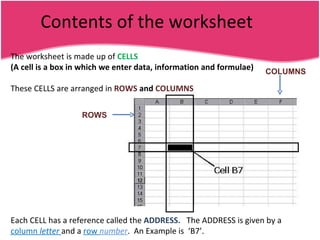
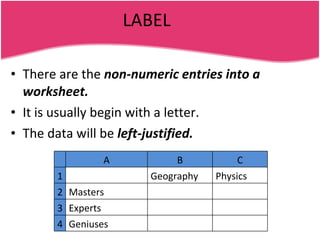
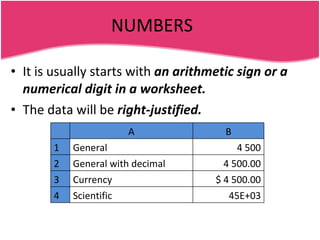
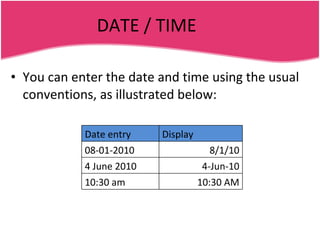
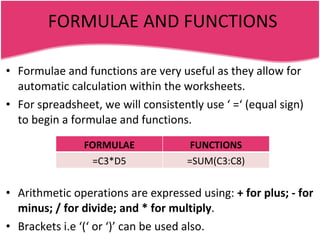
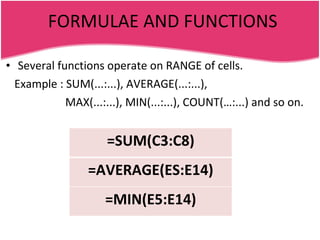
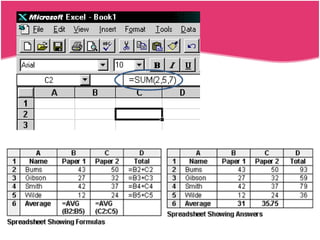
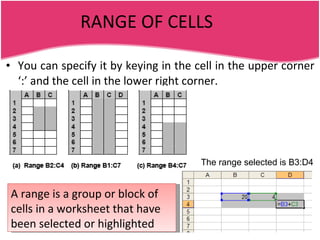
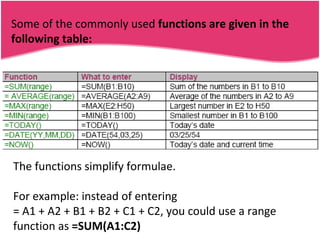
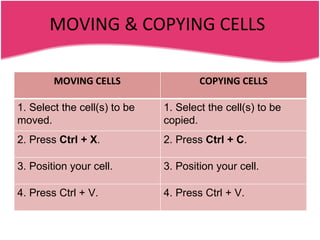
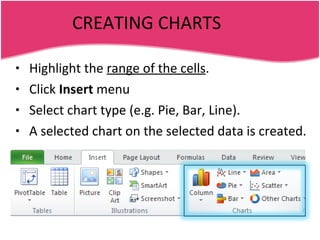
Spreadsheets allow users to enter data into a table with rows and columns and perform calculations automatically. Formulas and functions can be used to calculate values within cells. Data can be sorted, charts can be created from cell ranges, and cells or ranges of cells can be moved or copied.