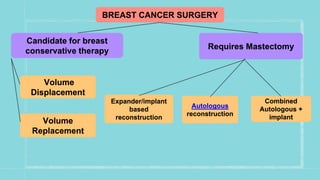
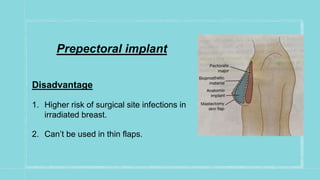
This document discusses various breast reconstruction surgeries and techniques. It covers oncoplastic breast surgery procedures like volume displacement and replacement to reconstruct the breast after tumor removal. It also discusses the different options for breast reconstruction including implant-based, autologous techniques using tissues from the abdomen, back, thighs, or buttocks. The timing of reconstruction and complications are summarized. Monitoring of reconstructed flaps and radiological surveillance is also covered briefly.