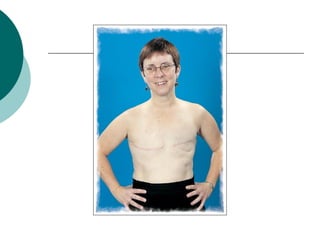
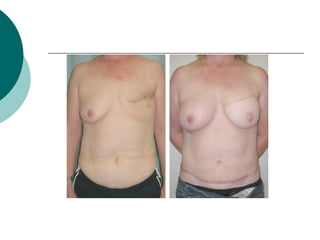
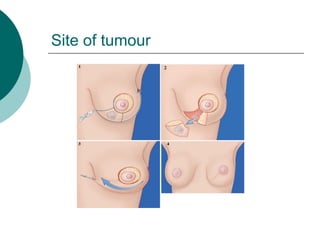
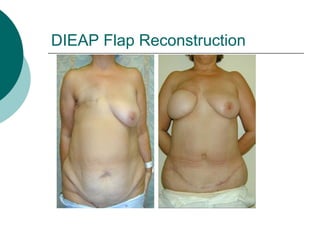
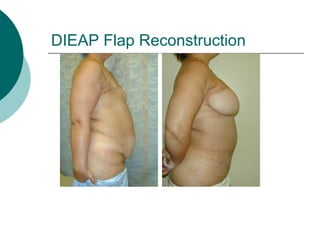
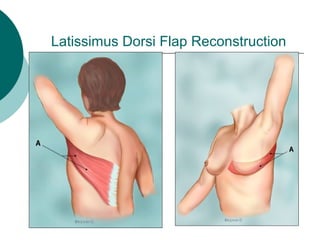
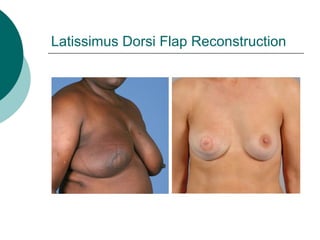
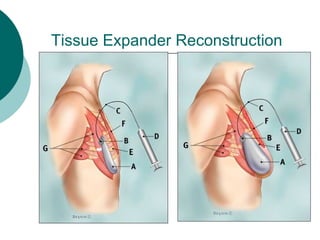
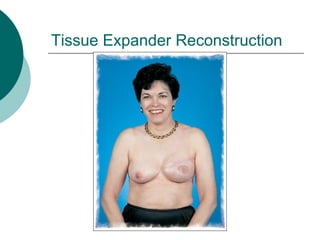
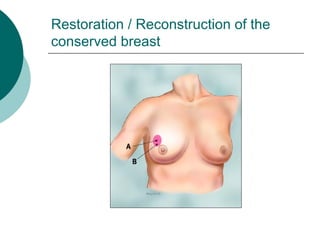
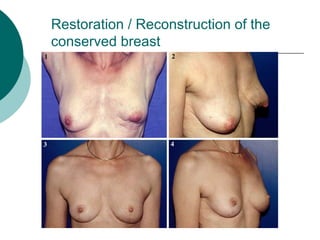
The document discusses breast reconstruction options for women with breast cancer. It outlines the key decisions around mastectomy versus breast conservation, immediate versus delayed reconstruction, and types of reconstruction including autologous techniques using the patient's own tissue or implants/expanders. Reasons for reconstructing the conserved breast are also reviewed, such as achieving symmetry or correcting shape/nipple issues. Patient factors, tumor characteristics, treatment plans, and lifestyle/expectations must all be considered in personalized decision making around reconstruction.