel_Breif_Overview-pptx-22-320.jpg)











